Americans Want Less Government A Historical and Contemporary Look
Americans Want Less Government – a sentiment echoing through history, from the Founding Fathers to modern-day tea parties. This desire for limited government involvement in our lives is a cornerstone of American political thought, woven into the fabric of our nation’s identity. It’s a complex issue, fueled by a blend of historical events, economic concerns, and social anxieties.
This desire for less government influence isn’t a new phenomenon; it’s deeply rooted in American history. From the Revolution’s fight against a powerful monarchy to the era of the “New Deal” and beyond, Americans have grappled with the balance between individual freedom and the role of government. The desire for less government often arises from a belief in individual responsibility, self-reliance, and a distrust of centralized power.
Historical Context
The desire for less government in the United States is deeply rooted in the country’s history and founding principles. From the outset, American political thought has wrestled with the delicate balance between individual liberty and the need for a strong central authority. This tension has manifested in various historical events and movements, shaping the ongoing debate over the role of government in citizens’ lives.The American Revolution itself was a testament to the desire for limited government.
The colonists revolted against British rule, seeking to escape the perceived tyranny of a distant and overreaching monarchy. The Declaration of Independence articulated this sentiment, proclaiming that all men are endowed with certain unalienable rights, including the right to “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.” These rights, the document asserted, are not granted by government but inherent to human nature, and therefore should not be subject to arbitrary governmental control.
The Founding Fathers and the Principles of Limited Government
The Founding Fathers, deeply influenced by Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke, believed in a government of limited powers, designed to protect individual rights and liberties. They sought to create a system of checks and balances, dividing governmental authority among different branches and levels, to prevent any one entity from becoming too powerful.
- The Constitution of the United States, drafted in 1787, established a federal system of government, dividing power between the national government and the states. This division was intended to ensure that the federal government did not infringe on the rights and autonomy of individual states and their citizens.
- The Bill of Rights, added to the Constitution in 1791, explicitly guarantees fundamental freedoms such as freedom of speech, religion, the press, and assembly. These rights are considered essential for a free and democratic society, and they serve as a bulwark against government overreach.
- The concept of “federalism,” enshrined in the Constitution, reflects the Founding Fathers’ commitment to limited government. It establishes a balance of power between the federal government and state governments, with each level having its own distinct areas of authority. This division of power aims to prevent any one level from becoming too dominant and to ensure that government remains accountable to the people.
The Anti-Federalist Movement and the Fear of Tyranny
Not all Americans were enthusiastic about the Constitution and the new federal government it established. The Anti-Federalist movement, led by figures like Patrick Henry and George Mason, argued that the Constitution granted too much power to the central government and could potentially lead to tyranny. They believed that a strong federal government would threaten individual liberties and the autonomy of the states.
- The Anti-Federalists argued that the Constitution lacked a bill of rights, which they saw as crucial for protecting individual freedoms. Their concerns led to the eventual adoption of the Bill of Rights, which serves as a cornerstone of American civil liberties.
- The Anti-Federalists also feared that the Constitution’s broad language, particularly regarding the “necessary and proper” clause, would allow the federal government to expand its power beyond its intended limits. This concern reflects the ongoing debate over the interpretation of the Constitution and the appropriate balance between federal and state power.
The Legacy of American Individualism and Limited Government
The desire for less government in the United States is intertwined with the nation’s strong tradition of individualism. This concept, deeply rooted in American history and culture, emphasizes the importance of individual autonomy, self-reliance, and personal responsibility.
- American individualism has been a driving force behind the desire for limited government, as it suggests that individuals should be free to make their own choices and pursue their own interests without undue interference from the state. This belief has fueled movements advocating for smaller government, lower taxes, and fewer regulations.
- The concept of “rugged individualism,” popularized by President Herbert Hoover during the Great Depression, emphasizes self-reliance and the belief that individuals should be responsible for their own success. This ideology has been influential in American political thought, particularly among those who advocate for less government intervention in the economy and social welfare.
“Government is not the solution to our problem; government is the problem.”
The recent surge in inflation has many Americans feeling frustrated and longing for less government intervention in their lives. As the Fed prepares for another jumbo rate hike, the debate about inflation heats up, with even Elon Musk weighing in on the issue. Elon Musk wades into inflation debate as fed tees up another jumbo rate hike.
Ultimately, the desire for less government intervention stems from a belief that individuals are best equipped to manage their own finances and make their own decisions, leading to a more prosperous and independent society.
Ronald Reagan
Political Spectrum and Ideologies
The desire for less government involvement is a complex issue that resonates across the American political spectrum, with varying degrees of intensity and specific policy preferences. Understanding the perspectives of different political ideologies and the role of political parties in shaping public opinion is crucial to grasping the dynamics of this debate.
Perspectives on Government Involvement Across the Political Spectrum
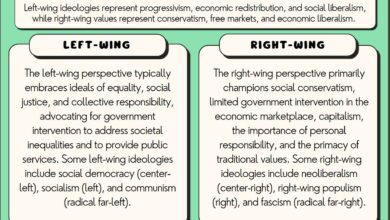
The American political spectrum is characterized by a range of views on government involvement, with liberals, conservatives, and libertarians holding distinct positions.
- Liberals generally favor a more active role for government in addressing social and economic issues. They believe that government intervention is necessary to promote equality, protect individual rights, and provide essential services. For example, liberals often support government programs like Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid, which provide social safety nets for vulnerable populations. They also advocate for government regulation of businesses to protect consumers and the environment.
- Conservatives, on the other hand, tend to favor a more limited role for government, emphasizing individual responsibility and free-market principles. They believe that government intervention often hinders economic growth and individual liberty. Conservatives often support policies that reduce government spending, lower taxes, and deregulate businesses. They may also favor a stronger national defense and traditional social values.
- Libertarians take a more extreme stance, advocating for minimal government intervention in all aspects of life. They believe that individuals should be free to make their own choices without government interference. Libertarians oppose most forms of government regulation, including taxes, social welfare programs, and military intervention. They strongly believe in individual liberty and limited government power.
Role of Political Parties
Political parties play a significant role in shaping public opinion on government involvement by articulating their platforms and policies.
- The Democratic Party generally aligns with liberal ideology, advocating for a more active role for government in addressing social and economic issues. Their platform often includes policies such as expanding access to healthcare, strengthening social safety nets, and regulating businesses to protect consumers and the environment.
- The Republican Party typically aligns with conservative ideology, emphasizing individual responsibility, free-market principles, and a limited role for government. Their platform often includes policies such as tax cuts, deregulation, and a strong national defense.
Influence of Political Ideologies
Various political ideologies have influenced the desire for less government involvement in American society.
- Classical liberalism, which emphasizes individual liberty and limited government, has been a major influence on the desire for less government. Classical liberals believe that individuals should be free to pursue their own interests without government interference. This ideology has contributed to the development of libertarianism and other movements advocating for limited government.
- Libertarianism, a more extreme form of classical liberalism, advocates for minimal government intervention in all aspects of life. Libertarians believe that individuals should be free to make their own choices without government interference. They oppose most forms of government regulation, including taxes, social welfare programs, and military intervention.
- Conservatism, while not necessarily advocating for complete government withdrawal, often emphasizes a limited role for government in economic and social matters. Conservatives believe that government intervention often hinders economic growth and individual liberty. They often support policies that reduce government spending, lower taxes, and deregulate businesses.
Economic Impact: Americans Want Less Government
The debate surrounding the role of government in the economy is deeply intertwined with economic arguments for and against reduced government involvement. Proponents of limited government often argue that free markets, with minimal government intervention, lead to greater economic efficiency, innovation, and prosperity. Conversely, advocates for a more active government role believe that government regulation, taxation, and spending are necessary to address market failures, protect vulnerable populations, and promote economic stability.
The Impact of Government Regulation on Economic Growth
Government regulations can impact economic growth in both positive and negative ways. While regulations can protect consumers, promote fairness, and safeguard the environment, they can also increase costs for businesses, stifle innovation, and hinder competition. The impact of regulation on economic growth is a complex issue that depends on various factors, including the nature and stringency of the regulation, the industry affected, and the overall economic environment.
For instance, regulations aimed at protecting consumers from harmful products or practices can reduce market inefficiencies and increase consumer confidence, ultimately leading to greater economic activity. However, overly burdensome regulations can impose significant compliance costs on businesses, leading to reduced investment, job creation, and economic growth.
The Impact of Taxation on Economic Growth
Taxation is a fundamental tool for governments to finance public services, redistribute wealth, and influence economic activity. However, the impact of taxation on economic growth is a subject of ongoing debate. High tax rates can discourage investment and work effort, leading to reduced economic output. On the other hand, taxes can be used to fund essential public goods and services that contribute to economic growth, such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
The American people are increasingly vocal about wanting less government interference in their lives. This sentiment is only amplified by revelations like the special master order revealing Biden’s direct involvement in the Trump raid and six other bombshells , which further fuels the distrust in government institutions and their actions. It seems clear that Americans are yearning for a return to smaller, more accountable government.
The optimal level of taxation for maximizing economic growth is a complex issue that depends on factors such as the tax structure, the level of government spending, and the overall economic environment.
The desire for less government intervention is a sentiment shared by many Americans, who often feel burdened by regulations and taxes. However, the recent job market report, which shows the addition of 315,000 new jobs despite a rising unemployment rate amid a slowing economy , might prompt a re-evaluation of this perspective. Perhaps a more active role for government in supporting economic stability could be seen as a benefit by those who are struggling to make ends meet.
The Impact of Government Spending on Economic Growth
Government spending can stimulate economic activity by creating jobs, increasing demand for goods and services, and supporting infrastructure development. However, excessive government spending can lead to higher debt levels, inflation, and reduced private investment. The impact of government spending on economic growth is also influenced by the type of spending. For example, infrastructure spending can have a significant multiplier effect, leading to increased economic activity and job creation.
Conversely, spending on social programs or transfer payments may have a smaller impact on economic growth.
Keynesianism and Classical Economics
Keynesian economics, developed by John Maynard Keynes, emphasizes the role of government intervention in stabilizing the economy, particularly during periods of recession. Keynesians argue that government spending can increase aggregate demand, stimulate economic activity, and reduce unemployment.Classical economics, in contrast, emphasizes the role of free markets and minimal government intervention. Classical economists believe that markets are self-regulating and that government intervention can often distort market signals and hinder economic efficiency.
“In the long run, we are all dead. Economists set themselves too easy, too useless a task if in tempestuous seasons they can only tell us, that when the storm is long past, the ocean is flat again.”
John Maynard Keynes
Keynesian and classical economic theories offer contrasting perspectives on the role of government in the economy. Keynesians advocate for active government intervention to manage economic fluctuations, while classical economists emphasize the importance of free markets and limited government intervention.
Examples of Economic Policies Aiming to Reduce Government Involvement
Supply-Side Economics
Supply-side economics, often associated with the Reagan administration, focuses on reducing taxes and regulations to stimulate economic growth. Proponents argue that lower taxes and less regulation encourage investment, innovation, and job creation.
Privatization
Privatization involves transferring ownership and control of government-owned assets or services to the private sector. Proponents argue that privatization leads to greater efficiency, innovation, and lower costs.
Deregulation
Deregulation involves reducing or eliminating government regulations in specific industries. Proponents argue that deregulation reduces costs for businesses, promotes competition, and stimulates economic growth.These examples illustrate different approaches to reducing government involvement in the economy, each with its own set of potential benefits and drawbacks. The effectiveness of these policies depends on various factors, including the specific industries targeted, the overall economic environment, and the implementation details.
Social Impact
The desire for less government, often associated with libertarian and conservative ideologies, has significant social implications. Reducing the role of government in various aspects of life can lead to changes in how society functions, impacting everything from healthcare and education to social welfare programs and personal freedoms.
The Role of Government in Addressing Social Issues, Americans want less government
Government plays a crucial role in addressing social issues, from poverty and inequality to healthcare access and education. It provides a framework for social programs and policies designed to promote equity, improve living standards, and protect vulnerable populations. These programs can include:
- Social Security: Provides retirement, disability, and survivor benefits to millions of Americans.
- Medicare and Medicaid: Provide health insurance to seniors, people with disabilities, and low-income individuals.
- SNAP (Food Stamps): Provides food assistance to low-income households.
- TANF (Temporary Assistance for Needy Families): Provides financial assistance to families with children.
- Public Education: Provides free education to all children, regardless of their family’s income.
These programs are often funded through taxes, which can be a point of contention for those who favor less government involvement. However, proponents of government intervention argue that these programs are essential for ensuring a fair and just society. They point to the fact that these programs have helped to reduce poverty, improve health outcomes, and increase educational attainment.
Public Opinion and Trends
The desire for less government involvement in American society is a complex issue, shaped by various factors and influenced by public opinion trends. Understanding the public’s perception of government involvement is crucial for comprehending the political landscape and its impact on policy decisions.
Trends in Public Opinion
Public opinion on government involvement has fluctuated over time, reflecting changing economic conditions, social issues, and political events. Numerous surveys and polls have provided insights into these shifts. For example, the Pew Research Center has consistently tracked public sentiment on the role of government, revealing fluctuations in support for a more active or less active role.
- Economic Conditions: Public opinion on government involvement often correlates with economic conditions. During periods of economic hardship, there tends to be greater support for government intervention to address issues like unemployment, healthcare, and social welfare. Conversely, during periods of economic prosperity, there might be a stronger preference for limited government intervention and lower taxes.
- Social Issues: Public opinion on government involvement is also influenced by social issues, such as healthcare, education, and environmental protection. For example, public support for government-funded healthcare programs has grown in recent years, reflecting concerns about rising healthcare costs and access to quality care. Similarly, public opinion on environmental protection has shifted, with increased support for government regulation to address climate change and environmental pollution.
- Political Events: Major political events, such as wars, economic crises, or natural disasters, can significantly influence public opinion on government involvement. For instance, the aftermath of the 9/11 terrorist attacks led to a surge in support for government action to combat terrorism, including increased security measures and expanded surveillance.
Factors Influencing Public Opinion
Several factors contribute to shaping public opinion on government involvement.
- Political Ideology: Individuals’ political ideologies play a significant role in their views on government involvement. Generally, those who identify as liberal or progressive tend to favor a more active role for government in addressing social and economic issues, while those who identify as conservative or libertarian often prefer a more limited government role.
- Personal Experiences: Individuals’ personal experiences can also influence their views on government involvement. For example, someone who has benefited from government assistance programs may be more supportive of government intervention, while someone who has experienced negative interactions with government bureaucracy may be less supportive.
- Media and Public Discourse: The media and public discourse play a crucial role in shaping public perceptions of government involvement. News coverage, opinion pieces, and political debates can influence public opinion by highlighting certain issues, framing them in specific ways, and promoting particular narratives.
Challenges and Solutions
The desire for less government involvement in people’s lives is a complex issue with potential benefits and drawbacks. While proponents argue for increased individual freedom and economic efficiency, detractors highlight concerns about social safety nets, inequality, and the potential for unchecked market forces. Addressing these challenges requires careful consideration of alternative approaches and a nuanced understanding of the potential consequences.
Addressing Inequality and Social Safety Nets
A key concern with reduced government involvement is the potential for increased inequality. When government programs like social security, healthcare, and unemployment insurance are scaled back, vulnerable populations may face greater hardship.
- Expanding Private Sector Solutions: One approach is to encourage private sector solutions to address social needs. This could involve expanding access to affordable healthcare through market-based mechanisms, promoting private retirement savings plans, and encouraging community-based organizations to provide social services.
- Strengthening Community Networks: Another approach is to strengthen community networks and encourage local initiatives to address social needs. This could involve supporting community centers, faith-based organizations, and volunteer groups that provide support services and social safety nets.
- Promoting Job Training and Education: Investing in job training and education programs can help individuals acquire the skills needed to succeed in a competitive economy. This can reduce reliance on government assistance by equipping individuals with the means to support themselves.
The debate surrounding Americans wanting less government is far from settled. It’s a complex issue with no easy answers. However, understanding the historical context, the various political perspectives, and the potential economic and social implications of this desire is crucial for informed dialogue and constructive solutions. As we move forward, it’s essential to find a balance that preserves individual liberty while addressing the challenges of a modern society.