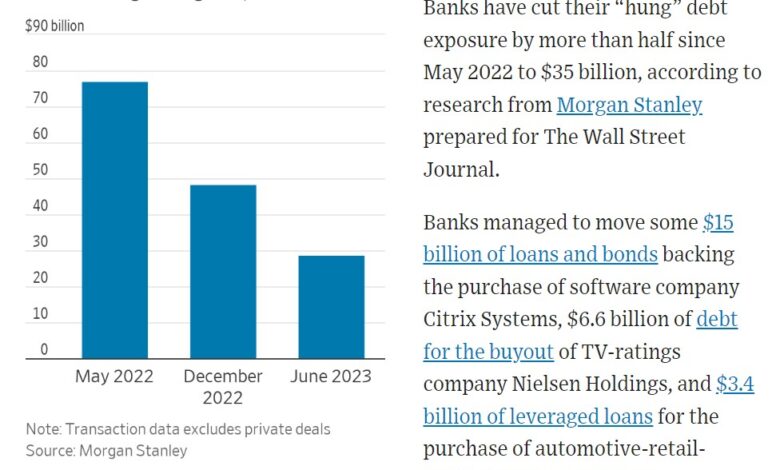
Banks Borrow Billions to Maintain Liquidity: Fed Data Shows
Banks borrow billions to maintain liquidity fed data show – Banks Borrow Billions to Maintain Liquidity: Fed Data Shows – This headline might seem alarming, but it’s a reflection of the complex dynamics at play within the financial system. Recent data from the Federal Reserve reveals a surge in bank borrowing, raising questions about the health of the economy and the potential implications for lending and credit availability.
This trend is driven by a combination of factors, including rising interest rates, regulatory pressures, and concerns about potential economic downturns. Banks are essentially borrowing from each other to ensure they have enough cash on hand to meet their obligations and maintain their liquidity levels.
While this borrowing is a normal part of the financial system, the sheer volume of it raises concerns about the overall stability of the economy.
The Current State of Bank Liquidity
Bank liquidity is a crucial aspect of the financial system, signifying a bank’s ability to meet its short-term obligations and maintain its financial stability. It refers to the bank’s capacity to readily convert assets into cash to cover unexpected withdrawals or meet other immediate financial demands.
Maintaining adequate liquidity is essential for banks to operate effectively and to avoid potential financial distress.
It’s fascinating to see how banks are borrowing billions to maintain liquidity, as shown in recent Fed data. This move suggests a cautious approach to lending, perhaps reflecting concerns about the broader economic landscape. While the recent job report shows the US economy added 223,000 new jobs us economy added 223000 new jobs as labor market continues to slow , the slowing labor market may be a contributing factor to this cautious banking behavior.
This careful approach to lending could be a sign that banks are preparing for potential economic headwinds.
Recent Federal Reserve Data on Bank Borrowing
The Federal Reserve closely monitors bank liquidity and provides data on borrowing activities. The recent data reveals a significant increase in bank borrowing from the Federal Reserve, particularly through the Discount Window and the Reverse Repurchase Agreements (RRP) facility.
It’s fascinating to see how banks are borrowing billions to maintain liquidity, as reported by the Fed. This highlights the ongoing challenges within the financial system, especially as we navigate economic uncertainties. Meanwhile, gun owners of America are voicing their strong opposition to the omnibus bill , arguing that it pushes forward President Biden’s gun control agenda.
It’s a reminder that even amidst financial concerns, political debates continue to shape the nation’s priorities.
This increase in borrowing suggests that banks are facing challenges in maintaining their liquidity levels.
Factors Contributing to Increased Bank Borrowing
Several factors contribute to the rise in bank borrowing, reflecting potential concerns about the economic outlook and the financial system’s stability.
- Elevated Inflation and Interest Rate Hikes:The recent surge in inflation has prompted the Federal Reserve to implement aggressive interest rate hikes. These hikes increase the cost of borrowing for banks, potentially reducing their profitability and increasing the demand for liquidity.
- Uncertainty in the Economic Outlook:The global economic environment is characterized by heightened uncertainty, including geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and rising energy prices. This uncertainty may lead banks to hold more liquid assets as a precautionary measure to mitigate potential risks.
- Potential for a Recession:The possibility of a recession, coupled with the aggressive interest rate hikes, is causing banks to become more cautious about lending and to seek additional liquidity to manage potential loan losses.
Implications of Borrowing Trends for the Financial System
The increase in bank borrowing has implications for the overall financial system. While the Federal Reserve’s lending facilities provide a vital safety net, excessive borrowing can indicate underlying stress in the financial system.
- Potential for Reduced Lending:If banks become more risk-averse due to concerns about the economic outlook, they may reduce lending activity, which could stifle economic growth.
- Increased Financial Market Volatility:Increased borrowing and uncertainty can lead to heightened volatility in financial markets, potentially affecting asset prices and investor sentiment.
- Systemic Risk:In extreme cases, widespread liquidity shortages could pose a systemic risk to the financial system, potentially leading to a financial crisis.
Reasons Behind Bank Borrowing
Banks borrowing billions is not a new phenomenon. It’s a common practice, especially when faced with liquidity pressures or to meet regulatory requirements. This borrowing can take various forms, and the reasons behind it are multifaceted.
Types of Loans Banks Take Out, Banks borrow billions to maintain liquidity fed data show
Banks borrow money for various reasons, and the specific types of loans they take out reflect these purposes. Some of the most common types include:
- Overnight Repo Loans:These short-term loans are typically used to meet daily liquidity needs, allowing banks to manage their cash positions and ensure they have enough funds to meet customer withdrawals or other obligations.
- Term Repo Loans:These loans are used for longer-term funding needs, such as to finance investments or meet regulatory capital requirements. Term repo loans typically have maturities of several weeks or months.
- Discount Window Loans:These loans are offered by central banks as a lender of last resort, providing banks with emergency funding when other sources are unavailable. Discount window loans are typically short-term and come with higher interest rates than other types of loans.
Impact of Rising Interest Rates
Rising interest rates can significantly impact bank borrowing activities. As interest rates increase, the cost of borrowing money rises, making it more expensive for banks to take out loans. This can lead to a reduction in borrowing activity, as banks may choose to reduce their reliance on borrowed funds and seek alternative sources of financing.
For example, during periods of rising interest rates, banks may seek to increase their deposit-taking activities to reduce their dependence on borrowed funds.
Regulatory Pressures and Capital Requirements
Regulatory pressures and capital requirements play a significant role in influencing bank borrowing. Regulations often require banks to maintain certain levels of capital reserves, which can necessitate borrowing to meet these requirements. For example, the Basel III framework, a set of international banking regulations, requires banks to hold a certain percentage of their assets as capital reserves.
Banks may need to borrow to meet these capital requirements, particularly if they have experienced losses or have a high concentration of risky assets.
It’s fascinating to see how banks are borrowing billions to maintain liquidity, as reported by the Fed. This financial maneuvering is a reflection of the current economic climate, and it’s worth considering how these actions might impact the average person.
Meanwhile, an analyst has suggested that young black voters aren’t particularly enthused about the Biden-Harris ticket. This lack of excitement could have significant political implications, especially given the importance of this demographic in elections. Whether it’s the banking sector or the political landscape, it’s clear that we’re living in a time of constant change and flux.
Impact of Bank Borrowing on the Economy: Banks Borrow Billions To Maintain Liquidity Fed Data Show
Banks borrowing billions from the Federal Reserve can have significant implications for the overall economy. While it helps maintain liquidity and prevent financial instability, it can also influence lending activity, credit availability, interest rates, and inflation.
Impact on Lending Activity and Credit Availability
When banks borrow from the Fed, they have more funds available to lend to businesses and consumers. This can lead to increased lending activity and greater credit availability, potentially stimulating economic growth. However, if banks become overly reliant on Fed borrowing, it could lead to a situation where they are less willing to lend their own funds, potentially hindering credit availability.
Impact on Interest Rates and Inflation
Increased borrowing by banks can impact interest rates and inflation. When banks borrow heavily from the Fed, they can reduce the amount of money available in the market, leading to higher interest rates. Higher interest rates can discourage borrowing and investment, potentially slowing down economic growth.
Additionally, increased bank borrowing can contribute to inflation, as banks may pass on the higher borrowing costs to consumers in the form of higher loan rates and fees.
Potential Risks Associated with High Levels of Bank Borrowing
High levels of bank borrowing can pose risks to the economy. If banks become overly reliant on Fed borrowing, it could create a moral hazard, where they become less cautious in their lending practices. This could lead to excessive risk-taking and potential financial instability.
Additionally, if banks are unable to repay their loans to the Fed, it could create a liquidity crisis and further destabilize the financial system.
The Role of the Federal Reserve

The Federal Reserve (Fed), the central bank of the United States, plays a crucial role in managing bank liquidity and ensuring financial stability. Its actions directly impact the borrowing behavior of banks and influence the overall health of the economy.
Tools and Policies for Managing Bank Liquidity
The Fed utilizes a range of tools and policies to manage bank liquidity and address potential risks associated with bank borrowing. These tools are designed to ensure that banks have sufficient funds to meet their obligations and maintain a healthy level of liquidity.
- The Federal Funds Rate:The Fed sets the target federal funds rate, which is the interest rate at which banks lend reserves to each other overnight. By adjusting this rate, the Fed influences the cost of borrowing for banks, impacting their lending activities and overall liquidity.
- Discount Rate:The discount rate is the interest rate at which banks can borrow directly from the Fed. This rate is typically higher than the federal funds rate, acting as a backstop to ensure banks have access to liquidity in emergency situations.
- Reserve Requirements:The Fed sets reserve requirements, which determine the percentage of deposits that banks must hold in reserve. By adjusting these requirements, the Fed can influence the amount of funds available for lending in the banking system.
- Open Market Operations:The Fed conducts open market operations by buying or selling U.S. Treasury securities in the open market. Buying securities injects liquidity into the banking system, while selling securities withdraws liquidity.
- Quantitative Easing (QE):During periods of economic stress, the Fed can implement quantitative easing, a policy of purchasing large quantities of long-term assets to inject liquidity into the financial system and stimulate economic activity.
Impact of the Fed’s Actions on Bank Borrowing
The Fed’s actions directly impact the borrowing behavior of banks by influencing the cost of borrowing, the availability of funds, and the overall risk environment.
- Lowering the Federal Funds Rate:When the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it becomes cheaper for banks to borrow from each other, encouraging them to increase their lending activities and potentially leading to higher levels of bank borrowing.
- Providing Liquidity Through Open Market Operations:By injecting liquidity into the banking system through open market operations, the Fed can make it easier for banks to obtain funds, potentially increasing their borrowing capacity.
- QE and Bank Borrowing:Quantitative easing can stimulate bank borrowing by increasing the demand for loans and lowering interest rates, making it more attractive for banks to borrow.
- Impact of Interest Rate Hikes:Conversely, when the Fed raises interest rates, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow, potentially reducing their borrowing activities and leading to a tightening of credit conditions.
Communication Strategies and Market Sentiment
The Fed’s communication strategies play a significant role in shaping market sentiment and influencing the borrowing behavior of banks.
- Transparency and Communication:The Fed’s communication strategy emphasizes transparency and clarity, providing regular updates on its economic outlook, policy decisions, and the rationale behind its actions.
- Press Conferences and Statements:The Fed holds press conferences and issues statements following policy meetings, providing insights into its thinking and expectations for the economy.
- Forward Guidance:The Fed uses forward guidance to communicate its intentions regarding future policy actions, helping market participants understand the direction of monetary policy and adjust their borrowing decisions accordingly.
Future Outlook and Implications
Predicting the future of bank borrowing is a complex task, as it hinges on various economic factors, both domestic and global. However, by analyzing current trends and understanding the dynamics of bank liquidity, we can shed light on potential future scenarios and their implications for the financial system and the broader economy.
Impact of Global Economic Events
Global economic events, such as trade wars, geopolitical tensions, and pandemics, can significantly impact bank liquidity. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic triggered a surge in bank borrowing as businesses and individuals sought financial support. Similarly, the ongoing war in Ukraine has disrupted global supply chains and increased uncertainty, leading to a rise in risk aversion among banks.
Key Factors Influencing Bank Borrowing Behavior
Several key factors will influence bank borrowing behavior in the coming months. These include:
- Interest Rate Movements:Rising interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, potentially leading to a decline in bank borrowing. Conversely, falling interest rates can incentivize borrowing, leading to an increase in bank liquidity.
- Economic Growth:Strong economic growth typically leads to increased demand for credit, prompting banks to borrow more to meet those needs. Conversely, a weakening economy can lead to a decline in borrowing as businesses and individuals become more cautious.
- Regulatory Changes:Changes in regulations, such as stricter capital requirements or new lending restrictions, can impact bank borrowing behavior. For instance, stricter capital requirements might limit the amount of money banks can lend, reducing their need to borrow.
- Risk Aversion:In times of economic uncertainty or heightened market volatility, banks tend to become more risk-averse, leading to a decrease in lending and borrowing.
Implications for the Financial System and the Economy
The trends in bank borrowing can have significant implications for the financial system and the broader economy.
- Financial Stability:Excessive bank borrowing can increase systemic risk, potentially leading to financial instability. Conversely, a lack of liquidity can hinder banks’ ability to lend, impacting economic growth.
- Economic Growth:Bank borrowing is crucial for economic growth. When banks borrow and lend, they facilitate investment and economic activity. However, excessive borrowing can lead to asset bubbles and unsustainable growth.
- Inflation:Increased bank borrowing can contribute to inflation by injecting more money into the economy. However, the relationship between bank borrowing and inflation is complex and influenced by other factors.
Wrap-Up
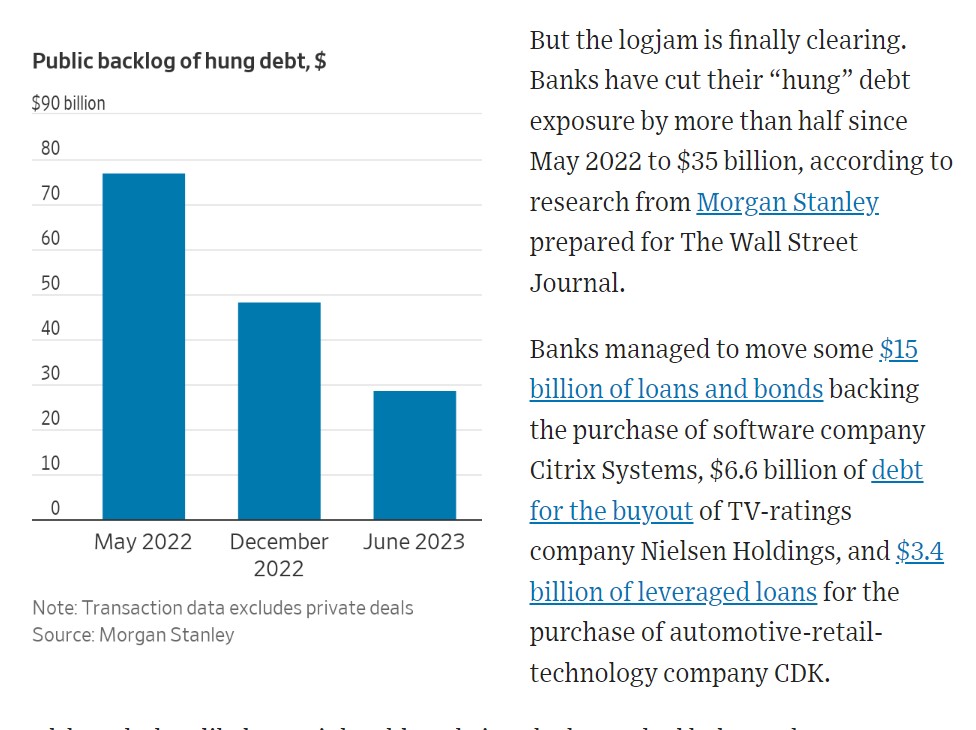
The recent surge in bank borrowing underscores the delicate balance between financial stability and economic growth. The Federal Reserve is closely monitoring the situation and using its tools to ensure that banks have access to the liquidity they need. However, the potential impact of this borrowing trend on lending, interest rates, and inflation remains a significant concern.
It’s a complex issue with far-reaching implications, and understanding the dynamics at play is crucial for navigating the economic landscape ahead.