A Tale of Two Economies: Interest Rates Diverge in Canada and US
A tale of two economies interest rate policy in canada and us set to diverge – A Tale of Two Economies: Interest Rates Diverge in Canada and US sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The economic landscapes of Canada and the United States are on divergent paths, each facing unique challenges and opportunities.
The Bank of Canada and the Federal Reserve are navigating these differences with distinct interest rate policies, shaping the trajectory of both economies. This article explores the contrasting economic conditions, analyzes the rationale behind diverging interest rate policies, and delves into the potential implications for businesses, consumers, and the global economy.
While both countries are experiencing inflation, the rate of inflation in the US is higher than in Canada. Additionally, the unemployment rate in the US is lower than in Canada, suggesting a stronger labor market. The differing economic paths are driven by a complex interplay of factors including supply chain disruptions, energy prices, and government policies.
Understanding these nuances is crucial to grasping the implications of diverging interest rate policies.
Diverging Economic Paths
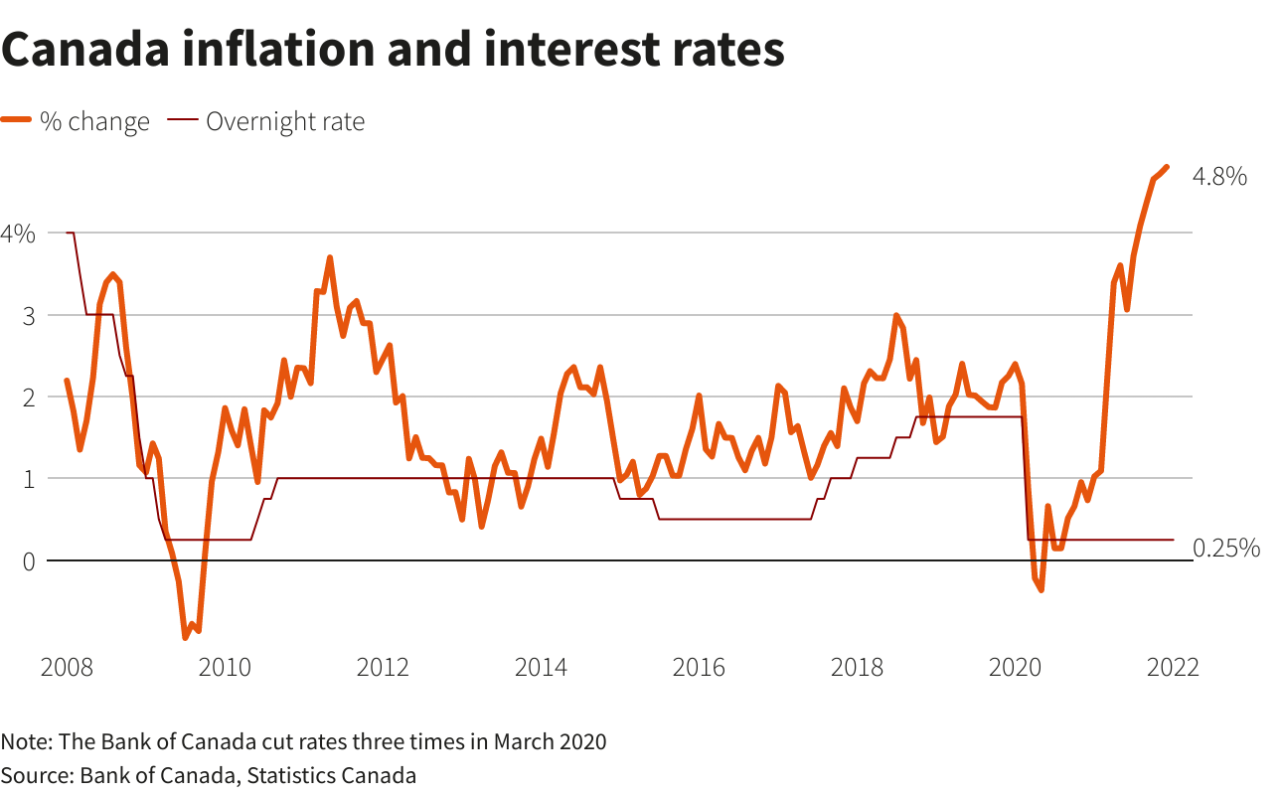
While the US and Canada share a close economic relationship, their recent trajectories have diverged, leading to different policy responses. This divergence is reflected in the contrasting economic conditions of the two countries.
It’s fascinating to watch the divergence of interest rate policies between Canada and the US, with the Bank of Canada expected to hold steady while the Federal Reserve continues its aggressive tightening. This economic divergence, however, pales in comparison to the social and political divide on issues like abortion access, as exemplified by Maryland’s GOP Governor Larry Hogan’s recent veto of a bill to expand abortion access, which sparked significant controversy and debate.
Despite these contrasting landscapes, both economic and social, the world continues to spin, and we’ll be watching closely to see how these developments unfold.
Economic Indicators
The economic performance of Canada and the US can be compared based on key indicators like inflation, unemployment, and GDP growth.
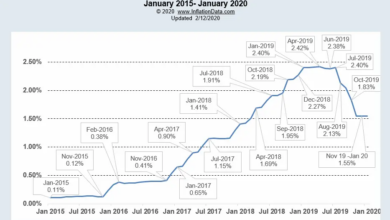
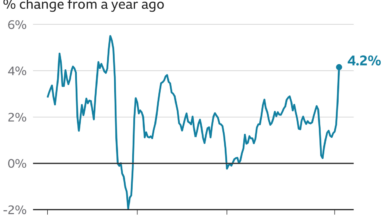
- Inflation: The US has experienced higher inflation than Canada, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) rising by 6.4% in January 2023, compared to 2.3% in Canada. The difference is largely attributed to the US’s more robust economic recovery and greater reliance on imported goods, which are subject to global price pressures.
- Unemployment: The US unemployment rate has been consistently lower than Canada’s. In January 2023, the US unemployment rate was 3.4%, while Canada’s was 5%. This difference reflects the stronger US labor market, driven by factors like a larger service sector and a higher rate of labor force participation.
- GDP Growth: While both countries experienced strong GDP growth in 2021, the US economy grew at a faster pace in 2022, expanding by 2.9% compared to Canada’s 3.8%. This difference can be attributed to the US’s more robust consumer spending and a larger manufacturing sector.
Factors Contributing to Diverging Paths, A tale of two economies interest rate policy in canada and us set to diverge
Several factors have contributed to the diverging economic paths of the US and Canada, including:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Both countries have faced supply chain disruptions, but the US has been more affected by these disruptions, leading to higher inflation and slower economic growth. This is because the US is more reliant on global supply chains for manufactured goods and consumer products.
- Energy Prices: The US is a major energy producer, and the recent rise in energy prices has benefited the US economy. Canada, on the other hand, is a net importer of energy, making it more vulnerable to rising energy prices.
- Government Policies: The US government has implemented more expansionary fiscal policies than Canada, leading to a larger budget deficit. This has contributed to higher inflation in the US but has also supported economic growth. Canada’s more cautious fiscal approach has resulted in lower inflation but also slower economic growth.
Interest Rate Policies
The Bank of Canada and the Federal Reserve, the central banks of Canada and the United States, respectively, play a crucial role in managing their respective economies by setting interest rate policies. These policies aim to control inflation, stimulate economic growth, and maintain financial stability.
However, the current economic conditions and outlook have led to divergent interest rate strategies in both countries.
Interest Rate Policies of the Bank of Canada and the Federal Reserve
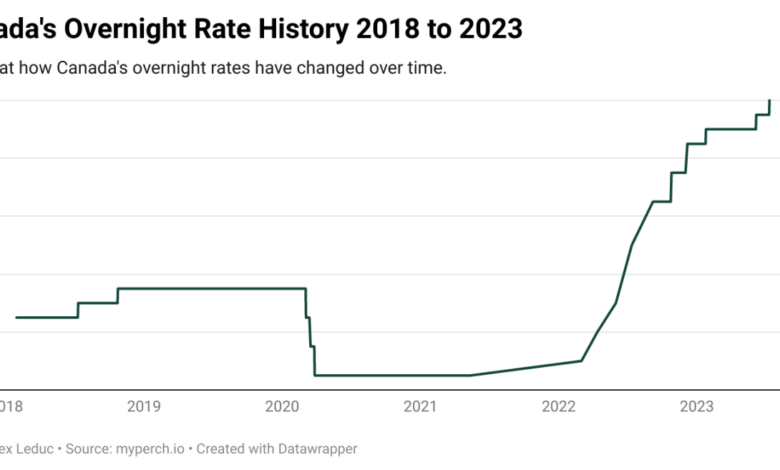
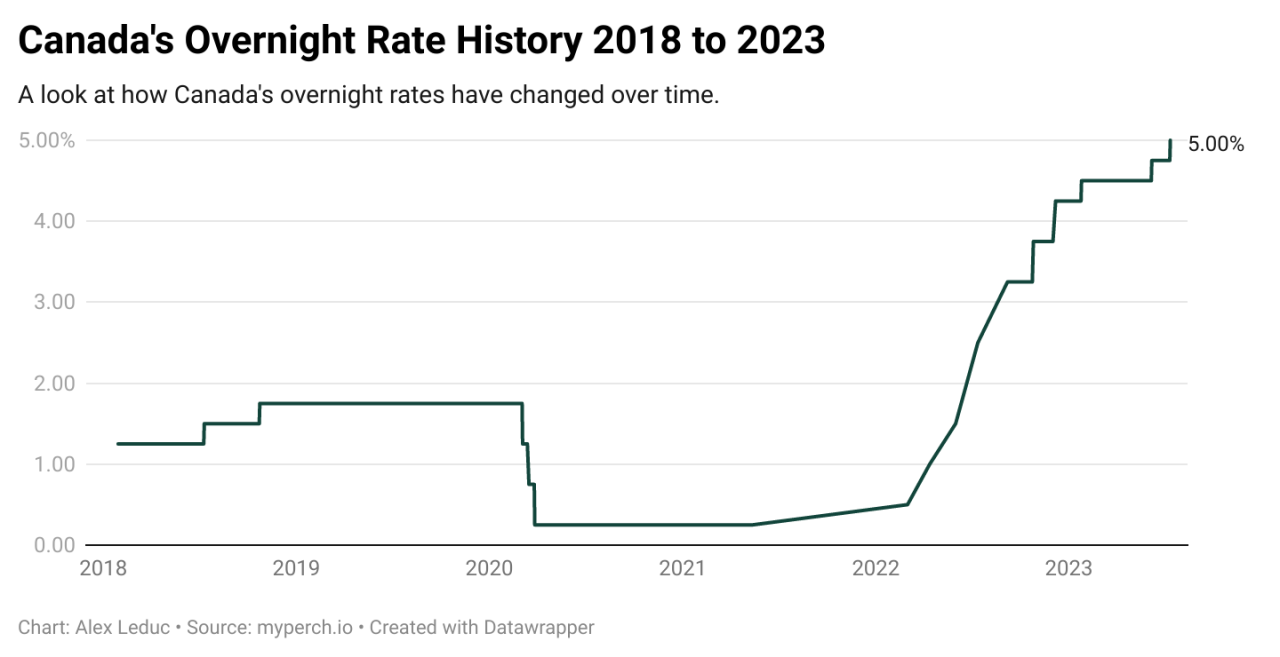
The Bank of Canada has been raising interest rates since March 2022, aiming to curb inflation, which has been persistently above its 2% target. As of October 2023, the policy interest rate stands at 5%, the highest level since 2000.
The Federal Reserve, on the other hand, has also been raising interest rates, but at a slower pace, with the federal funds rate currently at 5.25-5.5%. The Fed’s approach has been more cautious, considering the potential impact of aggressive rate hikes on economic growth.
Impact of Diverging Interest Rate Policies
The diverging interest rate policies of Canada and the US have significant implications for both economies.
Impact on Borrowing Costs
Higher interest rates in Canada will increase borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially slowing down investment and consumer spending. Conversely, the US, with its relatively lower interest rates, may experience a less pronounced impact on borrowing costs. This could lead to a more robust investment environment in the US compared to Canada.
Impact on Investment
The higher interest rates in Canada may discourage investment, as businesses may find it more expensive to borrow money for expansion or new projects. In contrast, the lower interest rates in the US may encourage investment, as businesses can access capital at a lower cost.
This could lead to a divergence in investment levels between the two countries.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Higher interest rates in Canada can also dampen consumer spending, as households face higher borrowing costs for mortgages, auto loans, and other forms of credit. This could lead to a slowdown in economic activity. Conversely, the US may experience a less pronounced impact on consumer spending due to lower interest rates.
Impact on Currency Exchange Rates
The diverging interest rate policies can also affect currency exchange rates. Higher interest rates in Canada may attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of the Canadian dollar. Conversely, lower interest rates in the US may lead to a depreciation of the US dollar.
This could impact trade flows between the two countries.
It’s fascinating to see how the US and Canada are taking different approaches to inflation, with the US Federal Reserve aggressively raising interest rates while Canada’s Bank of Canada is taking a more measured approach. But while economists debate the merits of each strategy, a very different kind of divergence is happening in the world of food safety, with a G Specialty Foods Inc.
issuing a voluntary recall of food products containing Jif and Smuckers peanut butter due to the potential salmonella contamination. This kind of news reminds us that even in a world of complex economic policies, the everyday challenges of health and safety remain a constant.
Currency Exchange Rates
The recent divergence in interest rate policies between Canada and the US has had a significant impact on the exchange rate between the two currencies. The Canadian dollar has been depreciating against the US dollar, reflecting the relative attractiveness of US assets compared to Canadian ones.
Recent Fluctuations and Key Drivers
The Canadian dollar has been weakening against the US dollar since early 2022, driven by several factors.
- Interest Rate Differentials:The US Federal Reserve has been raising interest rates at a faster pace than the Bank of Canada. This has made US dollar assets more attractive to investors seeking higher returns, increasing demand for the US dollar and putting downward pressure on the Canadian dollar.
- Economic Growth Differentials:The US economy is expected to grow at a faster pace than the Canadian economy in the coming months. This is due to a combination of factors, including a stronger labor market and higher consumer spending. The stronger US economic outlook has further boosted demand for the US dollar.
- Commodity Prices:The Canadian dollar is often referred to as a “commodity currency” because its value is closely tied to the price of commodities such as oil and natural gas. The recent decline in commodity prices has weighed on the Canadian dollar.
It’s fascinating to watch the diverging paths of interest rate policy in Canada and the US, especially as the upcoming elections in Virginia, which are drawing intense national interest money , could have ripple effects on both economies. The outcome of these elections could influence investor sentiment and potentially impact the Federal Reserve’s decisions on interest rates, further complicating the already contrasting approaches taken by the Bank of Canada and the Fed.
- Geopolitical Factors:The war in Ukraine has also contributed to uncertainty in global markets, which has made the Canadian dollar more volatile.
Implications for the Exchange Rate
The diverging interest rate policies between Canada and the US are likely to continue to put downward pressure on the Canadian dollar. This is because the interest rate differential is expected to widen further in the coming months, making US assets even more attractive to investors.
The widening interest rate differential between the US and Canada is expected to put downward pressure on the Canadian dollar.
Impact on Trade and Investment Flows
A weaker Canadian dollar can have both positive and negative implications for the Canadian economy.
- Exports:A weaker Canadian dollar makes Canadian exports more competitive in global markets, which can boost economic growth. For example, a weaker Canadian dollar can make Canadian manufactured goods more affordable to US consumers, leading to increased exports.
- Imports:However, a weaker Canadian dollar also makes imports more expensive, which can lead to higher inflation. For example, a weaker Canadian dollar can make imported goods, such as cars and electronics, more expensive for Canadian consumers.
- Investment:A weaker Canadian dollar can also make it more attractive for foreign investors to invest in Canada. This is because a weaker Canadian dollar means that foreign investors can buy more Canadian assets with their own currency.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers: A Tale Of Two Economies Interest Rate Policy In Canada And Us Set To Diverge
The divergence in interest rate policies between Canada and the US is likely to have significant ramifications for businesses and consumers in both countries. The varying cost of borrowing, investment opportunities, and consumer spending patterns will be influenced by these contrasting monetary strategies.
Impact on Businesses
The divergence in interest rates presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses operating in Canada and the US. The higher interest rates in the US will make borrowing more expensive for American businesses, potentially leading to a slowdown in investment and economic growth.
Conversely, lower interest rates in Canada could stimulate business activity and investment.
- Borrowing Costs:Businesses in the US will face higher borrowing costs compared to their Canadian counterparts, potentially impacting their ability to expand operations, invest in new projects, and manage existing debt. This could lead to a decrease in capital expenditures and economic growth in the US.
- Investment Decisions:The higher cost of borrowing in the US could discourage businesses from investing in expansion or new projects, potentially leading to slower economic growth. Canadian businesses, on the other hand, may find it more attractive to invest and expand, as borrowing costs are lower.
- Profitability:The impact of diverging interest rates on business profitability will depend on various factors, including the industry, business model, and debt levels. Businesses with significant debt exposure in the US could see their profitability decline due to higher interest expenses.
Conversely, businesses in Canada with lower debt levels could benefit from lower interest rates, potentially leading to improved profitability.
Impact on Consumers
The divergence in interest rate policies will also have a significant impact on consumers in both countries, primarily affecting mortgage rates, consumer spending, and overall affordability.
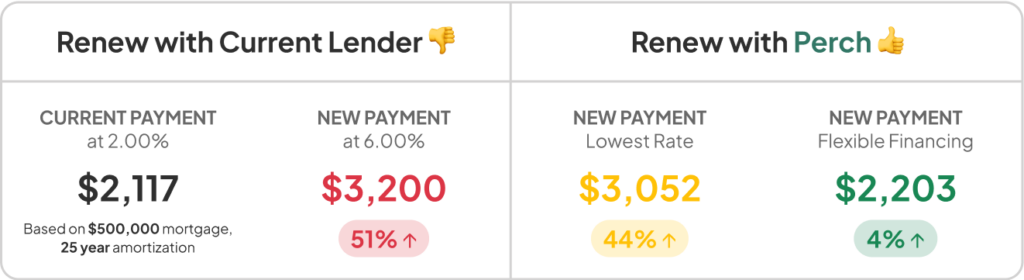
- Mortgage Rates:Higher interest rates in the US will lead to higher mortgage rates, making homeownership more expensive for American consumers. Conversely, lower interest rates in Canada will likely result in lower mortgage rates, making homeownership more affordable for Canadians.
- Consumer Spending:Higher interest rates in the US could dampen consumer spending, as individuals may face higher borrowing costs for purchases like cars and appliances. Lower interest rates in Canada could encourage consumer spending, as borrowing becomes more affordable.
- Overall Affordability:The diverging interest rate policies could exacerbate affordability challenges in the US, particularly for those with high debt levels or limited income. In contrast, Canadians may experience improved affordability due to lower borrowing costs and potentially lower housing costs.
Final Review
The divergence in interest rate policies between Canada and the US presents a fascinating case study in economic management. As both countries navigate their unique economic challenges, the impact of these policies on businesses, consumers, and currency exchange rates will be closely watched.
The future holds both risks and opportunities, and understanding the interplay of these forces will be critical for navigating the evolving economic landscape.