CDC Reports 80,000 Flu Deaths Last Winter, Highest in 40 Years
Cdc 80000 people died of flu last winter in u s highest death toll in 40 years – CDC Reports 80,000 Flu Deaths Last Winter, Highest in 40 Years – a stark reminder of the influenza virus’s enduring threat. The winter of 2022-2023 saw an unprecedented surge in flu cases, resulting in a staggering death toll not witnessed in four decades.
This grim statistic raises serious concerns about the virus’s evolving nature and the effectiveness of our public health response.
The severity of the recent flu season was attributed to a confluence of factors. The return to pre-pandemic routines, coupled with a decline in immunity due to reduced exposure to the virus during lockdowns, created a perfect storm for widespread transmission.
The dominant circulating strain, H3N2, known for its ability to cause severe illness, further exacerbated the situation.
Flu Season Severity
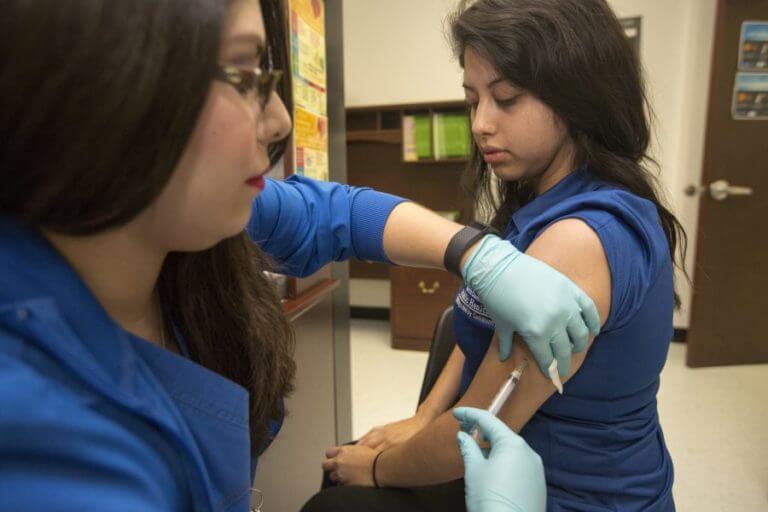
The 2022-2023 flu season was particularly severe in the United States, resulting in the highest death toll in four decades. This season saw a resurgence of influenza activity after a relatively mild period during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Historical Overview of Flu Seasons
Flu seasons in the US vary significantly from year to year, with factors such as the circulating strains, population immunity, and public health measures influencing their severity. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) tracks flu activity and publishes weekly reports throughout the season.
Comparison of Death Tolls
The 2022-2023 flu season saw a stark increase in deaths compared to previous seasons. The CDC estimates that between 29,000 and 52,000 deaths were attributed to influenza during the 2022-2023 season, marking the highest death toll since the 1979-1980 season.
Factors Contributing to the Severity of the 2022-2023 Flu Season
Several factors likely contributed to the severity of the 2022-2023 flu season, leading to the elevated death toll:
- Reduced Population Immunity:The COVID-19 pandemic led to widespread social distancing and mask-wearing practices, which also reduced exposure to influenza viruses. This resulted in a decrease in overall population immunity, making individuals more susceptible to infection.
- Circulating Strains:The dominant influenza strain circulating during the 2022-2023 season, H3N2, is known to be associated with more severe illness and higher mortality rates, particularly among older adults and individuals with underlying health conditions.
- Delayed Vaccination:There was a decline in flu vaccination rates during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. This lower vaccination coverage may have contributed to the higher number of cases and deaths.
- Increased Healthcare Burden:The simultaneous presence of COVID-19 and influenza placed a significant burden on healthcare systems, potentially leading to delays in diagnosis and treatment, which could have contributed to the higher death toll.
Impact on Healthcare System
The 2022-2023 flu season was a particularly challenging one for the U.S. healthcare system, as it was characterized by a surge in cases, hospitalizations, and deaths. The high number of flu cases put a significant strain on healthcare resources, leading to challenges in providing timely and adequate care to patients.
Hospitalizations and ICU Admissions
The strain on healthcare resources during the 2022-2023 flu season was particularly evident in the number of hospitalizations and ICU admissions related to the flu. According to the CDC, the number of flu-related hospitalizations was significantly higher than in previous years.
It’s truly shocking to think that 80,000 people died from the flu last winter in the U.S., the highest death toll in 40 years. It makes you wonder about the state of our healthcare system, and it’s even more concerning when you consider the recent discovery of a loaded gun in the jail where Jeffrey Epstein “killed himself.” loaded gun found in jail where jeffrey epstein killed himself While the flu epidemic is a natural event, it’s hard not to question the circumstances surrounding Epstein’s death, especially in light of the loaded gun found in the jail.
This just adds another layer of distrust to the already fragile public confidence in our institutions.
The peak of the flu season saw a surge in hospitalizations, with many hospitals reaching capacity. This strain on resources led to challenges in providing timely care to patients, including longer wait times for beds and limited access to specialized care.
The CDC estimates that during the peak of the 2022-2023 flu season, there were over 100,000 flu-related hospitalizations per week in the United States.
Impact on Healthcare Workers
The high number of flu cases also had a significant impact on healthcare workers, who were tasked with caring for a surge of patients while also dealing with their own health concerns. This resulted in increased workload, burnout, and fatigue among healthcare workers.
A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that during the 2022-2023 flu season, there was a significant increase in the number of healthcare workers reporting burnout and fatigue.
Public Health Response: Cdc 80000 People Died Of Flu Last Winter In U S Highest Death Toll In 40 Years
The 2022-2023 flu season in the United States was particularly severe, resulting in the highest death toll in four decades. This prompted a robust public health response aimed at mitigating the spread of the virus and protecting vulnerable populations.
Public Health Measures Implemented, Cdc 80000 people died of flu last winter in u s highest death toll in 40 years
Public health officials implemented a comprehensive strategy to address the severe flu season, including:
- Increased Surveillance and Monitoring:The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and state health departments enhanced surveillance systems to track the spread of the flu virus, identify emerging strains, and monitor influenza-related hospitalizations and deaths. This data informed public health decisions and allowed for timely interventions.
- Vaccination Campaigns:Public health agencies launched extensive vaccination campaigns to encourage widespread influenza vaccination. This included public awareness initiatives, partnerships with healthcare providers, and efforts to reach vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, young children, and individuals with underlying health conditions.
- Antiviral Medications:Public health officials promoted the use of antiviral medications, such as Tamiflu and Relenza, for the treatment of influenza infections. These medications can reduce the severity and duration of symptoms, particularly in high-risk individuals.
- Infection Control Measures:Public health messages emphasized the importance of basic infection control measures, such as handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and staying home when sick. Healthcare facilities also implemented strict infection control protocols to prevent the spread of the virus.
The CDC reported that 80,000 people died from the flu last winter in the U.S., marking the highest death toll in 40 years. This grim statistic underscores the importance of taking seasonal flu seriously, especially given the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
With the economic and social fallout of the virus still unfolding, it’s crucial to remember that we’re not out of the woods yet. In a major development, Trump signed a $2 trillion stimulus bill after the House approved a historic coronavirus response , which will hopefully provide much-needed relief and support to individuals and businesses.
However, the flu season is still upon us, and it’s essential to stay vigilant and take the necessary precautions to protect ourselves and our loved ones.
Effectiveness of Public Health Measures
The effectiveness of public health measures in mitigating the spread of the flu during the 2022-2023 season was mixed. While vaccination campaigns played a significant role in reducing the number of flu-related hospitalizations and deaths, the high death toll highlights the challenges of controlling influenza outbreaks.
- Vaccination Effectiveness:Influenza vaccines were effective in reducing the risk of flu-related hospitalization and death, particularly among high-risk individuals. However, vaccine effectiveness varied depending on the age group and the specific influenza strains circulating during the season. For example, the vaccine was less effective against the dominant H3N2 strain, which contributed to the severity of the outbreak.
- Challenges in Reaching Vulnerable Populations:Despite public health efforts, vaccination rates remained lower than desired among vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and young children. This highlights the ongoing need to improve access to vaccination services and address vaccine hesitancy in these groups.
- Antiviral Medication Use:While antiviral medications can be effective in treating influenza infections, their use was not as widespread as it could have been. This could be attributed to factors such as limited access to healthcare, delayed diagnosis, and insufficient awareness of the benefits of antiviral therapy.
The CDC reported a staggering 80,000 flu deaths last winter, marking the highest toll in 40 years. This grim statistic underscores the vulnerability of our population to respiratory illnesses, and the recent economic downturn only exacerbates the situation. As the CCP virus continues to disrupt daily life, jobless claims jump as ccp virus bites into us labor market , leaving many struggling to afford basic necessities, including healthcare.
This further compounds the risk of widespread illness, making the CDC’s flu death toll a sobering reminder of the importance of preventative measures and accessible healthcare for all.
Role of Vaccination
Vaccination is a cornerstone of influenza prevention and remains the most effective way to protect individuals and communities from the virus.
- Reduced Risk of Infection and Complications:Vaccination significantly reduces the risk of contracting influenza and developing serious complications, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and hospitalizations. It can also protect individuals from spreading the virus to others.
- Reduced Severity of Illness:Even if vaccinated individuals do contract influenza, they are likely to experience milder symptoms and a shorter duration of illness. This is especially important for high-risk individuals who are more vulnerable to severe complications.
- Community Protection:Widespread vaccination contributes to herd immunity, which protects those who are unable to be vaccinated, such as infants, individuals with weakened immune systems, and those with allergies to vaccine components. This is particularly important during periods of high influenza activity.
Risk Factors and Vulnerable Populations

The recent flu season’s severity underscores the importance of understanding risk factors and identifying vulnerable populations. Recognizing these factors allows us to tailor preventive measures and ensure adequate healthcare resources for those most at risk.
Demographic Groups at Increased Risk
Certain demographic groups are disproportionately affected by severe flu complications. These groups require targeted interventions and increased awareness during flu season.
- Young children (under 5 years old):Their immune systems are still developing, making them more susceptible to infection and complications.
- Older adults (over 65 years old):Their immune systems weaken with age, increasing their vulnerability to severe flu.
- Pregnant women:Flu infection can pose a greater risk to both mother and fetus, potentially leading to complications like preterm labor or low birth weight.
- People with chronic health conditions:Individuals with conditions like asthma, diabetes, heart disease, or weakened immune systems are more likely to experience severe flu complications.
Risk Factors Associated with Increased Flu Severity
Several factors can increase the severity of flu illness, leading to hospitalization or even death. Understanding these factors is crucial for individual risk assessment and informed decision-making.
- Age:As mentioned earlier, very young children and older adults are particularly vulnerable.
- Underlying health conditions:Chronic conditions like asthma, diabetes, heart disease, and lung disease significantly increase the risk of severe complications.
- Weakened immune system:Individuals with compromised immune systems due to conditions like HIV/AIDS, cancer treatments, or organ transplantation are at higher risk.
- Vaccination status:Unvaccinated individuals are at significantly higher risk of severe illness and complications.
- Obesity:Excess weight can compromise lung function and increase the risk of respiratory complications.
- Smoking:Smoking damages the lungs, making them more susceptible to flu infection and complications.
- Lack of access to healthcare:Individuals without adequate healthcare access may not receive timely treatment, increasing their risk of complications.
Protecting Vulnerable Populations
Protecting vulnerable populations from severe flu complications requires a multi-pronged approach.
- Vaccination:The most effective way to prevent severe flu illness is through vaccination. Encourage everyone in vulnerable groups to get vaccinated annually.
- Hand hygiene:Frequent handwashing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizer can significantly reduce the spread of flu viruses.
- Covering coughs and sneezes:Using tissues or the crook of the elbow to cover coughs and sneezes helps prevent the spread of germs.
- Avoiding close contact with sick individuals:Stay away from people who are sick to minimize the risk of infection.
- Staying home when sick:If you are sick, stay home from work or school to avoid spreading the virus to others.
- Seeking medical attention promptly:If you experience flu symptoms, especially if you are in a vulnerable group, seek medical attention immediately.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle:Eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly can boost your immune system and reduce the risk of severe flu illness.
End of Discussion

The recent flu season serves as a stark reminder of the importance of vigilance and preparedness. As we navigate the post-pandemic world, it’s crucial to prioritize vaccination, maintain good hygiene practices, and stay informed about evolving health recommendations. The flu remains a formidable opponent, and our collective efforts are essential in mitigating its impact.