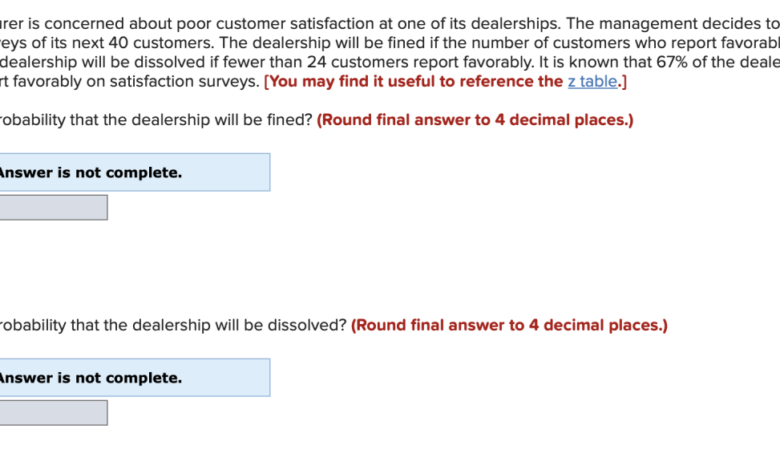
Big Automakers Failing to Protect Customer Privacy Report
The “Big Automakers Are Failing to Protect Customer Privacy Report” sets the stage for a concerning revelation about the vulnerabilities within the automotive industry. It paints a picture of a landscape where our personal data, collected by our vehicles, is not always treated with the care and respect it deserves.
This report dives deep into the practices of major car manufacturers, exposing the concerning ways in which our privacy is being compromised.
The report highlights the vast amount of data being collected by connected vehicles, including our driving habits, location data, and even personal preferences. It then delves into how this data is being used, often without our explicit consent, and explores the potential consequences for individuals whose privacy is breached.
The report’s findings raise serious questions about the ethical implications of data collection in the automotive industry and the need for stronger regulations to protect consumers.
The Nature of the Privacy Breach
The automotive industry, like many others, is grappling with the increasing complexity of data security and privacy. Big automakers, while investing heavily in connected car technologies, are falling short in protecting the sensitive data they collect from their customers. This failure has led to a growing concern about the potential misuse of personal information and the vulnerability of automotive systems to cyberattacks.
Data Collection and Usage Practices
The data collected by big automakers encompasses a wide range of information, including:
- Personal Information:This includes driver’s name, address, phone number, and email address. This data is often used for marketing purposes, vehicle maintenance scheduling, and customer support.
- Vehicle Usage Data:This includes information about driving habits, location, speed, acceleration, and braking patterns. This data is used to improve vehicle performance, optimize fuel efficiency, and develop new features.
- Vehicle Diagnostic Data:This includes information about the vehicle’s health, performance, and maintenance needs. This data is used to diagnose problems, schedule repairs, and improve vehicle reliability.
- In-Car Interactions:This includes information about the driver’s voice commands, music preferences, and navigation choices. This data is used to personalize the driving experience and develop new features.
While some of this data is collected with the user’s consent, the extent to which automakers are transparent about their data collection practices and the purposes for which this data is used remains a point of contention. Additionally, the lack of clear guidelines and regulations regarding data privacy in the automotive industry raises concerns about the potential misuse of this information.
Examples of Data Breaches and Privacy Violations
In recent years, several high-profile data breaches and privacy violations have exposed the vulnerabilities of automotive data security systems.
- 2015 Jeep Cherokee Hack:Researchers demonstrated the ability to remotely control a Jeep Cherokee through its connected car system. This vulnerability allowed hackers to take control of the vehicle’s brakes, steering, and other critical functions. This incident highlighted the potential risks of connected car technology and the need for robust security measures.
- 2017 Tesla Data Breach:Hackers gained access to a database containing sensitive information about Tesla owners, including their names, addresses, and email addresses. This breach raised concerns about the security of Tesla’s data storage and the potential for misuse of personal information.
- 2021 Hyundai and Kia Data Breach:A group of hackers gained access to a database containing personal information about Hyundai and Kia owners, including their names, addresses, and vehicle identification numbers. This breach led to a class-action lawsuit alleging that the companies failed to adequately protect customer data.
Vulnerabilities in Automotive Data Security Systems
Several factors contribute to the vulnerabilities in current automotive data security systems.
- Lack of Standardized Security Practices:The automotive industry lacks a standardized approach to data security, which makes it difficult for automakers to ensure that their systems are adequately protected. This lack of standardization creates opportunities for hackers to exploit vulnerabilities in different vehicle models.
It’s crazy how big automakers are failing to protect customer privacy, but at least they’re not the only ones with questionable security practices. I was shocked to read about the 9 boxes of Biden documents taken from a Boston office that weren’t reviewed for classified materials ! It makes you wonder if we can trust anyone with our data these days, whether it’s our car’s location or our personal information.
- Outdated Software:Many vehicles are equipped with outdated software that is vulnerable to known security exploits. Automakers often struggle to keep up with the rapid pace of software development, which leaves their vehicles open to attack.
- Insufficient Encryption:Some automakers fail to adequately encrypt sensitive data, making it vulnerable to interception and theft. This lack of encryption can expose customer information to hackers and other unauthorized individuals.
- Poor Password Management:Automakers often use weak passwords or fail to implement multi-factor authentication, making it easier for hackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. This lack of strong password management practices increases the risk of data breaches.
Consequences for Customers: Big Automakers Are Failing To Protect Customer Privacy Report
The privacy breaches by major automakers can have severe consequences for customers. Their personal data, including driving habits, location, and even financial information, is at risk. These breaches can lead to a range of problems, from identity theft to financial loss and reputational damage.
Financial Consequences, Big automakers are failing to protect customer privacy report
Data breaches can lead to financial consequences for customers in several ways. Stolen credit card information can be used for fraudulent purchases. Hackers can also access bank account details, leading to unauthorized withdrawals. In some cases, customers may even have to pay for credit monitoring services to protect themselves from identity theft.
For example, in 2017, Equifax, a credit reporting agency, suffered a data breach that affected millions of customers. The breach exposed sensitive personal information, including Social Security numbers and credit card details. Many customers had to take steps to protect themselves from identity theft, including freezing their credit reports and monitoring their accounts.
Reputational Consequences
Data breaches can also damage a customer’s reputation. If personal information is leaked online, it can be used to create fake social media profiles or spread false information about the customer. This can lead to embarrassment, social isolation, and even damage to a customer’s professional life.
For instance, in 2019, a data breach at Marriott Hotels exposed the personal information of millions of guests, including their names, addresses, and credit card details. This incident led to a significant loss of trust in Marriott, and some customers may have hesitated to book stays at the hotel chain in the future.
Emotional Consequences
Data breaches can also have significant emotional consequences for customers. The fear of identity theft and financial loss can cause anxiety and stress. Customers may also feel violated and betrayed by the companies that have failed to protect their data.
For example, in 2017, the data breach at Yahoo affected billions of users. This incident caused widespread anxiety and fear among users, as they worried about the potential for their personal information to be misused.
Legal Repercussions
Customers whose data is misused may have legal recourse. They can sue the company responsible for the breach for damages, including financial losses and emotional distress. They may also be able to file complaints with regulatory agencies. For instance, in 2018, the European Union passed the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which gives individuals more control over their personal data and provides them with the right to sue companies that misuse their data.
The news about big automakers failing to protect customer privacy is concerning, especially considering how much data they collect. It seems like every day there’s a new report about a breach or data misuse. Meanwhile, Wall Street opened lower today on inflation concerns, with investors focused on the Fed’s upcoming speeches.
You can read more about the market situation here. Hopefully, the automakers will take this privacy issue seriously and implement stronger security measures to protect their customers’ data.
Consequences for Customers
| Type of Consequence | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Financial | Identity theft, fraudulent purchases, unauthorized withdrawals, credit monitoring costs |
| Reputational | Fake social media profiles, false information spread, damage to professional life |
| Emotional | Anxiety, stress, feeling violated and betrayed |
| Legal | Damages for financial losses and emotional distress, complaints with regulatory agencies |
Industry Practices and Regulations
The automotive industry is grappling with a complex landscape of data privacy practices and regulations. While automakers have made strides in adopting data protection measures, concerns remain about the adequacy of these practices and the effectiveness of existing regulations. This section examines the data privacy practices of different automakers, analyzes the current regulatory landscape, and explores the role of industry self-regulation.
It’s hard to believe that while we’re grappling with the news of big automakers failing to protect customer privacy, catastrophic hurricane Idalia is wreaking havoc on Florida and Georgia. It’s a stark reminder that even as we navigate the digital world, real-world disasters continue to impact lives.
Perhaps it’s time we prioritize safeguarding both our personal data and our physical well-being, ensuring a safer future for all.
Data Privacy Practices of Different Automakers
Automakers collect vast amounts of data from their vehicles and customers, ranging from driving habits and location data to personal information and vehicle performance metrics. While there is no single approach to data privacy across the industry, some common practices and variations exist:
- Data Collection and Use Policies:Most automakers have published data privacy policies outlining the types of data they collect, how they use it, and the choices customers have regarding their data. However, these policies can vary in clarity and comprehensiveness, leading to confusion and potential misuse of data.
- Data Sharing Practices:Automakers often share data with third-party partners, such as service providers, data analytics companies, and marketing firms. The extent and nature of data sharing vary significantly, raising concerns about the security and privacy of customer data in the hands of third parties.
- Data Retention Policies:The duration for which automakers retain customer data varies widely. Some companies have clear data retention policies, while others lack transparency, leading to concerns about the potential for prolonged storage and misuse of data.
- Data Security Measures:Automakers employ various data security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. However, the effectiveness of these measures can differ significantly, and concerns persist about the vulnerability of connected vehicles to cyberattacks.
Regulatory Landscape for Data Privacy in the Automotive Industry
The regulatory landscape for data privacy in the automotive industry is evolving rapidly. Key regulations and frameworks include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):This European Union regulation imposes stringent requirements on data collection, processing, and storage, affecting automakers operating in the EU. GDPR mandates data minimization, transparency, and customer consent for data processing.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA):This California law grants consumers rights regarding their personal data, including the right to know, access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their data. It applies to businesses operating in California, including automakers.
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC):The FTC has authority to investigate and enforce unfair or deceptive trade practices, including data privacy violations. The FTC has issued guidance and enforcement actions related to data security and privacy in the automotive industry.
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA):This agency has regulatory authority over vehicle safety, including cybersecurity. NHTSA is increasingly focusing on data privacy and security concerns related to connected vehicles.
Effectiveness of Existing Regulations in Protecting Customer Privacy
The effectiveness of existing regulations in protecting customer privacy in the automotive industry is a subject of ongoing debate. While regulations provide a framework for data protection, challenges remain:
- Enforcement and Compliance:Enforcement of data privacy regulations can be challenging, particularly in a globalized industry. Ensuring compliance across different jurisdictions and with evolving regulations requires significant resources and effort.
- Scope and Applicability:Some regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, have limited scope and may not fully address all data privacy concerns in the automotive industry. For instance, these regulations may not cover all types of data collected by automakers or the sharing of data with third parties.
- Technological Advancements:Rapid technological advancements in the automotive industry, such as the emergence of autonomous vehicles, pose new challenges for data privacy regulations. Existing regulations may not adequately address the unique privacy risks associated with these technologies.
Industry Self-Regulation in Addressing Data Privacy Concerns
Industry self-regulation plays a role in addressing data privacy concerns in the automotive industry. Automakers have formed industry associations and adopted self-regulatory frameworks to promote responsible data practices. These initiatives often include:
- Data Privacy Principles:Industry associations have developed data privacy principles outlining best practices for data collection, use, sharing, and security. These principles provide guidance for automakers and help establish industry standards.
- Certification Programs:Some industry associations offer certification programs for automakers that demonstrate compliance with data privacy principles and best practices. These certifications can provide assurance to consumers and regulators about the company’s commitment to data privacy.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing:Industry associations facilitate collaboration and information sharing among automakers on data privacy issues. This helps to identify emerging threats, develop best practices, and improve data protection measures.
Consumer Awareness and Empowerment
The automotive industry’s shift towards connected vehicles has brought unprecedented convenience and features, but it has also raised significant concerns about data privacy. Consumers, often unaware of the extent of data collection and its potential misuse, are at risk of having their personal information compromised.
This section delves into consumer awareness regarding data privacy in the automotive sector, explores ways to protect privacy while using connected vehicles, and provides resources for consumers to learn more about their rights.
Consumer Awareness of Data Privacy
While consumer awareness of data privacy in general has increased, awareness specifically within the automotive sector remains relatively low. A significant portion of consumers are unaware of the vast amount of data collected by their vehicles, including location, driving habits, and personal information.
This lack of awareness can lead to a sense of vulnerability and a lack of control over personal data.
Protecting Privacy in Connected Vehicles
Consumers can take proactive steps to protect their privacy while using connected vehicles. These steps involve understanding the data collected, controlling data sharing, and utilizing privacy-enhancing features.
Resources for Consumer Education
Consumers can access various resources to learn more about data privacy and their rights. These resources include:
- Privacy Policy Reviews:Carefully review the privacy policies of vehicle manufacturers and connected car services to understand the data collected, its use, and sharing practices.
- Consumer Protection Agencies:Contact consumer protection agencies, such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States, for information and assistance regarding data privacy issues.
- Privacy Advocacy Groups:Engage with privacy advocacy groups, such as the Electronic Privacy Information Center (EPIC), for updates on data privacy regulations and best practices.
- Online Resources:Explore online resources, including websites and articles, that provide comprehensive information on data privacy in the automotive sector.
Practical Steps to Mitigate Privacy Risks
The following table Artikels practical steps consumers can take to mitigate privacy risks associated with connected vehicles:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Disable Unnecessary Data Sharing | Review vehicle settings and disable data sharing features that are not essential, such as location tracking when not driving. |
| Use Privacy-Enhanced Features | Utilize features like in-vehicle data encryption and anonymization to protect personal information. |
| Limit Data Collection | Avoid using features that collect excessive personal data, such as voice assistants for non-essential tasks. |
| Review and Delete Data | Regularly review the data collected by the vehicle and connected services, and delete unnecessary information. |
| Stay Informed | Stay updated on data privacy regulations, industry best practices, and emerging technologies related to connected vehicles. |
Future Directions
The automotive industry is at a crossroads, grappling with the need to balance innovation with data privacy concerns. The connected car ecosystem, while offering a wealth of benefits, presents a unique set of challenges that require innovative solutions to safeguard customer data.
This section explores potential technological solutions, the role of innovation, emerging trends, and a roadmap for improving data privacy practices within the automotive industry.
Technological Solutions for Enhanced Data Privacy
Technological solutions play a crucial role in addressing data privacy concerns in the automotive industry. These solutions can help protect sensitive information while enabling the seamless functionality of connected car features.
- Differential Privacy: This technique adds noise to data before it is shared, making it difficult to identify individuals while preserving the overall data trends. For instance, a car manufacturer could use differential privacy to analyze driving patterns without revealing specific driver information.
- Homomorphic Encryption: This allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it, ensuring data privacy throughout the processing lifecycle. This technology can be applied to secure data analysis, such as analyzing vehicle performance data while protecting the identity of the owner.
- Federated Learning: This approach enables training machine learning models on decentralized data without sharing raw data. Car manufacturers can leverage federated learning to improve safety features by analyzing driving data from multiple vehicles without compromising individual privacy.
The Role of Innovation in Addressing Privacy Concerns
Innovation is essential for developing effective data privacy solutions in the automotive industry. By embracing new technologies and approaches, manufacturers can proactively address privacy concerns and build trust with consumers.
- Privacy-by-Design: This principle emphasizes integrating privacy considerations into every stage of product development. Car manufacturers can implement privacy-by-design principles to ensure that data collection and usage are minimized and that data is protected throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle.
- Data Minimization: This principle advocates for collecting only the data necessary for a specific purpose. By minimizing data collection, manufacturers can reduce the risk of privacy breaches and enhance user trust. For example, a navigation system might only require basic location data for route planning, avoiding the collection of unnecessary personal information.
- Transparency and Control: Transparency and control over data are crucial for building consumer trust. Car manufacturers should clearly communicate their data practices and provide users with options to control their data sharing and access preferences. This could include providing users with clear explanations of how their data is used, offering granular control over data sharing settings, and allowing users to delete their data at any time.
Emerging Trends and Challenges
The connected car ecosystem is constantly evolving, bringing new trends and challenges to data privacy. Understanding these emerging trends is essential for developing effective privacy solutions.
- Data Sharing and Collaboration: As vehicles become increasingly connected, there is a growing trend of data sharing between car manufacturers, third-party providers, and other stakeholders. This creates opportunities for data-driven services but also raises concerns about data security and privacy. Effective data sharing protocols and mechanisms are needed to ensure that data is shared responsibly and securely.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing enables data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance. However, it also presents new challenges for data privacy. Secure data storage and processing mechanisms are essential to protect data at the edge.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming the automotive industry, enabling features like autonomous driving and personalized experiences. However, AI systems rely on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about data privacy. AI models must be trained and deployed in a way that respects data privacy and minimizes bias.
Roadmap for Improving Data Privacy Practices
Improving data privacy practices in the automotive industry requires a multi-faceted approach. This roadmap Artikels key steps that manufacturers can take to enhance data privacy and build consumer trust.
- Establish Clear Data Privacy Policies: Car manufacturers should develop comprehensive data privacy policies that clearly define their data collection, usage, and sharing practices. These policies should be easily accessible to consumers and regularly updated to reflect evolving industry standards and regulations.
- Implement Strong Data Security Measures: Robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. Manufacturers should implement strong encryption protocols, access controls, and data loss prevention measures to safeguard data throughout its lifecycle.
- Provide Transparency and Control: Consumers should have clear visibility into how their data is used and the ability to control their data sharing preferences. Car manufacturers should provide user-friendly dashboards that allow users to view and manage their data, access data usage reports, and choose how their data is shared with third parties.
- Promote Data Privacy Education: Car manufacturers should invest in educating consumers about data privacy and the importance of protecting their information. This could include providing online resources, interactive guides, and educational campaigns to raise awareness and empower consumers to make informed decisions about their data.
- Engage with Stakeholders: Collaboration with industry stakeholders, including regulators, consumer groups, and technology providers, is essential for developing effective data privacy solutions. Manufacturers should actively participate in industry forums and working groups to share best practices, develop industry standards, and address emerging privacy challenges.
Epilogue
The “Big Automakers Are Failing to Protect Customer Privacy Report” serves as a stark reminder that our data is valuable and deserves protection. It urges both automakers and consumers to take a proactive approach to data privacy. Automakers must prioritize secure data collection and transparent data usage practices.
Consumers, on the other hand, need to be aware of the risks and take steps to safeguard their privacy while using connected vehicles. This report is a crucial step towards building a more secure and responsible future for data privacy in the automotive industry.

