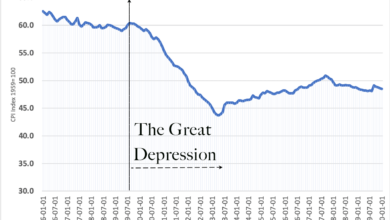
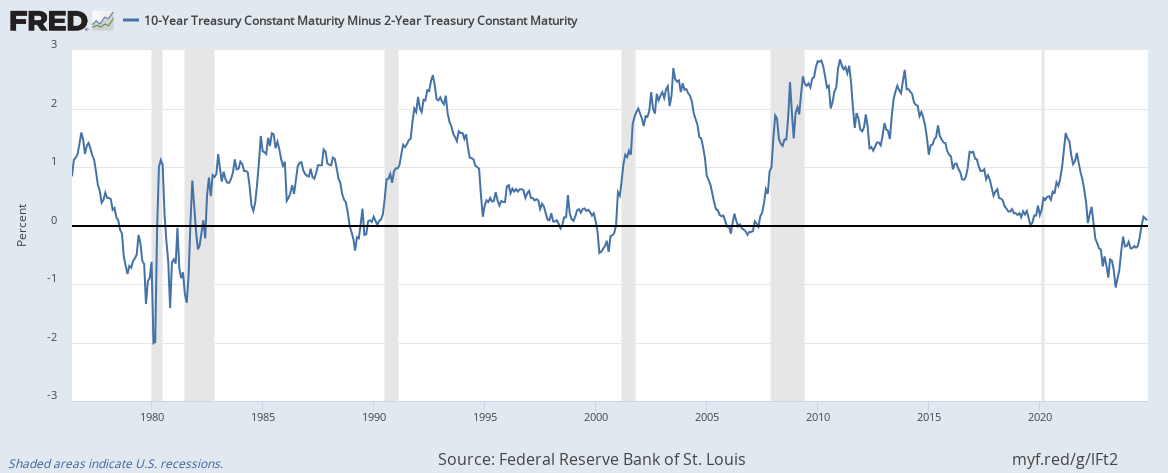
Bond Market Not Signaling Recession, Experts Say
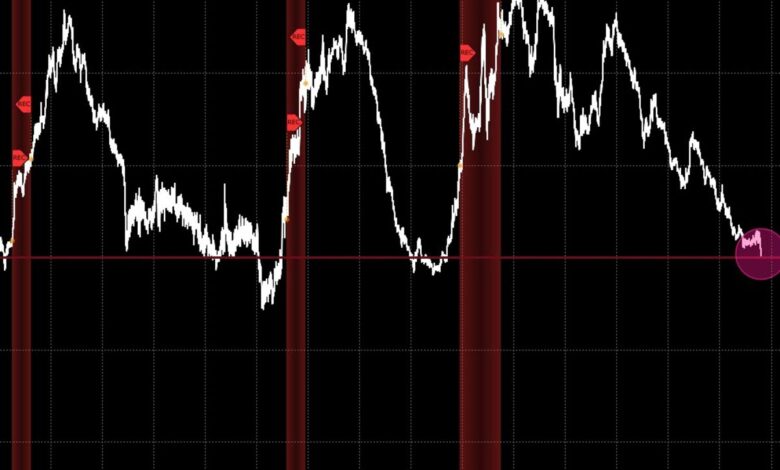
Bond market not signaling recession experts say, despite recent trends in bond yields that have some worried. While bond yields have been climbing, experts argue that these increases don’t necessarily point to an impending economic downturn. They cite a number of factors, including inflation expectations, monetary policy, and robust economic growth projections, as reasons why the bond market might not be a reliable indicator of recession this time around.
The current state of the bond market has sparked a debate among economists and market analysts. Some believe that the recent rise in bond yields is a warning sign of a looming recession, while others maintain that it is simply a reflection of factors such as inflation and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy. This divergence of opinions underscores the complexities of interpreting bond market signals and the importance of considering a range of economic indicators.
Alternative Economic Indicators to Consider
While the bond market’s signals can be insightful, it’s crucial to consider other economic indicators for a comprehensive view of the current economic landscape. These indicators provide a broader perspective, potentially revealing discrepancies or divergences from the bond market’s signals.
Key Economic Indicators Beyond the Bond Market
Beyond the bond market, several economic indicators offer valuable insights into the health and trajectory of the economy. These indicators can help refine our understanding of the current economic climate and provide a more nuanced perspective than the bond market alone.
Consumer Spending
Consumer spending is a significant driver of economic growth, accounting for a substantial portion of GDP in most developed economies. A robust and sustained increase in consumer spending generally indicates a healthy economy. Conversely, a decline in consumer spending can signal weakening economic conditions.
Labor Market Data
The labor market provides valuable insights into the economy’s health. Key indicators include unemployment rates, job creation, and labor force participation. A strong labor market, characterized by low unemployment and robust job creation, typically points to a healthy economy. Conversely, a weak labor market, with high unemployment and declining job creation, can signal economic weakness.
Inflation Data
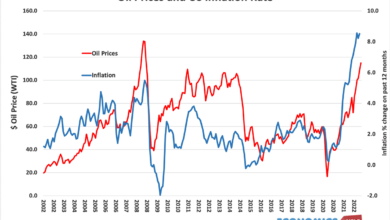
Inflation, the rate at which prices rise over time, is a crucial economic indicator. Inflation can impact consumer spending, business investment, and the overall economy. While moderate inflation is generally considered healthy for economic growth, high or volatile inflation can destabilize the economy.
Manufacturing Activity
The manufacturing sector is a significant contributor to economic output and a barometer of economic health. Indicators such as manufacturing output, purchasing managers’ indexes (PMI), and new orders can provide insights into the health of the manufacturing sector and its potential impact on economic growth.
Housing Market Data
The housing market is another significant component of the economy. Indicators such as housing starts, existing home sales, and home price indices can provide insights into the health of the housing market and its impact on economic growth.
While some experts are predicting a recession based on economic indicators, the bond market doesn’t seem to be signaling the same. This disconnect is likely due to a confluence of factors, including the recent news that Biden’s student loan relief plan will lead to severe tax hikes and more inflation, according to economists. This, in turn, could impact investor confidence and potentially fuel inflation, further complicating the economic outlook.
Government Spending and Taxation
Government spending and taxation policies can significantly impact economic activity. Increased government spending can stimulate economic growth, while tax cuts can boost consumer spending and business investment. Conversely, government spending cuts or tax increases can slow economic growth.
Global Economic Indicators
The global economy significantly influences domestic economies. Indicators such as global trade data, international commodity prices, and global economic growth forecasts can provide insights into the global economic environment and its potential impact on domestic economies.
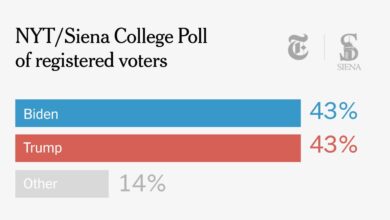
While the bond market is currently not signaling an impending recession, according to experts, the news cycle is dominated by the release of more information related to the investigation into former President Trump. A federal judge has unsealed more portions of the search warrant affidavit federal judge unseals more portions of trump search warrant affidavit , which could have a significant impact on the political landscape.
Regardless of the political drama, the bond market remains a key indicator of economic health, and its current stance suggests that a recession may not be on the immediate horizon.
Comparing Signals from Alternative Indicators to the Bond Market
It’s essential to compare the signals from these alternative economic indicators to the bond market data to identify potential discrepancies or areas of divergence. This comparison can help refine our understanding of the current economic climate and identify potential risks or opportunities.For instance, while the bond market might signal a recession, other indicators, such as strong consumer spending or robust job creation, might suggest otherwise.
This divergence could indicate that the bond market might be overreacting to certain factors, and the overall economic outlook might be more optimistic than the bond market suggests.Conversely, if the bond market signals a strong economy, while other indicators, such as high inflation or declining manufacturing activity, suggest otherwise, it might indicate that the bond market might be underestimating the risks to the economy.
Table of Economic Indicators
| Indicator Name | Current Value | Historical Trends | Potential Implications for Economic Growth ||—|—|—|—|| Consumer Spending | | | || Unemployment Rate | | | || Inflation Rate | | | || Manufacturing PMI | | | || Housing Starts | | | || Government Spending | | | || Global Trade Data | | | |
While experts say the bond market isn’t signaling an impending recession, it’s hard to ignore the seismic shifts happening elsewhere. The news that Elon Musk finally bought Twitter and fired top executives has certainly sent shockwaves through the tech industry. This kind of upheaval, coupled with the ongoing economic uncertainty, makes it clear that we’re in for a wild ride in the months ahead, regardless of what the bond market is saying.
Potential Risks and Uncertainties

While the bond market’s recent behavior may not signal an impending recession, it’s crucial to acknowledge that the current economic outlook is not without its share of risks and uncertainties. These factors could significantly influence the bond market’s ability to accurately predict economic downturns, making it essential to consider their potential impact.
Geopolitical Tensions
Geopolitical tensions can significantly impact the global economy and financial markets. Ongoing conflicts, such as the war in Ukraine, create uncertainty and volatility, disrupting supply chains, increasing commodity prices, and potentially leading to economic sanctions. These factors can negatively impact economic growth and inflation, making it difficult for investors to assess future economic prospects. For instance, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine has already caused significant disruptions in energy markets, leading to higher energy prices and increased inflation globally.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, leading to shortages of essential goods and services. Ongoing disruptions, such as factory closures, transportation delays, and labor shortages, continue to impact businesses and consumers. These disruptions can lead to higher prices, slower economic growth, and increased uncertainty, making it difficult for businesses to plan for the future.
Policy Changes
Central banks and governments are actively trying to manage inflation and economic growth, but their policy decisions can have unintended consequences. Aggressive interest rate hikes, for example, can slow economic growth but also increase the risk of a recession. Similarly, government spending policies can impact inflation and debt levels, creating uncertainty for investors.
Scenario Analysis
To better understand the potential impact of these risks and uncertainties, it’s helpful to consider different economic scenarios and their implications for the bond market.
Scenario 1: Continued Strong Economic Growth
In this scenario, the global economy continues to grow at a healthy pace, despite the challenges posed by geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions. Inflation gradually moderates as central banks successfully manage interest rates. In this scenario, bond yields are likely to rise as investors anticipate higher economic growth and inflation.
Scenario 2: Recession
A significant economic slowdown or recession could lead to a decline in bond yields as investors seek safe-haven assets. This scenario could be triggered by a combination of factors, such as a sharp increase in interest rates, a prolonged supply chain crisis, or a major geopolitical event.
Scenario 3: Stagflation
Stagflation, a combination of high inflation and slow economic growth, could create a challenging environment for investors. In this scenario, bond yields might remain elevated as investors worry about inflation eroding the value of their investments.
Implications for Investors and Businesses: Bond Market Not Signaling Recession Experts Say
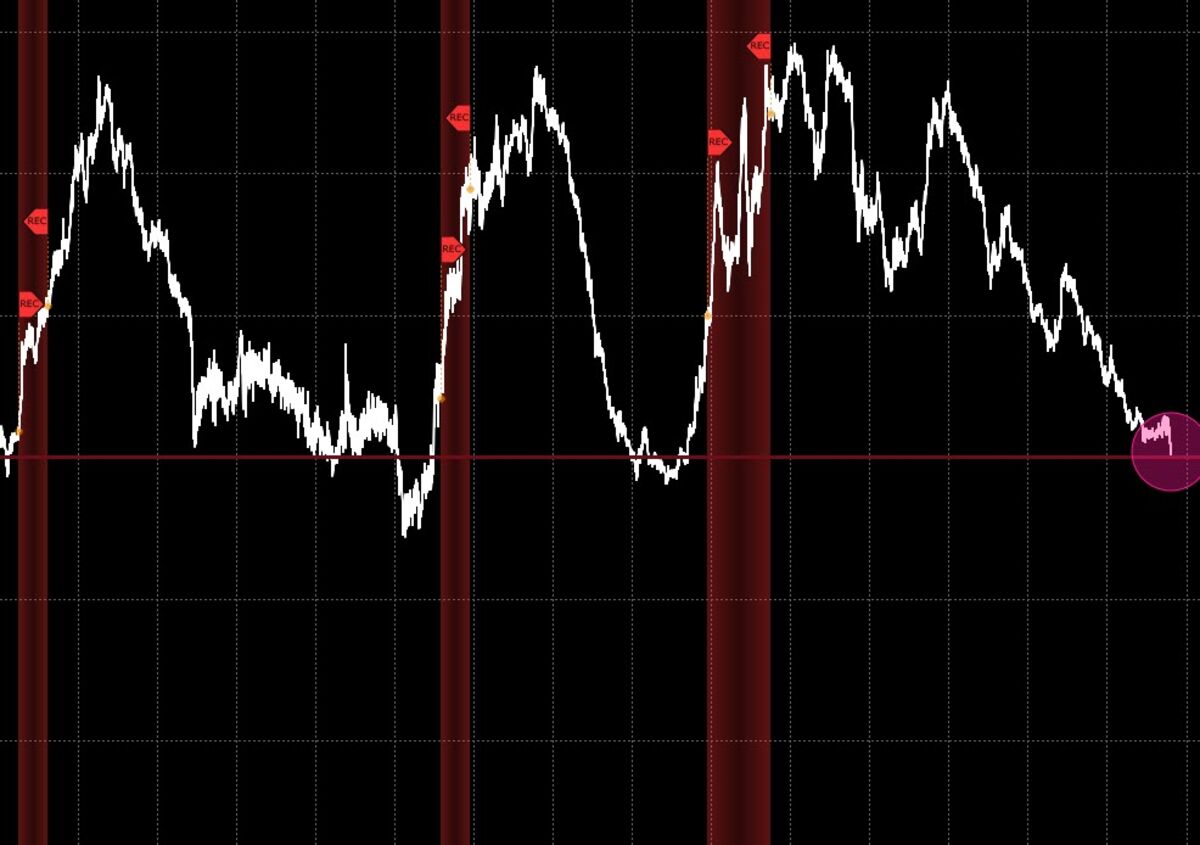
The current bond market signals, while not necessarily predicting an imminent recession, present a significant challenge for investors and businesses. Understanding the implications of these signals is crucial for navigating the uncertain economic landscape.
Impact on Investors
Investors, particularly those with exposure to fixed-income securities, need to be aware of the potential for rising interest rates and their impact on bond yields. As interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds with lower yields declines. This is because investors can now purchase new bonds with higher yields, making older bonds less attractive. Investors with a long-term investment horizon may consider diversifying their portfolios by allocating a portion of their assets to alternative investments, such as equities or real estate, which may be less susceptible to interest rate fluctuations.
They should also re-evaluate their risk tolerance and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Investment Strategies for Businesses
Businesses need to carefully consider the potential impact of rising interest rates on their financing costs and overall profitability. They should review their debt structures and explore opportunities to refinance existing loans at lower interest rates before rates rise further.Businesses should also assess their capital expenditure plans and prioritize investments with high returns and short payback periods. This will help them to manage their cash flow and maintain profitability in an environment of rising borrowing costs.
Key Takeaways for Investors and Businesses, Bond market not signaling recession experts say
| Category | Investors | Businesses |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Mitigation |
|
|
| Opportunity Seizing |
|
|
The bond market is just one piece of the economic puzzle. While its signals are often closely watched, it’s crucial to consider a broader range of economic indicators to get a complete picture. Ultimately, the future of the economy depends on a multitude of factors, and the bond market alone cannot provide a definitive answer. Investors and businesses need to remain vigilant and adapt their strategies to navigate the current environment of uncertainty.