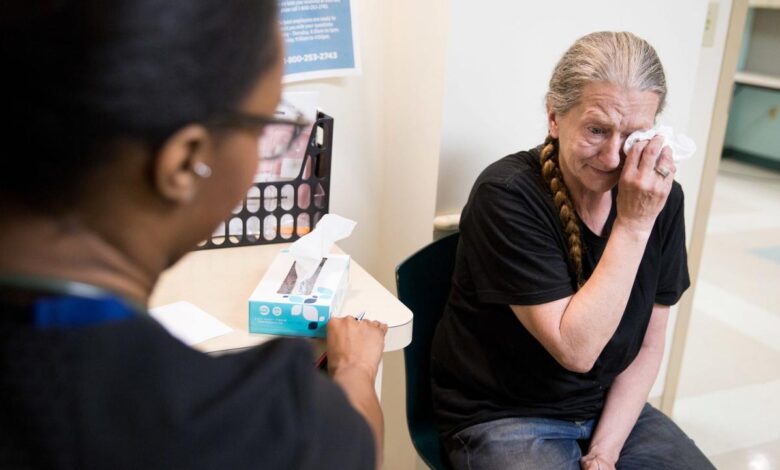
Burned Out, Addicted, and Self-Medicated: Americas Doctors Face a Crisis
Burned out addicted to drugs and self medicated americas doctors face a crisis – Burned out, addicted to drugs, and self-medicated, America’s doctors face a crisis. This isn’t just a problem for individual physicians; it’s a systemic issue that threatens the health of our nation. The pressures of modern medicine, from long hours and demanding patients to administrative burdens and financial strain, have driven many doctors to the brink.
The consequences are far-reaching, impacting not only their own well-being but also the quality of patient care and the future of healthcare itself.
The statistics are sobering. A significant percentage of doctors report experiencing burnout, and many turn to drugs and alcohol to cope with the overwhelming stress. This self-medication, often driven by a desperate need to function, creates a dangerous cycle that can lead to addiction and further exacerbate the problem.
The crisis is multifaceted, stemming from a complex interplay of factors that need to be addressed on both individual and systemic levels.
The Scope of the Crisis
The mental and physical well-being of America’s doctors is in a precarious state, marked by a pervasive crisis of burnout, drug addiction, and self-medication. These issues are not isolated incidents but rather a widespread phenomenon that impacts a significant portion of the medical profession.
Understanding the scope of this crisis requires examining the prevalence of these problems, the specific challenges doctors face, and the consequences for both individual practitioners and the healthcare system as a whole.
It’s heartbreaking to see the burnout and addiction plaguing our nation’s doctors. They’re often forced to self-medicate to cope with the overwhelming demands of their profession. But there’s hope! The goal was to convene these institutions that many folks didn’t even know existed to address this crisis, bringing together resources and support systems for our overworked and undervalued medical professionals.
We need to prioritize their well-being, so they can continue to provide the care we all deserve.
Prevalence of Burnout, Addiction, and Self-Medication
The prevalence of burnout, addiction, and self-medication among American doctors is a significant concern. Studies reveal that a substantial portion of the medical workforce is grappling with these issues. For instance, a 2021 study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) found that over 40% of physicians reported experiencing burnout, with a significant number reporting symptoms of depression and anxiety.
It’s heartbreaking to see the toll the burnout, addiction, and self-medication are taking on our healthcare heroes. While the crisis unfolds, it’s inspiring to see companies like PikmyKid achieving success with positive reviews and excellent ranking. Maybe a focus on wellness and support for our medical professionals could be a part of the solution to this growing problem.
The same study found that over 10% of physicians reported misusing prescription drugs, while another study published in the journal Addiction found that the rate of opioid addiction among doctors was significantly higher than in the general population.
Challenges Faced by Doctors
Doctors face a unique set of challenges that contribute to burnout, addiction, and self-medication. These challenges include:
- Long and Irregular Work Hours:Doctors often work long and irregular hours, which can lead to sleep deprivation, fatigue, and difficulty maintaining a healthy work-life balance. This can contribute to feelings of burnout and stress.
- High-Pressure Environment:The medical field is a high-pressure environment, where doctors are constantly facing life-or-death decisions and dealing with emotionally challenging situations. This can lead to stress, anxiety, and feelings of inadequacy.
- Lack of Support:Many doctors feel isolated and unsupported in their work, which can exacerbate feelings of burnout and stress. This lack of support can be attributed to factors such as inadequate staffing levels, limited access to mental health resources, and a culture of stoicism and self-reliance within the medical profession.
It’s a heartbreaking reality: many doctors, the very people we trust to heal us, are struggling with burnout, addiction, and self-medication. This crisis has deep roots, and it’s a reminder that even the most dedicated professionals can be vulnerable. The factors affecting the value of Bitcoin, such as market sentiment, regulation, and adoption, which factors affect the value of bitcoins note these points , are all complex and ever-changing, just like the challenges facing our healthcare system.
We need to prioritize mental health support for doctors and ensure they have the resources they need to thrive, both for their own well-being and for the health of our nation.
- Financial Pressures:Doctors face significant financial pressures, including high student loan debt, the cost of medical malpractice insurance, and the pressure to maintain a high income. These pressures can contribute to stress and anxiety.
The Impact of Burnout
Burnout, a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged or excessive stress, is a pervasive issue among doctors, impacting their well-being and ultimately affecting patient care.
Impact on Doctors’ Physical and Mental Health
Burnout can have profound consequences for doctors’ physical and mental health.
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases:The constant stress associated with burnout can lead to elevated levels of cortisol, a stress hormone. Prolonged exposure to high cortisol levels can increase the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and depression.
- Sleep Disturbances:Burnout often manifests as insomnia, difficulty falling asleep, and frequent awakenings. This lack of sleep can further exacerbate stress, leading to a vicious cycle.
- Substance Abuse:Some doctors turn to alcohol or drugs to cope with the overwhelming stress of their profession. This self-medication can lead to addiction and further complicate their health issues.
- Mental Health Conditions:Burnout can trigger or worsen existing mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Impact on Patient Care and Medical Errors
Burnout can significantly compromise patient care.
- Decreased Patient Satisfaction:Burned-out doctors may experience reduced empathy and patience, leading to lower patient satisfaction.
- Increased Medical Errors:Exhaustion and mental fatigue can impair cognitive function, increasing the likelihood of medical errors. Studies have shown a correlation between physician burnout and increased rates of adverse events.
- Reduced Communication:Burned-out doctors may have difficulty communicating effectively with patients and colleagues, leading to misunderstandings and miscommunication.
Impact on Doctors’ Personal Lives and Relationships
Burnout can spill over into doctors’ personal lives, impacting their relationships and overall well-being.
- Strained Relationships:Long working hours and emotional exhaustion can lead to strained relationships with family and friends. Doctors may find it difficult to maintain a healthy work-life balance.
- Social Isolation:Burnout can lead to social isolation, as doctors withdraw from social activities and interactions due to fatigue and emotional exhaustion.
- Reduced Quality of Life:The constant stress and demands of burnout can significantly reduce doctors’ overall quality of life. They may experience feelings of dissatisfaction, hopelessness, and a lack of fulfillment.
Contributing Factors
The doctor burnout crisis is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. Understanding these factors is crucial to addressing the problem effectively. This section will delve into the major contributors to the crisis, exploring their impact on physicians.
Factors Contributing to Doctor Burnout
The factors contributing to physician burnout can be categorized into several key areas:
| Factor | Description | Examples | Impact on Doctors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workload and Hours | Physicians often work long and unpredictable hours, leading to exhaustion and difficulty maintaining a healthy work-life balance. | Shift work, on-call duties, and long clinic hours. | Increased risk of fatigue, sleep deprivation, and burnout. |
| Administrative Burden | Doctors spend a significant amount of time on administrative tasks, such as paperwork, insurance billing, and electronic health record documentation, taking away from patient care. | Filling out forms, navigating complex insurance systems, and managing electronic health records. | Reduced time for patient interaction, increased frustration, and decreased job satisfaction. |
| Patient Demands and Expectations | Rising patient expectations and the increasing complexity of medical cases can lead to stress and burnout. | Patients seeking immediate answers, demanding specific treatments, and having unrealistic expectations. | Feeling overwhelmed, pressured, and unable to meet patient demands. |
| Financial Pressures | Financial concerns, such as student loan debt, rising malpractice insurance premiums, and pressure to increase revenue, can add to stress. | High medical school debt, increasing costs of practice, and pressure to meet financial targets. | Financial anxiety, feeling pressured to prioritize revenue over patient care, and potential burnout. |
“Physicians are increasingly feeling overwhelmed by the demands of their jobs, and this is leading to a crisis in burnout.”Dr. Pamela W. (American Medical Association)
The Future of Healthcare: Burned Out Addicted To Drugs And Self Medicated Americas Doctors Face A Crisis

The current crisis in healthcare, fueled by physician burnout and addiction, casts a long shadow over the future of medical care. Failing to address this issue could lead to a cascade of negative consequences, impacting the accessibility, quality, and sustainability of healthcare for all.
The Consequences of Inaction, Burned out addicted to drugs and self medicated americas doctors face a crisis
If the crisis continues unabated, the consequences will be far-reaching and severe. Imagine a future where:
- Hospitals struggle to recruit and retain physicians, leading to longer wait times for appointments and procedures.
- Burnout and stress among remaining doctors escalate, further compromising patient care and increasing medical errors.
- The mental and physical well-being of physicians deteriorates, leading to a decline in their ability to provide compassionate and effective care.
- The public loses trust in the medical profession, leading to a decrease in preventative care and increased reliance on expensive emergency services.
The Long-Term Impact on Healthcare
The long-term impact of the crisis on the availability and quality of healthcare will be significant.
- Reduced Access:Shortages of physicians will limit access to care, particularly in underserved areas, exacerbating health disparities.
- Decreased Quality:Burnout and stress will lead to a decline in the quality of care, resulting in more medical errors and poorer patient outcomes.
- Increased Costs:The increased reliance on emergency services and the need for more complex treatments due to delayed care will drive up healthcare costs for individuals and the system as a whole.
Redesigning Healthcare for Sustainability
To avert these dire consequences, healthcare systems must undergo a fundamental redesign to prioritize the well-being of doctors and ensure sustainable healthcare delivery.
- Focus on Physician Well-being:This includes providing support for mental health, reducing administrative burden, and fostering a culture of work-life balance.
- Promote Teamwork and Collaboration:Encouraging interdisciplinary collaboration can reduce physician workload and create a more supportive work environment.
- Invest in Technology:Implementing technology solutions can streamline administrative tasks, improve communication, and enhance patient care.
- Empower Physicians:Giving physicians a greater voice in decision-making and fostering a culture of respect and appreciation can help address burnout and improve morale.
Final Conclusion
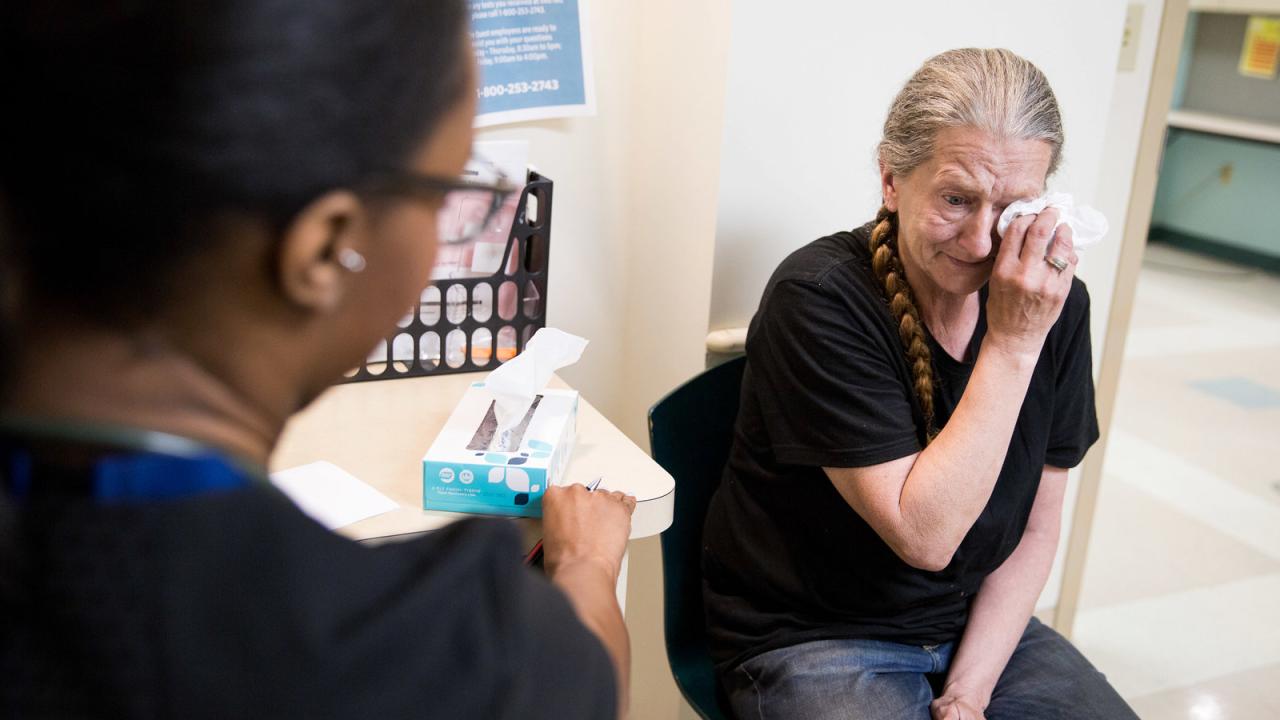
The crisis facing America’s doctors is a call to action. We must prioritize the well-being of our healthcare providers, recognizing that their health is inextricably linked to the health of our nation. By addressing the root causes of burnout, addiction, and self-medication, we can create a more sustainable and supportive environment for doctors, ensuring they can continue to provide the best possible care for generations to come.
This requires a comprehensive approach that includes everything from promoting self-care and fostering a culture of support within the medical community to addressing systemic issues such as excessive workload and administrative burden. The future of healthcare depends on it.

