Half of People With Coronavirus Have No Symptoms, Data Shows
Half of people with coronavirus have no symptoms data shows – Half of people with coronavirus have no symptoms, data shows, a startling revelation that has transformed our understanding of COVID-19. This silent spread, where individuals carry the virus without experiencing any noticeable symptoms, poses a significant challenge to containment efforts.
The implications are far-reaching, impacting public health policies, social behavior, and the very way we perceive this pandemic.
The presence of asymptomatic infections has dramatically altered the landscape of COVID-19, as it introduces a hidden layer of transmission that is difficult to track and control. The virus can spread silently through asymptomatic carriers, making it even more challenging to prevent its spread.
This has prompted a surge in research and public health initiatives focused on understanding, identifying, and mitigating the impact of asymptomatic infections.
Prevalence of Asymptomatic Coronavirus Infections: Half Of People With Coronavirus Have No Symptoms Data Shows
The discovery that a significant portion of individuals infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus exhibit no symptoms has profoundly impacted our understanding of the COVID-19 pandemic. This silent spread of the virus poses unique challenges for public health measures and highlights the importance of widespread testing and contact tracing.
Significance of Asymptomatic Infections in the Spread of COVID-19
Asymptomatic individuals, while not experiencing symptoms themselves, can still transmit the virus to others. This silent transmission plays a crucial role in the spread of COVID-19, particularly in settings where close contact is common, such as workplaces, schools, and public transportation.
Challenges in Identifying and Tracking Asymptomatic Individuals, Half of people with coronavirus have no symptoms data shows
Identifying and tracking asymptomatic individuals is a significant challenge due to the lack of visible symptoms. Traditional methods of disease surveillance, which rely on individuals reporting symptoms, are ineffective in detecting asymptomatic cases. This necessitates the use of widespread testing strategies, including random sampling and targeted testing of high-risk groups.
Studies and Data Supporting the Prevalence of Asymptomatic Infections
Numerous studies have provided evidence for the prevalence of asymptomatic COVID-19 infections. A study published in the journal Nature found that asymptomatic individuals accounted for approximately 40% of all COVID-19 cases in China. Another study, conducted in the United States, estimated that up to 80% of COVID-19 cases may be asymptomatic.
It’s mind-blowing to think that half of people with coronavirus have no symptoms, according to recent data. This makes it even more crucial to take precautions, especially with the supreme court lifting the last obstacle to allow enforcement of the public charge rule , which could make accessing healthcare even more difficult for some.
The combination of these factors underscores the need for accessible and affordable healthcare for everyone, regardless of their immigration status.
These findings highlight the importance of recognizing and addressing the silent spread of the virus.
It’s unsettling to think that half of people with coronavirus have no symptoms, making it even more challenging to contain the spread. This hidden transmission highlights the importance of transparency and timely information sharing, which is why Senator Hawley’s call for an international investigation into the Chinese Communist Party’s role in suppressing the truth about the virus, as seen in this article sen hawley calls for international investigation of chinese communist partys role in suppressing truth about ccp virus , is a crucial step towards understanding the pandemic’s origins and preventing future outbreaks.
The fact that so many people can be unknowingly carrying the virus underscores the need for global cooperation and a commitment to sharing accurate information.
Implications of Asymptomatic Transmission

The discovery that a significant portion of individuals infected with the coronavirus may experience no symptoms has profound implications for understanding and controlling the spread of the disease. Asymptomatic transmission, the spread of the virus from individuals who are unaware they are infected, poses a significant challenge to public health efforts.
Impact on Disease Spread
Asymptomatic individuals can unknowingly transmit the virus to others, contributing to the rapid spread of the disease within communities. This silent transmission makes it difficult to identify and isolate infected individuals, hindering efforts to contain the outbreak. The presence of asymptomatic carriers also makes it challenging to estimate the true prevalence of the virus in a population, as traditional testing methods may only identify symptomatic cases.
Community Transmission
Asymptomatic transmission plays a crucial role in community spread, particularly in situations where individuals are in close proximity to others. Examples of settings where asymptomatic transmission can be significant include workplaces, schools, and public transportation. The ability of asymptomatic individuals to spread the virus without exhibiting symptoms underscores the importance of public health measures aimed at reducing overall transmission, even among those who may not be experiencing symptoms.
Public Health Strategies for Mitigating Asymptomatic Transmission
- Universal Masking:Wearing masks in public settings, regardless of symptoms, can significantly reduce the transmission of respiratory droplets, including those from asymptomatic individuals. Masks serve as a barrier, preventing the spread of viral particles from both the wearer and others.
This strategy has been shown to be effective in reducing transmission rates in various settings.
- Increased Testing:Regular and widespread testing, including asymptomatic testing, is crucial for identifying infected individuals, even those who may not be showing symptoms. This allows for timely isolation of infected individuals, preventing further spread. Targeted testing strategies, such as testing in high-risk settings or among specific populations, can help to identify and control outbreaks more effectively.
- Contact Tracing:Contact tracing is a key public health strategy that involves identifying and monitoring individuals who have been in close contact with confirmed cases. This includes identifying and testing asymptomatic contacts to prevent further spread. Contact tracing efforts can be enhanced through the use of technology, such as mobile apps, to facilitate contact identification and communication.
- Social Distancing and Hygiene:Maintaining physical distance, practicing good hand hygiene, and avoiding large gatherings are essential measures for reducing the risk of transmission, including asymptomatic transmission. These measures help to minimize the number of close contacts individuals have, reducing the likelihood of spreading the virus.
It’s crazy to think that half of people with coronavirus have no symptoms, according to recent data. It makes me wonder how much this is contributing to the spread, especially with the political back-and-forth over relief bills. Trump’s refusal to sign the House Democrats’ bill because of “Green New Deal stuff” as reported here is just another example of how this pandemic has become a political football.
Meanwhile, we’re left wondering how many people are unknowingly spreading the virus, adding to the already complex situation.
Public Health and Social Impact
The discovery that a significant portion of individuals infected with the coronavirus exhibit no symptoms has profound implications for public health policies and social behavior. The silent spread of the virus poses a significant challenge to traditional containment strategies, requiring a shift in focus towards broader community-level interventions and a greater emphasis on public awareness and communication.
Impact on Public Health Policies
The presence of asymptomatic infections necessitates a reevaluation of public health policies aimed at controlling the spread of the virus. Traditional measures like isolation and quarantine, primarily focused on symptomatic individuals, become less effective. Instead, a broader approach is needed, encompassing:
- Increased Testing:Widespread testing, including asymptomatic individuals, is crucial for identifying and isolating infected individuals, regardless of their symptoms. This can help break the chain of transmission more effectively.
- Mask Mandates and Social Distancing:Maintaining physical distancing and wearing masks in public spaces remains essential, even for individuals who feel healthy. These measures serve as a barrier to transmission, even from asymptomatic carriers.
- Contact Tracing:Contact tracing efforts need to be intensified to identify and isolate individuals who may have been exposed to the virus, even if they are asymptomatic.
- Vaccination:Vaccination remains a critical tool for mitigating the spread of the virus, even among asymptomatic individuals. Vaccines can reduce the likelihood of transmission, even if an individual does not experience symptoms.
The Role of Public Awareness and Communication
Public awareness plays a crucial role in managing the risk of asymptomatic transmission. Effective communication strategies are needed to:
- Promote Understanding:Educating the public about the prevalence of asymptomatic infections and the importance of preventive measures, even in the absence of symptoms, is essential.
- Encourage Testing:Public health campaigns should encourage regular testing, even for individuals who feel healthy, to identify asymptomatic cases and prevent further spread.
- Promote Compliance:Clear and consistent messaging about the importance of mask-wearing, social distancing, and other public health guidelines is essential to ensure compliance and reduce the risk of transmission.
- Address Concerns:Addressing public concerns and misconceptions about asymptomatic infections can help build trust and encourage adherence to recommended guidelines.
Consequences of Asymptomatic Infections on Different Societal Groups
Asymptomatic infections can have different consequences on various societal groups:
| Societal Group | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|
| Healthcare Workers | Increased risk of exposure and infection, leading to staff shortages and potential disruptions in healthcare services. |
| Elderly and Individuals with Underlying Conditions | Higher risk of severe illness and death due to asymptomatic transmission, especially in settings like nursing homes and assisted living facilities. |
| Schools and Educational Institutions | Increased risk of transmission among students and staff, potentially leading to school closures and disruptions in education. |
| Businesses and Workplaces | Increased risk of workplace outbreaks, leading to productivity losses, business closures, and economic disruptions. |
Epilogue
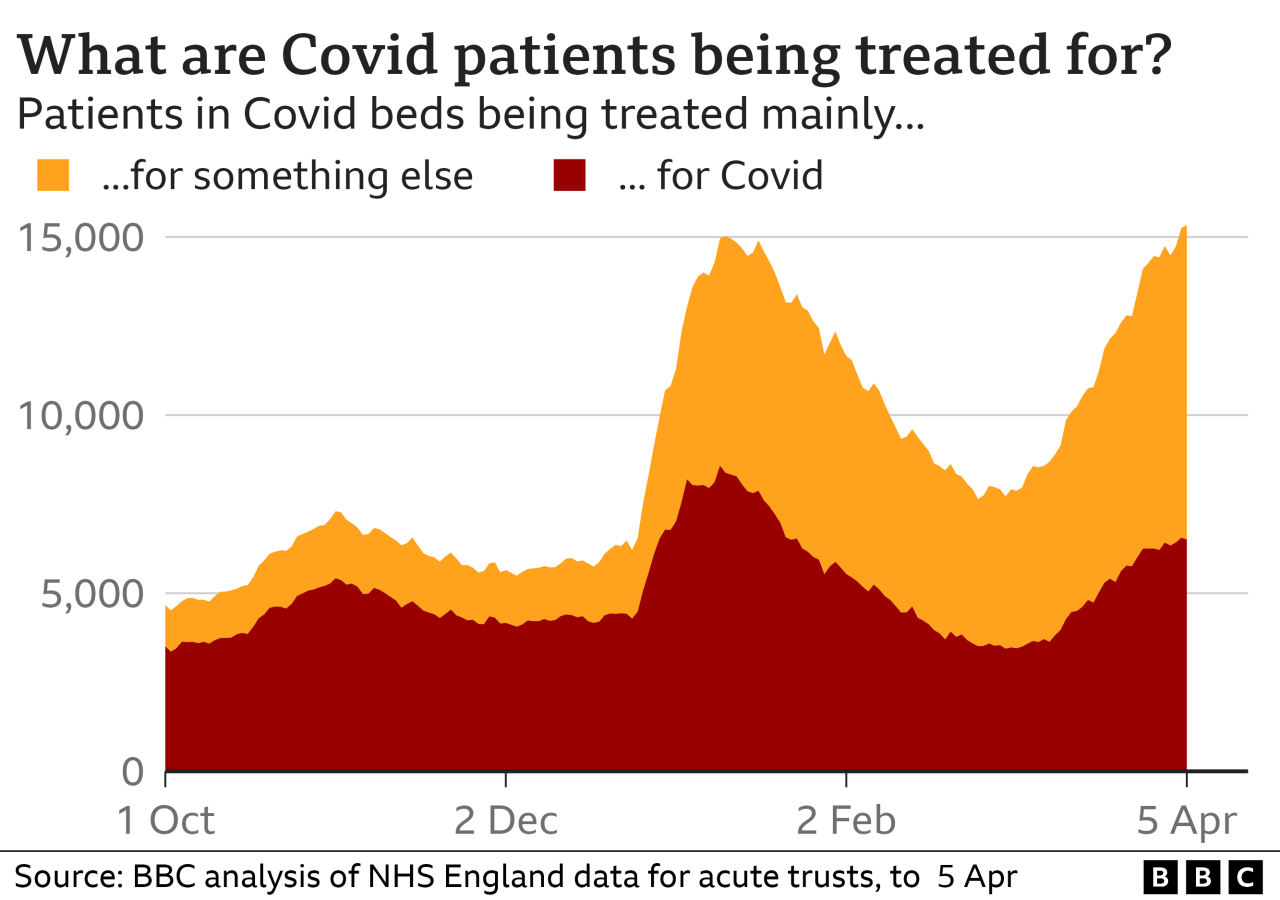
The discovery that half of people with coronavirus have no symptoms has fundamentally shifted our approach to the pandemic. Recognizing the silent spread of the virus has led to a renewed emphasis on public health measures like mask-wearing, social distancing, and widespread testing.
As we continue to learn more about asymptomatic infections, we can refine our strategies to combat this elusive foe. It is crucial to remember that even if we feel healthy, we can still be carrying the virus and unknowingly contributing to its spread.
By taking precautions and remaining vigilant, we can help protect ourselves and others from this invisible threat.