US Secures 100 Million Doses of Pfizer-BioNTech Vaccine
Us secures 100 million doses of pfizer biontech experimental coronavirus vaccine – US Secures 100 Million Doses of Pfizer-BioNTech Experimental Coronavirus Vaccine: This monumental agreement signifies a critical step in the US’s fight against the COVID-19 pandemic. The acquisition of 100 million doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, a groundbreaking mRNA vaccine, represents a significant boost to the nation’s vaccination efforts.
The agreement, announced in July 2020, was a testament to the US government’s commitment to securing a sufficient supply of vaccines to protect its citizens from the devastating effects of the virus. This strategic move aimed to accelerate the vaccination process and pave the way for a return to normalcy.
The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, developed through a collaborative effort between the American pharmaceutical giant Pfizer and the German biotechnology company BioNTech, was one of the first COVID-19 vaccines to receive emergency use authorization from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The vaccine’s rapid development and approval were attributed to the innovative mRNA technology it employed. This technology utilizes messenger RNA (mRNA) to instruct the body’s cells to produce a harmless fragment of the spike protein found on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the virus responsible for COVID-19.
The body then develops an immune response to this protein, equipping it to fight off future infections.
The US Secures 100 Million Doses of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine
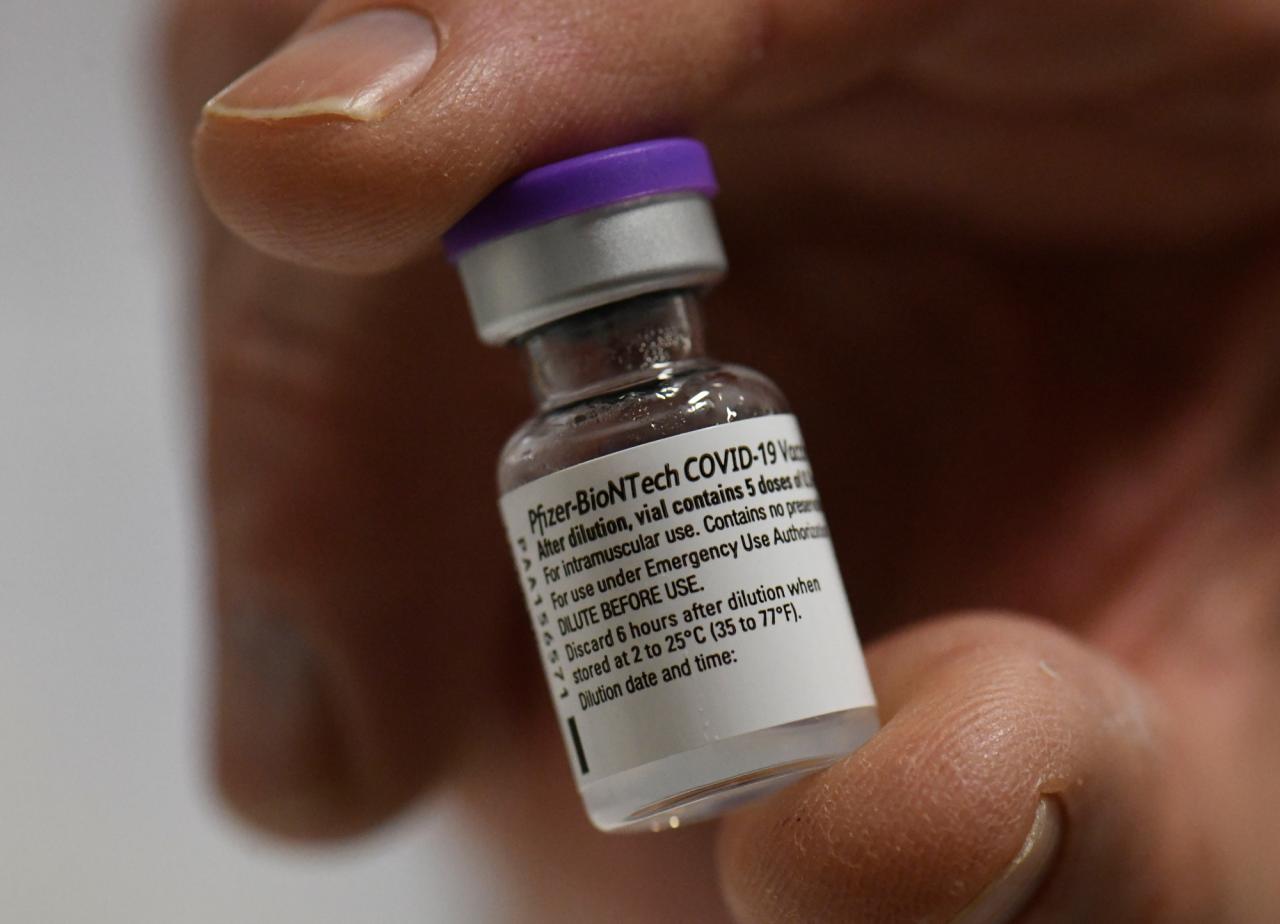
The US government has secured 100 million doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, a significant step in the nation’s fight against the pandemic. This agreement marks a major milestone in the US’s vaccination efforts, offering hope for a return to normalcy.
The Significance of the Agreement
This agreement is crucial for the US in its battle against the COVID-19 pandemic. The vaccine is highly effective, with clinical trials showing a 95% efficacy rate in preventing symptomatic COVID-19. Securing a large supply of this vaccine will allow the US to accelerate its vaccination program and reach herd immunity sooner.
Herd immunity occurs when a large portion of the population is immune to a disease, making it difficult for the disease to spread.
Timeline for Vaccine Delivery and Impact on the US Vaccination Effort
The first deliveries of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine are expected to begin in December 2020, with the remaining doses delivered throughout 2021. The US government has established a distribution plan that prioritizes healthcare workers, essential workers, and vulnerable populations. This timeline, coupled with the large number of doses secured, suggests a potential for rapid progress in vaccinating the US population.
The vaccination effort could significantly reduce the number of COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths.
Factors Contributing to the US Securing This Large Vaccine Supply
Several factors contributed to the US’s ability to secure this large vaccine supply. The US government engaged in early discussions with Pfizer-BioNTech and invested heavily in vaccine development through Operation Warp Speed. This initiative provided financial support and expedited regulatory processes, allowing for rapid development and production of the vaccine.
Furthermore, the US government placed large pre-orders for the vaccine, ensuring its place in line for distribution.
The Pfizer-BioNTech Vaccine: Us Secures 100 Million Doses Of Pfizer Biontech Experimental Coronavirus Vaccine
The Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, officially known as Comirnaty, has been a crucial tool in the global fight against the pandemic. Its development and approval were marked by unprecedented speed and scientific innovation, demonstrating the power of collaborative research and the urgency of the public health crisis.
Development and Approval Process
The development of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine was a rapid and complex process, driven by the need to combat the rapidly spreading COVID-19 pandemic. Here are the key milestones:
- January 2020:Pfizer and BioNTech initiate collaboration to develop an mRNA vaccine for COVID-19, utilizing BioNTech’s expertise in mRNA technology.
- April 2020:The first human trial of the vaccine begins, with initial data showing promising results in terms of safety and immunogenicity.
- July 2020:Phase 2/3 clinical trials commence, involving thousands of participants to evaluate the vaccine’s efficacy and safety.
- November 2020:Interim data from the Phase 2/3 trials demonstrate a high efficacy rate, prompting the companies to apply for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- December 2020:The FDA grants EUA for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, making it the first COVID-19 vaccine authorized for use in the United States.
- December 2020:The first doses of the vaccine are administered in the United States, marking a significant milestone in the global effort to combat the pandemic.
- August 2021:The FDA grants full approval to Comirnaty, based on the robust safety and efficacy data gathered during the clinical trials and post-authorization monitoring.
mRNA Technology
The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine utilizes mRNA technology, a groundbreaking approach to vaccine development.
- mRNA:Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a molecule that carries genetic instructions from DNA to ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized. In the context of vaccines, mRNA vaccines deliver a specific mRNA sequence that encodes for a viral protein, in this case, the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2.
- Mechanism of Action:Once injected, the mRNA vaccine enters cells and instructs them to produce the spike protein. The body’s immune system recognizes the spike protein as foreign and mounts an immune response, generating antibodies and T cells that can fight off the virus if encountered in the future.
Clinical Trials
Extensive clinical trials were conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.
- Phase 1/2 Trials:These trials, conducted in a small group of volunteers, evaluated the safety and immunogenicity of the vaccine. Initial data showed promising results, with participants developing strong immune responses to the spike protein.
- Phase 2/3 Trials:These large-scale trials involved thousands of participants and provided conclusive evidence of the vaccine’s efficacy. The trials demonstrated that the vaccine was highly effective in preventing COVID-19, with a reported efficacy rate of over 90% in preventing symptomatic disease.
- Post-Authorization Monitoring:Following EUA and full approval, the vaccine’s safety and efficacy are continuously monitored through ongoing surveillance and data collection. This ongoing monitoring helps ensure the vaccine remains safe and effective over time.
Public Health Implications
The securing of 100 million doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine represents a significant step towards mitigating the impact of the pandemic in the United States. The availability of this vaccine holds the potential to significantly alter the course of the pandemic, offering a beacon of hope for a return to normalcy.
Potential Benefits of Widespread Vaccination
Widespread vaccination against COVID-19 is expected to yield substantial public health benefits, including a reduction in transmission, hospitalizations, and deaths.
- Reduced Transmission:Vaccination can significantly reduce the likelihood of individuals becoming infected with COVID-19 and subsequently transmitting the virus to others. This is achieved through the development of immunity, enabling the body to recognize and fight off the virus more effectively.
- Reduced Hospitalizations:Vaccination can significantly reduce the risk of severe COVID-19 infection, leading to a decrease in hospitalizations. This is particularly important given the strain that the pandemic has placed on healthcare systems.
- Reduced Deaths:Vaccination can significantly reduce the risk of death from COVID-19. This is crucial in protecting vulnerable populations, such as older adults and those with underlying health conditions, who are at higher risk of severe illness and death.
Vaccine Hesitancy and Misinformation
Despite the potential benefits of widespread vaccination, there are significant concerns related to vaccine hesitancy and misinformation. These factors can hinder the effectiveness of vaccination efforts and prolong the pandemic.
- Vaccine Hesitancy:A significant portion of the population may be hesitant to receive the COVID-19 vaccine due to concerns about safety, efficacy, or potential side effects. These concerns may stem from misinformation, distrust of authorities, or past experiences with vaccines.
- Misinformation:The spread of misinformation about COVID-19 vaccines can undermine public confidence and discourage vaccination. This misinformation can be disseminated through social media, traditional media, and other channels.
Global Vaccine Access
The rapid procurement of COVID-19 vaccines by wealthy nations has raised concerns about global vaccine equity. While the US secured 100 million doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, many developing countries face significant challenges in accessing these life-saving vaccines.
US Vaccine Procurement Compared to Other Countries, Us secures 100 million doses of pfizer biontech experimental coronavirus vaccine
The US’s early and aggressive vaccine procurement strategy has given it a significant advantage in securing a large supply of vaccines. However, this approach has also been criticized for potentially hindering global access to vaccines. Other countries, particularly those with limited resources, have faced difficulties in securing sufficient doses.
This disparity in vaccine access has raised concerns about the potential for widening existing health inequalities.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Global Vaccine Distribution
The equitable distribution of vaccines is a complex issue with significant ethical implications. The World Health Organization (WHO) advocates for a fair and equitable distribution of vaccines, emphasizing the need to prioritize vulnerable populations and ensure that all countries have access to vaccines.
However, the reality is that wealthy nations have secured a disproportionate share of available vaccines, leaving many developing countries struggling to secure enough doses for their populations. This situation raises ethical concerns about the potential for vaccine nationalism and the need for a more collaborative approach to vaccine distribution.
Impact of US Vaccine Acquisition on Global Vaccine Equity
The US’s significant vaccine acquisition could have a significant impact on global vaccine equity. While the US has pledged to donate vaccines to other countries, the scale of its procurement efforts raises concerns about the potential for hindering vaccine access in developing countries.
The US’s actions have highlighted the need for a more coordinated and equitable approach to global vaccine distribution, ensuring that all countries have access to vaccines regardless of their economic status.
Conclusive Thoughts
The US’s acquisition of 100 million doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine marked a pivotal moment in the fight against COVID-19. It provided a glimmer of hope for a nation grappling with the pandemic’s devastating consequences. The vaccine rollout, while facing logistical challenges, progressed steadily, with millions of Americans receiving their vaccinations.
The availability of this vaccine, along with other COVID-19 vaccines, played a crucial role in mitigating the pandemic’s impact, reducing transmission rates, hospitalizations, and deaths. The US’s vaccine procurement efforts served as a model for other countries, highlighting the importance of strategic planning and proactive action in securing a sufficient vaccine supply.
The global vaccine landscape, however, remained complex, with disparities in vaccine access persisting. As the pandemic continued to evolve, the world grappled with the challenge of ensuring equitable vaccine distribution, leaving a lasting impact on the global health landscape.






