US Economy Faces New Hurdle: Child Care Crisis
Us economy faces new hurdle for recovery child care crisis – US Economy Faces New Hurdle: Child Care Crisis. This isn’t just a problem for families, it’s a major obstacle to economic recovery. The lack of affordable, accessible, and quality child care is impacting labor participation rates, holding back economic growth, and creating a ripple effect across industries.
The crisis is a perfect storm of affordability issues, limited availability, and concerns about the quality of care, making it a real struggle for parents to find reliable options.
The situation is creating a vicious cycle. Parents are forced to leave or reduce their work hours due to child care challenges, which impacts their earning potential and contributes to labor shortages. This, in turn, affects businesses and industries, hindering their ability to operate at full capacity.
It’s a complex problem with far-reaching consequences, and it’s time we address it head-on.
The Child Care Crisis

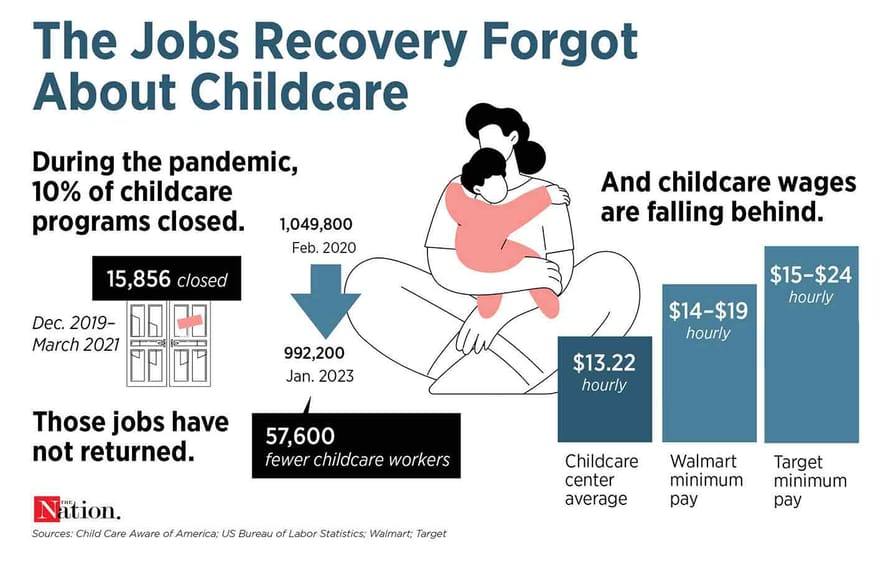
The United States is facing a severe child care crisis, a formidable obstacle to economic recovery. This crisis has far-reaching consequences, impacting families, businesses, and the overall economy. The lack of affordable, accessible, and high-quality child care is hindering labor force participation, stifling economic growth, and exacerbating existing inequalities.
The Impact of the Child Care Crisis on Families
The child care crisis imposes significant burdens on families, particularly those with young children. The high cost of child care often consumes a substantial portion of family income, leaving less for other essential needs. This financial strain can force families to make difficult choices, such as one parent staying home to care for children, leading to a loss of income and potential career advancement.
The shortage of available child care options can also lead to long waitlists, forcing families to scramble for care and potentially jeopardizing their employment.
Impact on the Workforce: Us Economy Faces New Hurdle For Recovery Child Care Crisis

The lack of affordable and accessible child care poses a significant obstacle to parents’ participation in the workforce, impacting both individual families and the broader economy. This shortage creates a ripple effect, hindering economic growth and exacerbating existing labor market challenges.
The Challenge of Balancing Work and Child Care
The absence of affordable and accessible child care options forces many parents to make difficult choices, often sacrificing their careers or reducing their work hours. This situation disproportionately affects women, who are more likely to be primary caregivers and shoulder the burden of finding and managing child care arrangements.
- Parents may face long waitlists, limited availability, and high costs for child care centers and home-based providers.
- The lack of flexibility in child care schedules can make it challenging for parents to find work that aligns with their child care needs.
- Many parents are forced to rely on informal care arrangements, such as family members or friends, which may not always be reliable or affordable.
Economic Consequences of Child Care Challenges, Us economy faces new hurdle for recovery child care crisis
The inability to find affordable and accessible child care can have severe economic consequences for both individuals and the economy as a whole.
- Parents may be forced to leave the workforce entirely, reducing household income and increasing financial strain.
- Reduced work hours due to child care responsibilities can lead to lower earnings and career stagnation.
- The loss of skilled workers from the workforce due to child care constraints diminishes the talent pool and hinders economic growth.
Impact on Industries Facing Labor Shortages
The child care crisis further exacerbates existing labor shortages across various industries. Businesses struggle to attract and retain workers, particularly those with young children, as the lack of affordable and accessible child care creates a significant barrier to employment.
- Industries like healthcare, education, and hospitality, which often rely on a workforce of women and parents, are particularly affected by the child care crisis.
- Businesses may face higher turnover rates and difficulty filling open positions, leading to reduced productivity and increased operational costs.
- The inability to attract and retain qualified workers due to child care constraints can stifle innovation and economic growth.
Government Policies and Initiatives
The child care crisis in the United States has been a long-standing issue, impacting families, businesses, and the overall economy. Recognizing the critical need for affordable and accessible child care, the government has implemented various policies and initiatives over the years.
This section will examine the effectiveness of these programs and explore potential solutions and policy proposals for improving access to quality child care.
Existing Government Policies and Their Effectiveness
The federal government has a number of programs aimed at supporting child care, including the Child Care and Development Fund (CCDF), the Head Start program, and the Early Head Start program. These programs provide subsidies to low-income families to help them afford child care, as well as support for early childhood education.
However, the effectiveness of these programs is often debated, with some arguing that they do not go far enough in addressing the child care crisis.
- The Child Care and Development Fund (CCDF)is the primary federal program for supporting child care for low-income families. It provides subsidies to help families pay for child care, and it also funds state-level child care programs. While CCDF has been successful in providing some financial assistance to families, critics argue that it is underfunded and does not reach enough families.
Furthermore, eligibility requirements for CCDF can be restrictive, making it difficult for some families to access the program.
- The Head Start programis a federal program that provides early childhood education to low-income children. Head Start programs offer a range of services, including preschool, health screenings, and family support. The program has been shown to be effective in improving children’s cognitive and social development, and it is considered a valuable resource for low-income families.
However, Head Start is also facing funding challenges, and it is not available to all children who could benefit from it.
- The Early Head Start programis a similar program to Head Start, but it serves children from birth to age three. Early Head Start programs provide comprehensive services, including child care, health care, and family support. Research has shown that Early Head Start programs can have a significant impact on children’s development, particularly for children from low-income families.
However, like Head Start, Early Head Start is underfunded and is not available to all children who could benefit from it.
Potential Solutions and Policy Proposals
There are a number of potential solutions and policy proposals that could be implemented to improve access to affordable and high-quality child care. These include:
- Increase funding for existing programs. One of the most straightforward solutions is to increase funding for existing programs like CCDF, Head Start, and Early Head Start. This would allow more families to access these programs and receive the support they need.
For example, a 2021 study by the Center for American Progress found that increasing CCDF funding by $20 billion per year could help an additional 1.5 million children access child care.
- Expand eligibility for child care subsidies. Another solution is to expand eligibility for child care subsidies to include more families, such as those with moderate incomes or those who work in essential industries. Expanding eligibility would help address the needs of a wider range of families and ensure that more children have access to quality child care.
For example, a 2020 report by the National Women’s Law Center found that expanding eligibility for child care subsidies could help reduce the child care costs for millions of families.
- Invest in early childhood education. Investing in early childhood education is crucial for children’s development and future success. This could include expanding access to high-quality preschool programs and providing additional support to teachers and early childhood educators. A 2019 report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine found that investing in early childhood education can have a significant return on investment, leading to improved educational outcomes and increased economic productivity.
- Promote public-private partnerships. Public-private partnerships can play a significant role in addressing the child care crisis. For example, the government could partner with private businesses to create more affordable child care options or provide tax incentives to businesses that offer on-site child care.
A 2022 report by the Pew Charitable Trusts found that public-private partnerships can be effective in expanding access to affordable child care and improving quality.
The Role of Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships can be a valuable tool for addressing the child care crisis. These partnerships can leverage the resources and expertise of both the public and private sectors to create innovative solutions that address the needs of families and businesses.
For example, the government could partner with private businesses to:
- Create more affordable child care options. The government could provide tax incentives or subsidies to private businesses that offer child care services at affordable rates. This could encourage businesses to invest in child care facilities or offer on-site child care programs.
- Develop innovative child care models. The government could partner with private businesses to develop and test new child care models, such as shared child care centers or virtual child care services. These partnerships could help to identify and scale up innovative solutions that address the unique needs of families and businesses.
- Increase access to quality child care. The government could partner with private businesses to improve the quality of child care services. This could include providing training and professional development opportunities for child care providers, as well as developing quality standards for child care centers.
Long-Term Economic Implications
The child care crisis, while immediately impacting working families, has far-reaching consequences that extend beyond the present. Its effects on productivity, innovation, and social mobility can shape the economic landscape for generations to come. This section delves into the long-term economic implications of the child care crisis, exploring its potential to exacerbate existing inequalities and hinder future economic growth.
Impact on Productivity and Innovation
The lack of affordable and accessible child care directly impacts workforce participation, particularly for women. When parents struggle to find reliable and affordable child care, they may be forced to reduce their work hours, leave the workforce entirely, or take on less demanding jobs that offer flexibility but lower pay.
This results in a loss of skilled labor and untapped potential, hindering overall productivity. Moreover, the child care crisis can stifle innovation. When parents are burdened with child care responsibilities, they may have less time and energy to pursue higher education, professional development, or entrepreneurial ventures.
This can lead to a less diverse and less dynamic workforce, ultimately slowing down economic growth.
Impact on Future Generations
The child care crisis has a significant impact on future generations. Children who lack access to high-quality early childhood education are at a disadvantage in terms of cognitive, social, and emotional development. This can lead to a cycle of poverty and limited opportunities, as children who are not prepared for school may struggle to succeed academically and, consequently, in the workforce.
Furthermore, the lack of affordable child care can limit the economic mobility of families. When parents are unable to work due to child care constraints, their children may grow up in households with lower incomes, potentially perpetuating cycles of poverty.
Exacerbation of Economic Inequalities
The child care crisis disproportionately affects low-income families, exacerbating existing economic inequalities. Low-income families often face the greatest challenges in accessing affordable and quality child care. This disparity can lead to a widening gap between the rich and the poor, as children from low-income families are less likely to receive the early childhood education they need to succeed.
The lack of affordable child care can also limit the economic mobility of low-income families, trapping them in a cycle of poverty.
Wrap-Up
The child care crisis isn’t just a temporary hurdle, it’s a long-term issue with significant economic implications. The lack of quality, affordable care impacts productivity, innovation, and social mobility. It’s a challenge that needs to be addressed through a combination of government policies, private sector initiatives, and a focus on long-term solutions.
We need to recognize the vital role child care plays in our economy and invest in solutions that ensure a brighter future for our workforce and our economy.