
Californias 10 Largest Wildfires: Causes and Impact
Californias 10 largest wildfires and what caused them – California’s 10 largest wildfires and what caused them are a stark reminder of the state’s vulnerability to these devastating events. From the Mendocino Complex Fire to the Thomas Fire, these blazes have scarred the landscape, displaced communities, and left an indelible mark on the environment.
The combination of dry vegetation, hot temperatures, and human activity creates a perfect storm for wildfire outbreaks, and the effects are felt far beyond the immediate burn area.
Understanding the causes of these wildfires is crucial to developing effective prevention and mitigation strategies. Climate change, human negligence, and natural factors all play a role, and addressing these issues is paramount to protecting California’s future. This article delves into the history of these catastrophic fires, exploring the contributing factors and the lasting impact on the state.
Overview of California Wildfires
California, known for its stunning landscapes and diverse ecosystems, is also facing a growing wildfire crisis. The state’s arid climate, dry vegetation, and increasingly hot temperatures have created a perfect storm for wildfires, leading to devastating consequences for communities, ecosystems, and the environment.
Factors Contributing to Wildfire Vulnerability, Californias 10 largest wildfires and what caused them
California’s wildfire vulnerability is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors.
- Climate Change:Rising temperatures and prolonged droughts have significantly increased the risk of wildfires. Higher temperatures dry out vegetation, making it more flammable, while droughts reduce soil moisture, creating ideal conditions for fire ignition and spread.
- Human Activity:Human activities play a significant role in starting wildfires. Careless handling of fire, equipment malfunctions, and arson are common causes. Additionally, development in wildland areas increases the interface between human settlements and flammable vegetation, making it easier for fires to spread.
California’s wildfires are a devastating reality, fueled by a combination of factors like climate change, drought, and human negligence. The recent news of a secret service director admitting significant operational failure in a Trump assassination attempt reminds us of the fragility of safety and security.
It’s a stark reminder that even in the face of natural disasters, we must remain vigilant about potential threats and work together to ensure our collective well-being.
- Vegetation:California’s diverse vegetation, including dense forests, chaparral, and grasslands, provides ample fuel for wildfires. The state’s forests, particularly those dominated by drought-tolerant trees like pines, are highly susceptible to fire.
- Wind Patterns:Strong winds, particularly Santa Ana winds, can rapidly spread wildfires, making them difficult to control. These winds, originating from the high desert, are dry and hot, creating conditions that accelerate fire movement.
Statistics on Wildfires
California’s wildfire problem is evident in the statistics. The state has experienced a significant increase in the number of wildfires, acres burned, and related costs in recent decades.
- Number of Wildfires:In the past decade, California has seen an average of over 7,000 wildfires annually, with some years exceeding 10,000.
- Acres Burned:The number of acres burned by wildfires has also risen dramatically. In 2020, a record-breaking 4.2 million acres were scorched, highlighting the severity of the wildfire crisis.
- Costs:Wildfires have a significant economic impact on the state, costing billions of dollars annually in firefighting costs, property damage, and lost revenue.
Top 10 Largest Wildfires in California
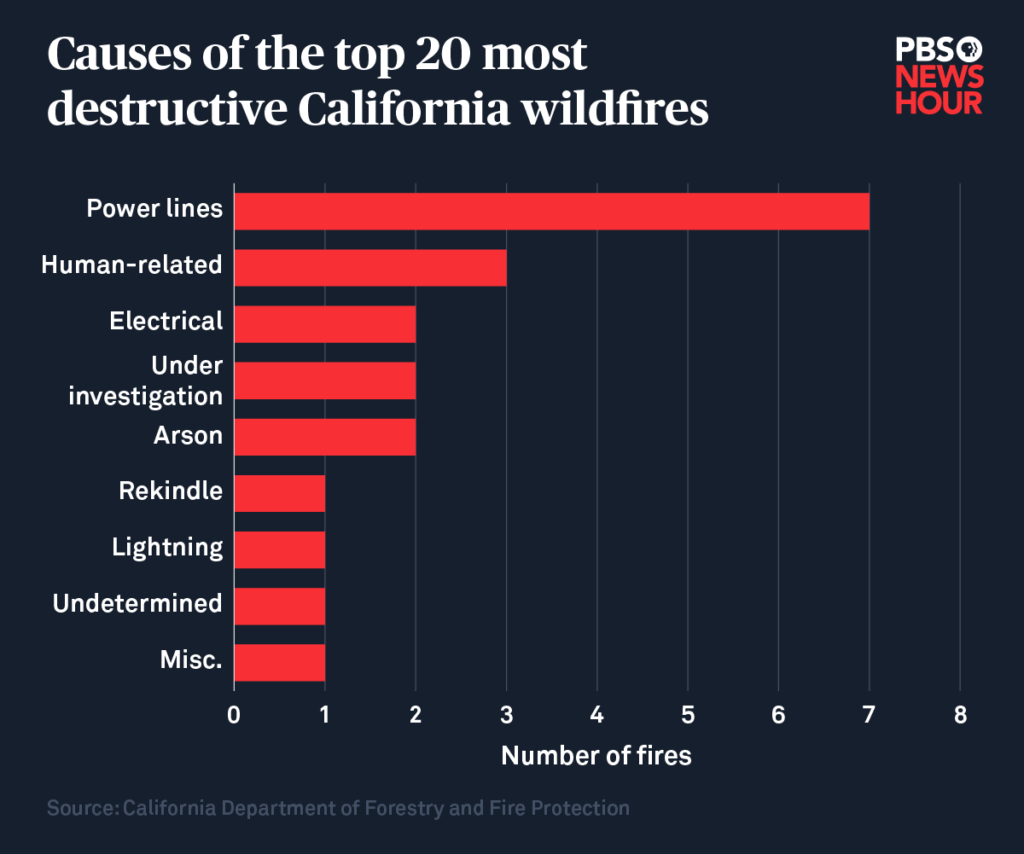
California has a long and tragic history of wildfires, with devastating impacts on the environment and communities. The state’s dry climate, abundant vegetation, and increasing human activity create a perfect storm for these destructive events. The 10 largest wildfires in California history, measured by acres burned, offer a stark reminder of the destructive power of these natural disasters.
Largest Wildfires in California History
| Rank | Name | Year | Acres Burned | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | August Complex | 2020 | 1,013,763 | Mendocino National Forest |
| 2 | Dixie Fire | 2021 | 963,309 | Plumas, Butte, Lassen, and Tehama Counties |
| 3 | Thomas Fire | 2017 | 281,893 | Ventura and Santa Barbara Counties |
| 4 | SCU Lightning Complex | 2020 | 396,624 | Santa Clara, Alameda, Contra Costa, San Mateo, and Santa Cruz Counties |
| 5 | Mendocino Complex | 2018 | 459,123 | Mendocino, Lake, and Colusa Counties |
| 6 | Rim Fire | 2013 | 257,314 | Tuolumne County |
| 7 | Cedar Fire | 2003 | 273,246 | San Diego County |
| 8 | Camp Fire | 2018 | 153,336 | Butte County |
| 9 | Creek Fire | 2020 | 300,000 | Fresno, Madera, and Mariposa Counties |
| 10 | Caldor Fire | 2021 | 221,939 | El Dorado, Amador, and Alpine Counties |
Causes of California Wildfires
California’s wildfire season has become increasingly intense and destructive in recent years, posing a significant threat to the state’s environment, communities, and economy. A complex interplay of factors, both human-induced and natural, contributes to the occurrence and severity of these fires.
Human Activities
Human activities play a significant role in igniting wildfires in California. These activities can be intentional or accidental, but their consequences are often devastating.
- Arson: Deliberately setting fires is a criminal act that can have dire consequences. Arson is a major cause of wildfires, especially during periods of drought when vegetation is dry and easily ignitable.
- Equipment Malfunctions: Machinery and equipment used in various industries, such as agriculture and construction, can malfunction and spark fires. These malfunctions can occur due to faulty equipment, lack of maintenance, or operator error.
- Careless Use of Fire: Improperly extinguished campfires, discarded cigarettes, and fireworks are common causes of wildfires. These activities can easily ignite dry vegetation, especially during hot and windy conditions.
- Power Lines: Power lines can malfunction or spark, igniting vegetation, especially during high winds or extreme weather events.
Natural Factors
Natural factors also contribute to the occurrence and spread of wildfires in California. These factors are often influenced by climate patterns and ecological conditions.
- Lightning: Lightning strikes can ignite dry vegetation, especially during thunderstorms. This is a natural cause of wildfires, particularly in remote areas.
- Drought: Prolonged periods of drought create dry conditions that make vegetation highly flammable. Drought-stricken vegetation is more susceptible to ignition and burns more intensely.
- Wind: Strong winds can quickly spread wildfires by carrying embers and accelerating the rate of combustion. High winds can also create fire whirls, which are intense and destructive fire vortices.
- Fuel Load: The amount of flammable vegetation, known as fuel load, influences the intensity and spread of wildfires. Dense vegetation, such as overgrown forests and brush, can create a significant fuel load.
Climate Change
Climate change is exacerbating wildfire risk in California by influencing key factors such as temperature, drought, and wind patterns.
- Increased Temperatures: Rising temperatures due to climate change increase the rate of evaporation and dry out vegetation, making it more susceptible to ignition. Warmer temperatures also lengthen the fire season, creating more opportunities for wildfires to start and spread.
- Drought Intensification: Climate change is intensifying drought conditions in California, leading to drier vegetation and increased fire risk. Drought-stricken areas are more vulnerable to wildfires, as vegetation is more easily ignited and burns more intensely.
- Wind Patterns: Climate change is altering wind patterns, making them more erratic and intense. Stronger winds can spread wildfires more rapidly, increasing their destructive potential.
Impact of Wildfires on California
California wildfires have devastating consequences, impacting the environment, economy, and the health of its residents. The state faces significant challenges in mitigating the impact of these fires, which are becoming more frequent and intense due to climate change.
Environmental Consequences
The environmental consequences of wildfires are far-reaching and multifaceted.
- Habitat Loss:Wildfires destroy vast swaths of natural habitats, leading to the displacement and even extinction of numerous plant and animal species. The loss of vegetation disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, impacting food chains and overall biodiversity. For example, the 2020 August Complex Fire, the largest wildfire in California’s history, burned over 1 million acres, decimating habitat for numerous endangered species, including the California condor and the Sierra Nevada red fox.
California’s wildfires, fueled by a combination of dry vegetation, strong winds, and human activity, have devastated the state for years. The 2020 wildfire season, in particular, saw a record number of blazes, including the August Complex Fire, which became the largest wildfire in California history.
The political landscape, however, also seems to be ablaze, with the Trump campaign announcing it won’t finalize the Harris debate until she’s officially nominated , adding fuel to the fire of political speculation. While the state grapples with the ecological and economic impact of the wildfires, the political drama continues to unfold, leaving many wondering about the future of both the environment and the nation.
- Air Pollution:Wildfires release significant amounts of smoke and particulate matter into the atmosphere, contributing to poor air quality and respiratory problems. Smoke can travel long distances, affecting air quality in neighboring states and even countries. The 2018 Camp Fire, which destroyed the town of Paradise, released an estimated 175,000 tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, highlighting the significant contribution of wildfires to climate change.
- Soil Erosion:Wildfires destroy vegetation that helps bind soil together, leaving the land vulnerable to erosion by wind and rain. This erosion can lead to sedimentation in waterways, damaging aquatic ecosystems and impacting water quality. The 2017 Thomas Fire, the largest wildfire in California history at the time, burned over 280,000 acres, leaving behind a landscape susceptible to erosion, which impacted water quality in nearby streams and rivers.
Socio-economic Impact
Wildfires have a significant impact on the economy and social fabric of California.
California’s 10 largest wildfires, fueled by a combination of dry conditions, strong winds, and human negligence, have left a devastating mark on the state. The recent blazes have highlighted the urgent need for effective fire prevention strategies and climate change mitigation.
In a separate but equally pressing matter, Bernie Sanders hasn’t ruled out a third run for presidency, suggesting a potential return to the political stage. Whether or not he decides to run, the fight against climate change, and the resulting impact on wildfires, will undoubtedly be a key issue in the upcoming election.
- Property Damage:Wildfires cause billions of dollars in property damage each year, destroying homes, businesses, and infrastructure. The 2018 Camp Fire, for instance, caused over $16 billion in property damage, making it the most expensive wildfire in California history.
- Displacement:Wildfires force thousands of people to evacuate their homes, leading to displacement and homelessness. The 2020 August Complex Fire displaced over 10,000 people, highlighting the social and economic consequences of wildfires.
- Economic Losses:Wildfires impact the economy in various ways, including lost tourism revenue, disrupted supply chains, and increased insurance premiums. The 2017 Thomas Fire, for example, led to a significant decline in tourism in the Santa Barbara area, highlighting the economic impact of wildfires on local communities.
Health Risks
Wildfires pose significant health risks to California residents, including respiratory problems and mental health issues.
- Respiratory Problems:Smoke from wildfires contains fine particulate matter and other pollutants that can irritate the lungs and exacerbate existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The 2018 Camp Fire led to a surge in hospital admissions for respiratory problems, highlighting the health risks associated with wildfire smoke.
- Mental Health Issues:Wildfires can cause significant stress and trauma, leading to mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The 2017 Thomas Fire, which caused widespread displacement and destruction, had a significant impact on the mental health of residents, highlighting the need for mental health support following wildfires.
Fire Prevention and Mitigation Efforts: Californias 10 Largest Wildfires And What Caused Them

California is a state known for its diverse landscapes, including vast forests and grasslands. These landscapes, however, are also susceptible to wildfires, which pose a significant threat to the state’s environment, infrastructure, and communities. To address this challenge, California has implemented various strategies to prevent and mitigate wildfires.
These efforts encompass controlled burns, community education, and the use of technology.
Controlled Burns
Controlled burns, also known as prescribed fires, are a crucial tool in wildfire prevention. They involve intentionally setting small, controlled fires under specific conditions to reduce fuel loads and create firebreaks. By burning away flammable vegetation, controlled burns prevent the spread of larger, more destructive wildfires.
The benefits of controlled burns include:
- Reducing the amount of fuel available for wildfires.
- Creating firebreaks that can help contain wildfires.
- Improving forest health by promoting the growth of new, fire-resistant vegetation.
- Reducing the risk of catastrophic wildfires that can damage ecosystems and communities.
However, controlled burns must be carefully planned and executed to ensure safety and effectiveness. Factors such as weather conditions, fuel type, and topography are carefully considered to minimize the risk of uncontrolled fire spread.
Community Education
Public awareness and education are critical components of wildfire prevention. By educating the public about wildfire risks, causes, and prevention measures, California aims to foster a culture of responsibility and preparedness. The California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (Cal Fire) plays a significant role in community education.
They conduct outreach programs, workshops, and public awareness campaigns to educate residents about wildfire safety. These programs emphasize the importance of:
- Creating defensible space around homes by removing flammable vegetation.
- Using safe practices when using fire for cooking, camping, or other purposes.
- Being aware of fire restrictions and adhering to them.
- Knowing how to evacuate safely during a wildfire.
Technology in Wildfire Detection and Response
Technological advancements have revolutionized wildfire detection and response in California. Aerial surveillance, early warning systems, and advanced fire modeling tools play a vital role in monitoring and managing wildfires.
- Aerial Surveillance: Aircraft equipped with infrared cameras can detect heat signatures, allowing firefighters to identify and respond to wildfires at an early stage. These cameras can also provide real-time information about the size, intensity, and direction of a wildfire, enabling firefighters to make informed decisions.
- Early Warning Systems: California has implemented a network of early warning systems, such as weather stations and fire detection cameras, to provide timely alerts about potential wildfire threats. These systems use data from sensors and satellite imagery to detect smoke, heat, and other indicators of wildfire activity.
By alerting communities in advance, these systems allow residents to evacuate and take necessary precautions.
- Advanced Fire Modeling Tools: Computer models can simulate wildfire behavior, predicting the spread and intensity of fires based on factors such as wind, temperature, and fuel conditions. These models assist firefighters in planning fire suppression efforts and allocating resources effectively.
Epilogue

As we grapple with the increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires in California, it’s clear that we need a multi-pronged approach to address this challenge. Investing in fire prevention measures, promoting public awareness, and addressing the root causes of these events is essential to safeguarding our communities and preserving the state’s natural beauty.
By understanding the past, we can work towards a future where the devastating impact of wildfires is minimized, and California’s resilience is strengthened.






