Australia Wildfires: 3 Billion Animals Lost, A Historic Disaster
Australia wildfires killed or displaced nearly 3 billion animals declared among worst wildlife disasters in history – Australia Wildfires: 3 Billion Animals Lost, A Historic Disaster – the words echo a tragedy of unimaginable scale. In the summer of 2019-2020, Australia’s landscapes were consumed by a firestorm that raged for months, leaving a trail of devastation unlike anything seen before.
The fires, fueled by a combination of drought, heatwaves, and strong winds, burned through millions of acres, leaving a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of climate change.
The impact on wildlife was catastrophic. Scientists estimate that nearly 3 billion animals perished or were displaced, making it one of the worst wildlife disasters in recorded history. The fires not only claimed countless lives but also destroyed critical habitats, threatening the survival of already vulnerable species.
The consequences of these fires extend far beyond the immediate loss of life, with long-term impacts on Australia’s ecosystems and biodiversity.
The Role of Climate Change: Australia Wildfires Killed Or Displaced Nearly 3 Billion Animals Declared Among Worst Wildlife Disasters In History
The devastating Australian bushfires of 2019-2020 were not just a natural disaster; they were a stark reminder of the impact of climate change on our planet. Climate change is exacerbating the frequency and intensity of wildfires, making them more dangerous and destructive.
Scientific Evidence Linking Climate Change to Wildfires
A growing body of scientific evidence has established a clear link between climate change and the increased risk of wildfires in Australia. Numerous studies have shown that rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changes in vegetation patterns due to climate change are directly contributing to the severity and frequency of wildfires.
- A study published in the journal Nature Climate Change in 2019 found that the risk of extreme fire weather in Australia has increased by 30% since 1900, primarily due to rising temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns.
- Another study, published in the journal Environmental Research Letters in 2020, analyzed data from the 2019-2020 bushfires and concluded that climate change significantly increased the likelihood of these fires, making them more intense and widespread.
Climate Factors Contributing to the Wildfires, Australia wildfires killed or displaced nearly 3 billion animals declared among worst wildlife disasters in history
The 2019-2020 bushfires were fueled by a combination of climate factors, including:
- Prolonged Drought:Australia experienced a prolonged drought in the years leading up to the bushfires, drying out vegetation and creating ideal conditions for fire ignition. The drought was exacerbated by climate change, which has led to reduced rainfall and increased evaporation rates.
- Heatwaves:The 2019-2020 bushfire season was marked by record-breaking heatwaves, which further increased the risk of fire ignition and spread. Climate change is making heatwaves more frequent and intense, creating a dangerous feedback loop that increases the likelihood of wildfires.
- Strong Winds:Strong winds played a significant role in spreading the fires rapidly across vast areas. Climate change can alter wind patterns, leading to more extreme wind events that can fuel wildfires and make them more difficult to control.
Ultimate Conclusion
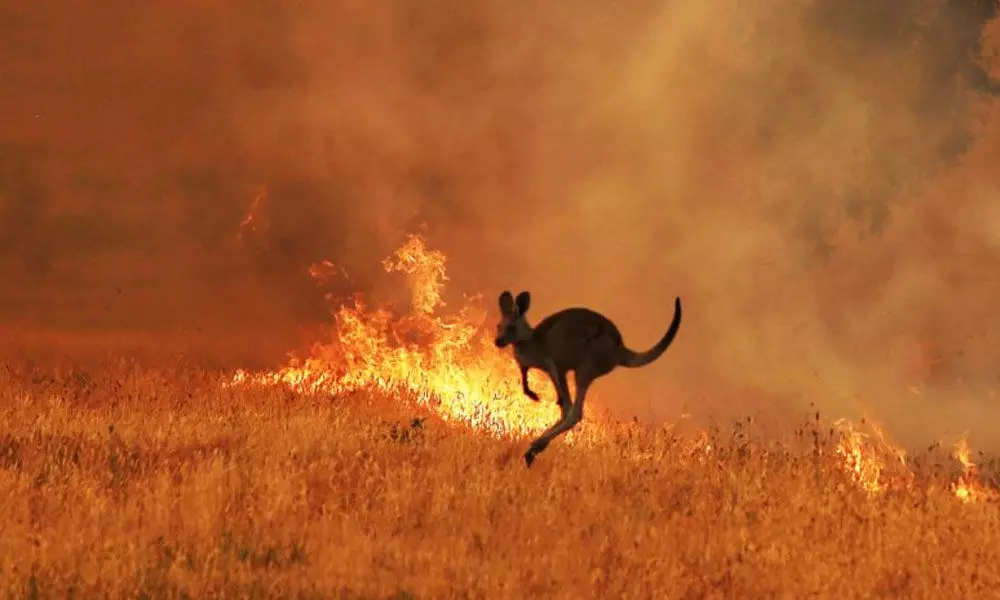

The Australian wildfires serve as a stark reminder of the urgent need to address climate change. The world witnessed the devastating impact of a warming planet, with consequences that extend far beyond Australia’s borders. We must learn from this tragedy, prioritizing fire management, conservation efforts, and taking decisive action to mitigate climate change.
Only then can we hope to protect our planet and prevent future disasters of this magnitude.