Fed Holds Rates Steady, Hints at Future Hikes
Federal reserve leaves interest rates unchanged but keeps open possibility of future hikes – Fed Holds Rates Steady, Hints at Future Hikes sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, has decided to keep interest rates unchanged at their current level.
This decision, while seemingly straightforward, carries significant implications for the economy, inflation, and the future course of monetary policy.
The Fed’s decision to hold rates steady comes amid a complex economic landscape. Inflation, while showing signs of cooling, remains elevated, and the economy is navigating a delicate balance between growth and stability. The Fed’s statement acknowledges these challenges, highlighting the need for continued vigilance and flexibility in managing monetary policy.
The Federal Reserve’s Decision
The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, has decided to leave interest rates unchanged at their current level. This decision comes after a series of interest rate hikes over the past year, aimed at curbing inflation.
Rationale for the Decision
The Federal Reserve’s decision to hold rates steady is driven by several factors. One key consideration is the recent slowdown in economic growth. The US economy has shown signs of cooling in recent months, with data indicating a decline in consumer spending and business investment.
The Federal Reserve is closely monitoring these trends and wants to avoid taking actions that could further dampen economic activity. Another factor influencing the decision is the ongoing uncertainty surrounding the global economy. The war in Ukraine, supply chain disruptions, and rising energy prices have created significant volatility in global markets.
The Federal Reserve wants to ensure that its monetary policy decisions are appropriate in light of these global uncertainties.
Potential Implications of the Decision
The Federal Reserve’s decision to leave interest rates unchanged has several potential implications for the economy. One potential outcome is that inflation could remain elevated for longer. Holding interest rates steady might not be enough to cool demand sufficiently, potentially leading to persistent inflationary pressures.On the other hand, the decision could help support economic growth.
By avoiding further interest rate hikes, the Federal Reserve aims to create a more favorable environment for businesses to invest and consumers to spend.Another potential implication is that the decision could increase the likelihood of future interest rate hikes. While the Federal Reserve has opted to hold rates steady for now, it has indicated that it is closely monitoring the economy and is prepared to adjust its monetary policy stance as needed.
Inflation and the Economy
The Federal Reserve’s decision to leave interest rates unchanged, while keeping open the possibility of future hikes, is heavily influenced by the current state of inflation and its impact on the economy. The Fed closely monitors inflation as a key indicator of economic health.
Current Inflation and its Impact on the Economy
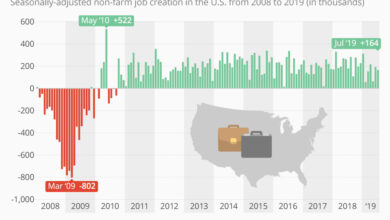
Inflation has been a significant concern in recent years, impacting consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic growth. While inflation rates have shown signs of cooling, they remain elevated compared to the Fed’s target.
The Federal Reserve’s decision to hold interest rates steady while leaving the door open for future hikes is a sign of the delicate balancing act they face. Economic uncertainty remains, and while inflation has cooled somewhat, it’s still a concern.
Meanwhile, across the pond, farmers in England are experimenting with burying burnt wood in their fields to capture CO2, highlighting the global focus on climate change mitigation. It’s interesting to see how these seemingly disparate issues are interconnected in the broader context of economic and environmental stability.
Comparison of Inflation Target with Current Inflation Levels
The Federal Reserve’s target inflation rate is 2%. However, current inflation levels, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), are significantly higher. The CPI rose by 4.9% in April 2023, indicating that inflation is still a concern.
Factors Contributing to Inflation
Several factors contribute to the current inflationary environment.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted global supply chains, leading to shortages and price increases for various goods and services. These disruptions have been slow to resolve, contributing to ongoing inflationary pressures.
- Strong Consumer Demand:Following the pandemic, pent-up demand from consumers led to increased spending, further driving up prices. The combination of government stimulus measures and a strong labor market fueled this demand.
- Rising Energy Prices:The war in Ukraine has significantly impacted global energy markets, leading to higher oil and gas prices. These energy price increases have rippled through the economy, contributing to broader inflation.
- Labor Market Tightness:A tight labor market, with low unemployment and high demand for workers, has put upward pressure on wages. Businesses have had to raise prices to offset rising labor costs, contributing to inflation.
Future Interest Rate Hikes

The Federal Reserve’s decision to leave interest rates unchanged, while keeping the possibility of future hikes open, has sparked much discussion about the potential timing and impact of such moves. The Fed’s statement highlights its commitment to controlling inflation, which remains a key concern.
Factors Influencing Future Rate Hikes
The Fed’s decision to leave interest rates unchanged was based on a careful assessment of current economic conditions. The central bank is closely monitoring several factors that could influence future rate hikes.
- Inflation:The Fed’s primary objective is to bring inflation down to its 2% target. Future rate hikes will largely depend on the trajectory of inflation, including core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices. If inflation remains stubbornly high, the Fed is likely to continue raising interest rates.
- Labor Market:The labor market remains strong, with low unemployment and robust job growth. However, the Fed is watching for signs of wage growth that could fuel inflation. If wage pressures intensify, the Fed might consider raising rates to cool the labor market and curb inflation.
The Federal Reserve’s decision to leave interest rates unchanged while keeping the possibility of future hikes open is a move that reflects the current economic climate. The report, were sounding the alarm bells head start report underscores workforce crisis edsurge news , highlights the significant workforce challenges facing the nation, which could impact the Fed’s future decisions on interest rates.
These challenges, coupled with ongoing inflation concerns, make it a delicate balancing act for the Fed as they navigate a path toward economic stability.
- Economic Growth:The Fed is also closely monitoring economic growth. While the economy has shown resilience, there are concerns about the impact of high interest rates and geopolitical uncertainty. If economic growth weakens significantly, the Fed might pause or even reverse its rate hike path.
- Global Economic Conditions:Global economic conditions can also influence the Fed’s decision. If global growth slows down or there are significant geopolitical shocks, the Fed might be less inclined to raise interest rates.
Impact of Future Rate Hikes on the Economy
Future interest rate hikes could have a significant impact on the economy.
- Borrowing Costs:Higher interest rates would make it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money. This could lead to reduced investment and spending, potentially slowing economic growth.
- Asset Prices:Rising interest rates could put downward pressure on asset prices, including stocks and bonds. This could lead to market volatility and potentially impact investment decisions.
- Inflation Control:The primary goal of interest rate hikes is to control inflation. By making borrowing more expensive, the Fed aims to reduce demand and slow down the pace of price increases. However, there is a risk that aggressive rate hikes could lead to a recession.
Market Reactions
The Federal Reserve’s decision to leave interest rates unchanged while signaling the possibility of future hikes sent ripples through the financial markets, eliciting a range of responses from investors and traders. The stock market, bond market, and currency markets all reacted to the Fed’s statement, reflecting the complex interplay of economic factors and investor sentiment.
Stock Market Reactions, Federal reserve leaves interest rates unchanged but keeps open possibility of future hikes
The stock market’s response to the Fed’s decision was generally positive, with major indices closing higher on the day of the announcement. This suggests that investors were reassured by the Fed’s commitment to keeping inflation under control, while also appreciating the central bank’s cautious approach to further interest rate increases.
The S&P 500, for example, rose by 0.6% on the day of the announcement, while the Nasdaq Composite gained 0.9%. This upward movement can be attributed to several factors, including the Fed’s acknowledgment of the resilience of the US economy and its willingness to adjust its monetary policy stance based on incoming economic data.
Bond Market Reactions
The bond market, on the other hand, exhibited a more mixed response to the Fed’s decision. While bond yields initially rose on the news of the potential for future rate hikes, they subsequently declined as investors digested the Fed’s overall message.
The yield on the 10-year Treasury note, a key benchmark for interest rates, rose slightly in the immediate aftermath of the announcement, but then retreated to levels slightly below its pre-announcement levels. This suggests that while some investors were concerned about the potential for higher interest rates in the future, others were reassured by the Fed’s data-dependent approach and the overall positive economic outlook.
Currency Market Reactions
The US dollar strengthened against a basket of major currencies following the Fed’s announcement, indicating that investors perceived the Fed’s stance as supportive of the dollar’s value. The US Dollar Index, which tracks the dollar’s performance against a weighted average of six other major currencies, rose by 0.3% on the day of the announcement.
This strengthening of the dollar can be attributed to several factors, including the Fed’s commitment to controlling inflation and the perception that the US economy is relatively strong compared to other major economies.
Economic Outlook
The Federal Reserve’s decision to leave interest rates unchanged while keeping the possibility of future hikes open offers a mixed outlook for the economy. The Fed’s stance reflects a delicate balancing act between combating inflation and supporting economic growth.
Economic Growth and Job Creation
The current economic climate presents a complex picture. While the economy has shown resilience in recent months, with unemployment remaining low and consumer spending holding steady, concerns about slowing growth persist. The Fed’s decision to hold rates steady suggests a cautious approach, recognizing the potential for a slowdown in the coming months.
The potential for economic growth and job creation depends heavily on factors like consumer confidence, business investment, and global economic conditions. A prolonged period of high interest rates could dampen business investment and slow economic growth, potentially leading to job losses.
Conversely, a more accommodative monetary policy could boost consumer spending and stimulate economic activity, leading to job creation.
Inflation
Inflation remains a key concern for the Fed, and its future trajectory will be crucial in determining the path of interest rates. The Fed’s decision to hold rates steady suggests that it is monitoring inflation closely and is prepared to act if necessary.
The Fed’s target inflation rate is 2%, and while inflation has eased somewhat in recent months, it remains elevated. A persistent decline in inflation would likely lead the Fed to maintain its current stance, while a resurgence of inflationary pressures could prompt the Fed to raise rates more aggressively.
Potential Economic Scenarios
The economic outlook is uncertain, and various scenarios are possible depending on the path of interest rates and other factors. The following table Artikels potential scenarios for the economy based on different interest rate scenarios:
| Scenario | Interest Rate Scenario | Economic Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Moderate Growth | Interest rates remain stable or increase gradually. | The economy continues to grow at a moderate pace, with job creation remaining steady. Inflation gradually declines toward the Fed’s target. |
| Scenario 2: Slowdown | Interest rates increase significantly. | Economic growth slows, and job creation weakens. Inflation remains elevated, but starts to decline more slowly. |
| Scenario 3: Recession | Interest rates rise aggressively, leading to a sharp economic contraction. | The economy enters a recession, with significant job losses and a decline in consumer spending. Inflation may fall rapidly due to reduced demand. |
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
The Federal Reserve’s decision to leave interest rates unchanged, while maintaining the possibility of future hikes, has significant implications for consumers and businesses. The potential effects on borrowing costs, investment decisions, and consumer spending are multifaceted and depend on various factors, including the specific sectors involved.
Impact on Borrowing Costs
The possibility of future interest rate hikes can influence borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. Higher interest rates make it more expensive to borrow money, potentially leading to:
- Increased mortgage rates:This could make homeownership less affordable, potentially slowing down the housing market. For example, a 0.5% increase in mortgage rates could add hundreds of dollars to monthly mortgage payments, making it challenging for some borrowers to afford a home.
The Federal Reserve’s decision to hold interest rates steady for now while keeping the door open for future hikes feels like a reflection of the current political climate. It’s a wait-and-see approach, just like the GOP’s apparent strategy on Israel, as highlighted by Vivek Ramaswamy’s accusation that the party is silencing debate on the issue ramaswamy accuses gop of silencing debate on israel.
Whether it’s economic policy or foreign relations, we’re in a period of uncertainty where even the most confident voices seem to be treading cautiously.
- Higher interest rates on personal loans:This could discourage consumers from taking out loans for major purchases like cars or home renovations. Higher interest rates on credit cards could also lead to increased debt burdens for consumers.
- Increased borrowing costs for businesses:Businesses might face higher interest rates on loans for expansion or investment projects, potentially impacting their growth plans. For example, a company planning to build a new factory might reconsider its investment if borrowing costs increase significantly.
Impact on Investment Decisions
The uncertainty surrounding future interest rate hikes can affect investment decisions for both consumers and businesses.
- Consumer spending:Consumers might delay major purchases like cars or appliances if they anticipate higher interest rates in the future. This could lead to a slowdown in consumer spending, impacting the overall economy.
- Business investment:Businesses might be hesitant to invest in new projects or expand their operations if they expect higher borrowing costs in the future. This could lead to slower economic growth and fewer job creation opportunities.
Impact on Consumer Spending
The potential for higher interest rates can influence consumer spending patterns.
- Reduced discretionary spending:Consumers might be more cautious with their spending on non-essential items like entertainment or travel if they anticipate higher borrowing costs in the future. This could lead to a decline in demand for discretionary goods and services.
- Increased savings:Consumers might choose to save more money if they expect interest rates to rise, leading to lower consumer spending and potentially impacting economic growth.
Potential Effects on Different Sectors
The impact of interest rate hikes can vary across different sectors of the economy:
| Sector | Potential Effects |
|---|---|
| Housing | Higher mortgage rates could slow down home sales and price growth. |
| Auto | Higher interest rates on car loans could make vehicle purchases less affordable, potentially leading to lower demand. |
| Retail | Higher interest rates could lead to reduced consumer spending on discretionary items, potentially impacting retail sales. |
| Manufacturing | Higher borrowing costs could make it more expensive for manufacturers to invest in new equipment or expand operations. |
Historical Context
The Federal Reserve’s current stance on interest rates, while seemingly cautious, echoes a pattern observed in previous economic cycles. Understanding the historical context of interest rate decisions can provide valuable insights into the potential implications of the Fed’s current approach.
Previous Instances of Interest Rate Maintenance and Hikes
Examining historical instances where the Federal Reserve maintained or raised interest rates reveals a complex interplay of economic factors and policy objectives.
- During the 1980s, under the chairmanship of Paul Volcker, the Fed implemented a series of aggressive interest rate hikes to combat rampant inflation. This period, known as the “Volcker Disinflation,” saw interest rates reach double-digit levels, leading to a recession but ultimately curbing inflation.
- In the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, the Fed adopted a policy of near-zero interest rates and quantitative easing to stimulate economic growth. As the economy recovered, the Fed gradually raised interest rates, a process that continued until 2018.
- The Fed’s decision to maintain or raise interest rates often depends on factors such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. For example, during periods of high inflation, the Fed may raise interest rates to cool down the economy and prevent prices from spiraling out of control.
Impact of Interest Rate Decisions on the Economy
Historical data reveals that interest rate decisions have a significant impact on the economy.
- Raising interest rates typically slows down economic growth by making it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest.
- Lower interest rates, on the other hand, can stimulate economic growth by making it cheaper for businesses to borrow and invest.
- Interest rate decisions can also affect the value of the dollar, influencing exchange rates and international trade.
Last Recap: Federal Reserve Leaves Interest Rates Unchanged But Keeps Open Possibility Of Future Hikes
The Fed’s decision to hold rates steady, while keeping open the possibility of future hikes, reflects a cautious approach to navigating the current economic climate. The future path of interest rates will depend on a multitude of factors, including the trajectory of inflation, the strength of the labor market, and global economic conditions.
This decision, while seemingly simple, carries significant weight, shaping the economic landscape for businesses, consumers, and investors alike.