
5 Main Eczema Causes & Natural Healing Through Diet
5 main causes of eczema and how to heal naturally through diet – Eczema, a chronic skin condition characterized by itchy, red, and inflamed patches, affects millions worldwide. While there’s no cure, managing eczema symptoms is possible with a holistic approach. This article dives into the 5 main causes of eczema and explores how to heal naturally through diet.
Understanding the root causes and implementing dietary changes can significantly improve your skin health and overall well-being.
We’ll delve into the science behind eczema, examining the role of genetics, environmental triggers, and the immune system. We’ll then explore the connection between diet and eczema, focusing on inflammation and the potential benefits of eliminating common food allergens.
This article will provide evidence-based dietary recommendations, including foods to include and avoid, along with natural remedies and lifestyle tips for managing eczema symptoms.
Understanding Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed, and often dry patches of skin. It affects people of all ages, but is most common in children. While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
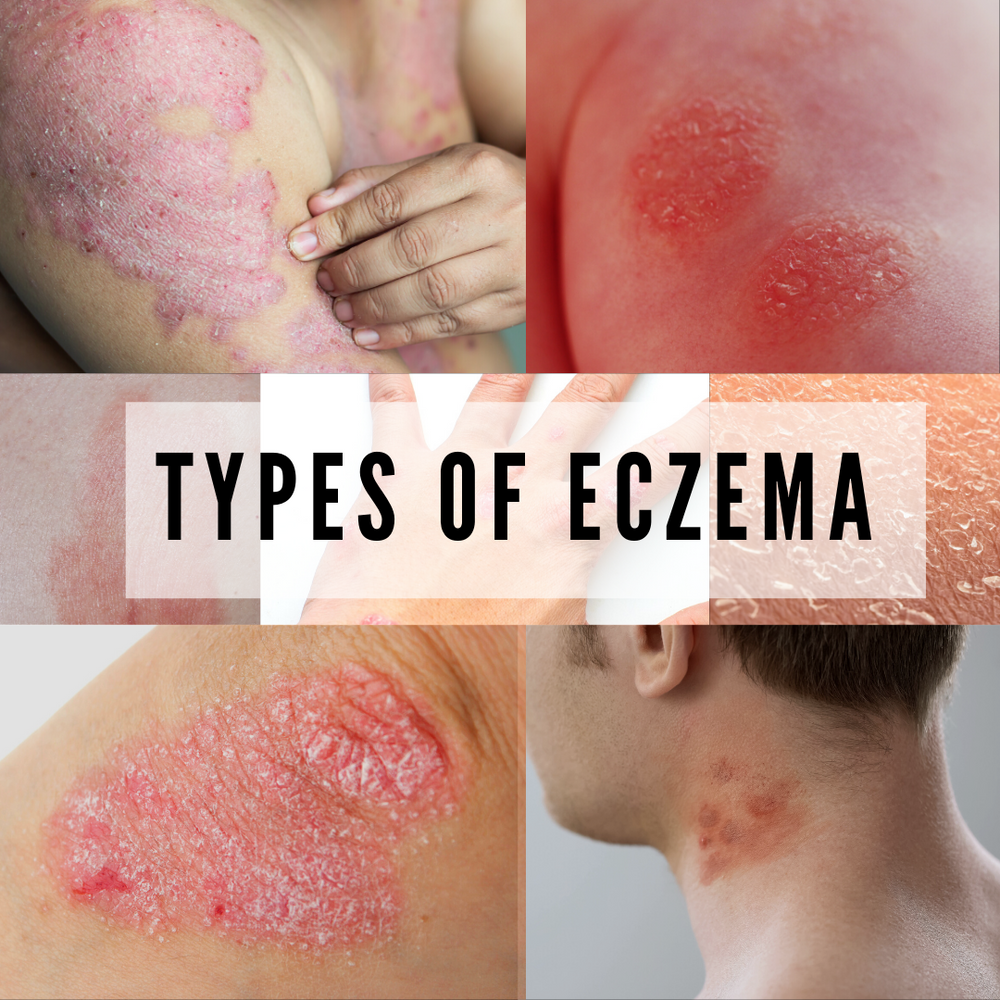
Types of Eczema
Eczema encompasses several types, each with its own distinct characteristics. Here are some of the most common types:
- Atopic Dermatitis:The most prevalent type, it is often associated with allergies and asthma. Symptoms include dry, itchy skin, red patches, and sometimes blisters.
- Contact Dermatitis:This type is triggered by direct contact with irritants or allergens. Symptoms include redness, itching, and swelling at the site of contact.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema:Characterized by small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet, this type is often associated with sweating.
- Nummular Eczema:This type presents as coin-shaped, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis:This type affects oily areas of the skin, such as the scalp, face, and chest. Symptoms include flaky, greasy patches and red, itchy skin.
Underlying Causes of Eczema
The development of eczema is influenced by a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors
- Family History:Eczema often runs in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. Studies have identified specific genes associated with an increased risk of developing eczema.
- Immune System:People with eczema tend to have an overactive immune system, which may trigger inflammation and skin reactions.
Environmental Factors
- Allergens:Exposure to allergens, such as dust mites, pollen, pet dander, and certain foods, can trigger eczema symptoms.
- Irritants:Contact with harsh chemicals, soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics can irritate the skin and worsen eczema.
- Climate:Dry weather and extreme temperatures can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
- Stress:Stress can trigger or worsen eczema flare-ups.
The Role of the Immune System in Eczema
The immune system plays a crucial role in the development of eczema. In people with eczema, the immune system overreacts to triggers, leading to inflammation and skin irritation. This overreaction is thought to be due to a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors.Recent research suggests that the immune system’s response to skin barrier defects may be a key factor in eczema development.
When the skin barrier is compromised, it allows allergens and irritants to penetrate the skin, triggering an immune response. This immune response can lead to chronic inflammation and the characteristic symptoms of eczema.
“The skin barrier is the first line of defense against environmental triggers. When it is compromised, the immune system becomes overactive, leading to inflammation and eczema symptoms.”Dr. [insert expert name], Dermatologist.
Top 5 Causes of Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation, itching, redness, and dryness. It’s a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and while there is no cure, understanding the causes can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Genetic Predisposition
A family history of eczema is a significant risk factor. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of eczema are more likely to develop the condition. This suggests a genetic component to eczema, although the exact genes involved are still being investigated.
Allergens
Allergens play a significant role in triggering eczema. These are substances that trigger an immune response in the body, leading to inflammation. Common allergens that can trigger eczema include:
- Pollen
- Dust mites
- Pet dander
- Mold
- Food allergens (e.g., peanuts, milk, eggs)
Irritants
Irritants are substances that can cause skin irritation and inflammation, even in people without eczema. Common irritants that can trigger eczema include:
- Soaps and detergents
- Perfumes and fragrances
- Wool and other rough fabrics
- Extreme temperatures (hot or cold)
- Certain chemicals (e.g., cleaning products)
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also contribute to eczema. These factors can include:
- Dry climates
- Low humidity
- Air pollution
- Exposure to smoke
Lifestyle Factors, 5 main causes of eczema and how to heal naturally through diet
Lifestyle factors can influence eczema severity.
- Stress: Stress can trigger eczema flare-ups by affecting the immune system. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can contribute to inflammation.
- Lack of Sleep: Sleep deprivation can weaken the immune system and make the skin more susceptible to inflammation.
The Role of Diet in Eczema
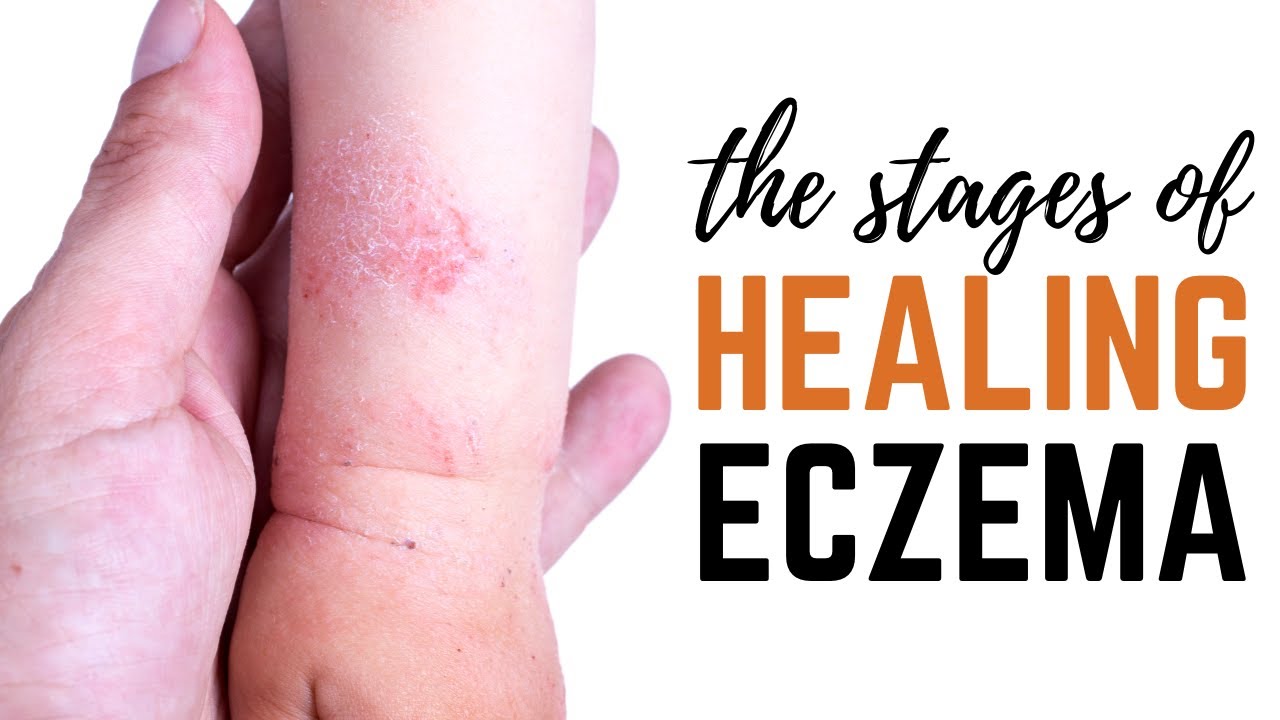
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by itchy, red, and inflamed patches of skin. While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, research suggests that a combination of genetic and environmental factors plays a role.
Diet is increasingly recognized as a significant contributor to eczema development and management, particularly due to its influence on inflammation.
Dietary Factors and Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural process that helps the body fight off infections and heal injuries. However, chronic inflammation can contribute to various health problems, including eczema. Certain foods can trigger inflammation in the body, potentially exacerbating eczema symptoms. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods may help reduce inflammation and improve eczema symptoms.
Eliminating Common Food Allergens
Food allergies are a common trigger for eczema flare-ups. Identifying and eliminating common food allergens from your diet can significantly improve eczema symptoms. Some of the most common food allergens include:
- Dairy: Cow’s milk protein is a common allergen that can trigger eczema in some individuals. Avoiding dairy products like milk, cheese, yogurt, and ice cream can help manage eczema symptoms.
- Gluten: Gluten is a protein found in wheat, rye, and barley. Gluten sensitivity or celiac disease can trigger eczema flare-ups. Eliminating gluten from your diet may be beneficial for managing eczema symptoms.
- Nuts: Tree nuts like almonds, walnuts, and pecans are common allergens that can trigger eczema. Avoiding nuts and nut-based products can help prevent eczema flare-ups.
Evidence-Based Dietary Recommendations
While there’s no one-size-fits-all diet for eczema, research suggests that certain dietary changes can be beneficial.
- Increase Omega-3 Fatty Acids:Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel, have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce eczema symptoms.
- Include Probiotics:Probiotics are live bacteria that promote gut health. A healthy gut microbiome is crucial for overall health and may help manage eczema symptoms. Probiotic-rich foods include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi.
- Limit Processed Foods:Processed foods are often high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and additives that can trigger inflammation. Reducing processed food intake may help improve eczema symptoms.
- Stay Hydrated:Drinking plenty of water is essential for overall health and may help keep skin hydrated, which is important for managing eczema.
Natural Healing Strategies
Beyond addressing the root causes of eczema, incorporating natural healing strategies can significantly enhance your skin’s health and overall well-being. This holistic approach focuses on nourishing your body from within and promoting a healthy environment for your skin to thrive.
Natural Remedies for Eczema
Natural remedies can provide relief from eczema symptoms and support the skin’s natural healing process. Here are some effective options:
- Aloe Vera:This plant’s gel contains anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties that soothe irritated skin and promote healing. Applying aloe vera gel directly to affected areas can help reduce redness, itching, and dryness.
- Oatmeal:Colloidal oatmeal, finely ground oatmeal, is a natural anti-inflammatory and emollient. Adding it to bathwater can relieve itching and soothe inflamed skin. Oatmeal-based lotions and creams are also effective.
- Coconut Oil:This oil is rich in lauric acid, which has antimicrobial properties. It acts as a natural moisturizer and can help restore the skin’s protective barrier, reducing dryness and irritation.
- Tea Tree Oil:This essential oil possesses antifungal and antibacterial properties. Diluting tea tree oil in a carrier oil like coconut oil and applying it to affected areas can help combat infections and reduce inflammation.
- Apple Cider Vinegar:Diluted apple cider vinegar can help restore the skin’s pH balance, which can be disrupted in eczema. It also has antifungal and antibacterial properties that can help manage infections.
Sample Weekly Meal Plan
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in supporting skin health and managing eczema. Here’s a sample weekly meal plan incorporating foods known to benefit the skin: Day 1
Breakfast
Oatmeal with berries and nuts
Lunch
Salad with grilled chicken or fish and a side of quinoa
Dinner
Eczema, a common skin condition, can be triggered by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental irritants, and even diet. Understanding the 5 main causes of eczema is crucial to finding natural solutions, like incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet.
For example, a recent transcript jeh johnson on food sensitivities emphasized the connection between certain foods and eczema flare-ups. By identifying and eliminating these triggers, you can take control of your eczema and experience lasting relief.
Salmon with roasted vegetables Day 2
Breakfast
Smoothie with spinach, banana, and almond milk
Lunch
Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread
Dinner
Chicken stir-fry with brown rice
Similarly, by taking control of your diet and adopting a more holistic approach to healing, you can begin to manage your eczema and embrace a healthier, more vibrant life.
ong>Day 3
Breakfast
Yogurt with fruit and granola
Lunch
Turkey sandwich on whole-wheat bread with avocado
Dinner
Vegetable curry with brown rice Day 4
Breakfast
Eggs with whole-wheat toast and avocado
Lunch
Leftover vegetable curry
Dinner
Baked chicken with sweet potato and broccoli Day 5
Breakfast
Oatmeal with berries and nuts
Lunch
Salad with grilled tofu and a side of quinoa
Dinner
Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread Day 6
Breakfast
Yogurt with fruit and granola
Lunch
Turkey sandwich on whole-wheat bread with avocado
Dinner
Salmon with roasted vegetables Day 7
Figuring out the root causes of eczema, like allergies, stress, or even gut health, is key to finding natural healing through diet. Sometimes, a fresh start is just what you need to tackle those challenges, and resort style living in Woodbridge development offers new beginnings with its serene atmosphere and focus on well-being.
This shift in environment could be the perfect opportunity to implement a new diet plan and focus on the natural healing process for your eczema.
Breakfast
Eggs with whole-wheat toast and avocado
Lunch
Leftover salmon with roasted vegetables
Dinner
Chicken stir-fry with brown rice
Managing Eczema Through Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle modifications can complement dietary changes and support skin health. Consider these strategies:* Stress Reduction:Stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your routine, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Sleep
Adequate sleep is essential for skin repair and regeneration. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
Avoid Irritants
Identify and avoid triggers that worsen your eczema, such as harsh soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics.
Moisturize Regularly
Moisturizing regularly helps to keep your skin hydrated and prevent dryness. Choose gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers that are specifically designed for eczema-prone skin.
When to Seek Professional Help: 5 Main Causes Of Eczema And How To Heal Naturally Through Diet
While natural remedies can be effective in managing eczema symptoms, it’s crucial to recognize when professional medical attention is necessary. Certain signs and symptoms indicate that your eczema may require a more specialized approach, potentially involving prescription medications or other therapies.
Understanding the Need for Medical Intervention
It’s important to seek professional help when eczema significantly impacts your quality of life, interferes with daily activities, or causes persistent discomfort. While natural remedies can provide relief, certain situations call for the expertise of a healthcare professional.
- Persistent or Severe Symptoms:If your eczema is widespread, doesn’t respond to home remedies, or causes intense itching, pain, or bleeding, it’s essential to consult a doctor.
- Infections:Eczema can make the skin more susceptible to infections. If you notice signs of infection, such as pus, redness, swelling, or fever, seek medical attention immediately.
- Complications:In some cases, eczema can lead to complications like skin thickening (lichenification) or permanent skin discoloration. If you observe these changes, it’s important to consult a dermatologist.
- Underlying Conditions:Eczema can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as allergies, food sensitivities, or autoimmune disorders. If your eczema is severe or persistent, a doctor can investigate potential underlying causes.
- Pregnancy or Breastfeeding:If you’re pregnant or breastfeeding and experiencing eczema, it’s important to consult a doctor about safe treatment options.
Treatment Options and Their Considerations
Depending on the severity and type of eczema, your doctor may recommend various treatment options, including:
- Topical Medications:These medications are applied directly to the skin and can help reduce inflammation, itching, and dryness. Common examples include corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and moisturizers.
- Phototherapy:This treatment involves exposing the affected skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light. Phototherapy can be effective for moderate to severe eczema, but it carries some risks, such as skin damage and an increased risk of skin cancer.
- Oral Medications:In severe cases, oral medications, such as antihistamines, immunosuppressants, or antibiotics, may be prescribed. These medications can have potential side effects, so it’s important to discuss them with your doctor.
- Biologics:These are newer medications that target specific proteins involved in the immune response. Biologics can be effective for severe eczema that doesn’t respond to other treatments, but they can be expensive and have potential side effects.
Finding a Qualified Dermatologist or Allergist
If you’re seeking professional help for eczema, it’s essential to find a qualified dermatologist or allergist. Here are some tips for finding a suitable healthcare provider:
- Ask for Recommendations:Talk to your primary care physician, friends, family, or other trusted sources for recommendations.
- Check Online Directories:Websites like the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI) provide directories of board-certified dermatologists and allergists.
- Consider Experience and Expertise:Look for a dermatologist or allergist who specializes in eczema or has extensive experience treating the condition.
- Read Reviews:Check online reviews and patient testimonials to get insights into the provider’s communication style, expertise, and overall patient satisfaction.
Final Conclusion
Taking control of your eczema starts with understanding its causes and implementing a holistic approach to healing. By addressing the 5 main causes of eczema and making dietary changes, you can significantly improve your skin health and reduce symptoms. Remember, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for your specific needs.
With knowledge, awareness, and a proactive approach, you can effectively manage eczema and live a more comfortable life.

