Nearly Half of Dementia Cases Could Be Prevented or Delayed: Lancet Commission Report
Nearly half of dementia cases could be prevented or delayed lancet commission – Nearly half of dementia cases could be prevented or delayed, according to a groundbreaking report by the Lancet Commission. This startling revelation highlights the potential for significant public health impact by addressing modifiable risk factors for dementia. The commission’s report underscores the importance of lifestyle choices, including regular physical activity, a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, in mitigating dementia risk.
The report also emphasizes the need for robust research and innovation to further understand the mechanisms of dementia and develop new prevention strategies. It calls for a global approach to tackling this growing public health challenge, recognizing the unique needs of different populations and the importance of collaboration across borders.
The Lancet Commission Report

The Lancet Commission on Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care, published in 2020, presented a comprehensive analysis of the global dementia crisis and proposed a framework for preventing and delaying the onset of the disease. The report’s key findings highlight the substantial potential for reducing the global burden of dementia through proactive measures.
Key Findings
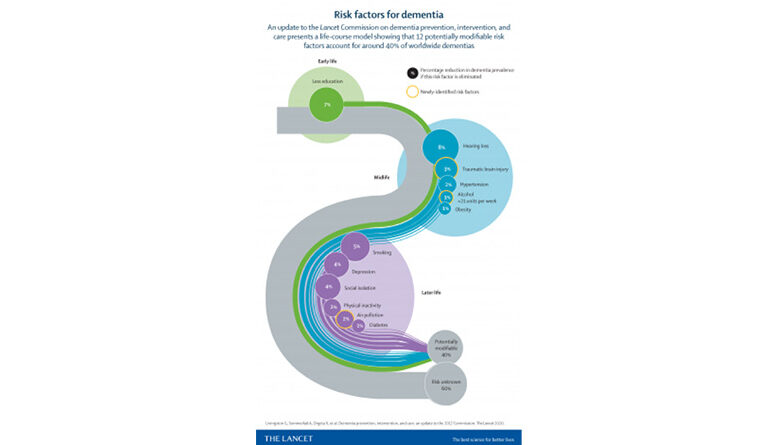
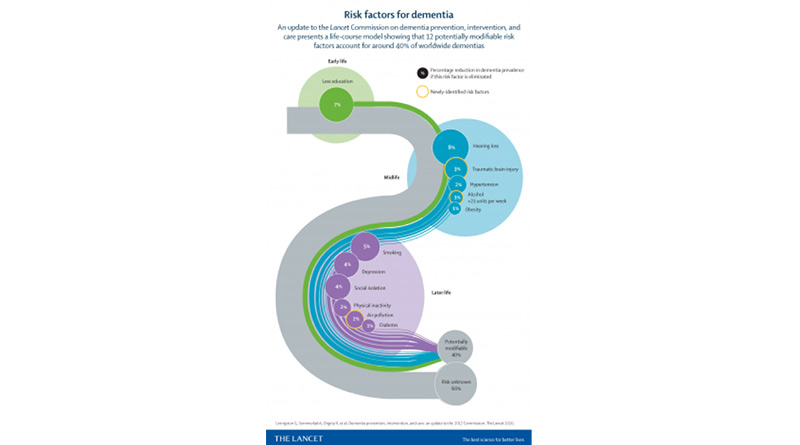
The Lancet Commission report emphasizes the significant role of modifiable risk factors in the development of dementia. The report asserts that nearly half of dementia cases could be prevented or delayed by addressing these risk factors. The commission identified nine modifiable risk factors, including:
- Hearing loss
- Less education
- Social isolation
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Depression
- Midlife hypertension
Recommendations for Preventing and Delaying Dementia
The Lancet Commission report Artikels a comprehensive set of recommendations for preventing and delaying dementia, encompassing public health, clinical, and research strategies.
Public Health Strategies
The report recommends implementing public health strategies to address modifiable risk factors and promote healthy aging. These strategies include:
- Promoting early identification and management of hearing loss.
- Enhancing educational opportunities throughout life.
- Reducing social isolation and promoting social engagement.
- Encouraging regular physical activity and healthy dietary habits.
- Implementing tobacco control measures.
- Addressing obesity and diabetes.
- Promoting mental health and well-being.
- Managing hypertension throughout life.
Clinical Strategies
The report recommends implementing clinical strategies to identify and manage individuals at risk for dementia. These strategies include:
- Developing and implementing effective screening tools for dementia risk factors.
- Providing comprehensive assessment and management of individuals with dementia risk factors.
- Developing and implementing effective interventions for individuals with dementia risk factors.
- Promoting early diagnosis and management of dementia.
Research Strategies
The report recommends investing in research to advance our understanding of dementia and develop new prevention and treatment strategies. These strategies include:
- Conducting research to identify new dementia risk factors and develop effective interventions.
- Developing new diagnostic tools for early detection of dementia.
- Developing new treatments for dementia.
- Conducting research to improve the care of people living with dementia.
Public Health Implications: Nearly Half Of Dementia Cases Could Be Prevented Or Delayed Lancet Commission
The Lancet Commission Report’s findings on dementia prevention have profound implications for public health policy and initiatives. The report underscores the significant potential for reducing the global burden of dementia by addressing modifiable risk factors. This presents a crucial opportunity for public health agencies and policymakers to prioritize dementia prevention as a key public health strategy.
The Lancet Commission’s findings on dementia prevention are a stark reminder of the importance of proactive health measures. While groundbreaking discoveries are happening in other fields, like the recent opening of the liquid mirror telescope in India , we must not lose sight of the urgent need to address preventable diseases like dementia.
Early intervention and lifestyle changes could make a significant difference in reducing the burden of this devastating condition.
Public Health Campaign for Dementia Prevention
A comprehensive public health campaign is essential to raise awareness about dementia prevention strategies and empower individuals to take action. The campaign should be multi-faceted, targeting diverse populations and utilizing various communication channels. Here are key elements of a public health campaign:
- Increase Awareness:Launch public awareness campaigns using television, radio, social media, and community events to educate the public about dementia, its risk factors, and the importance of prevention.
- Promote Healthy Lifestyles:Emphasize the role of healthy lifestyle choices in reducing dementia risk. This includes promoting physical activity, healthy diet, cognitive stimulation, and social engagement.
- Address Risk Factors:Highlight the importance of managing modifiable risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Encourage Early Detection:Promote early detection through regular health checkups and encourage individuals to seek medical advice if they experience any cognitive changes.
- Support for Caregivers:Provide resources and support for caregivers of individuals with dementia, acknowledging the significant challenges they face.
Role of Healthcare Professionals in Dementia Prevention, Nearly half of dementia cases could be prevented or delayed lancet commission
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in promoting dementia prevention strategies. They are uniquely positioned to provide personalized advice and support to patients and their families. Here are key responsibilities for healthcare professionals:
- Assess Risk Factors:Regularly assess patients for modifiable risk factors and provide guidance on lifestyle changes to mitigate these risks.
- Promote Healthy Habits:Encourage patients to adopt healthy habits such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and cognitive stimulation.
- Early Detection and Intervention:Screen for early signs of cognitive decline and refer patients for further evaluation if necessary.
- Educate and Empower:Educate patients and families about dementia, its risk factors, and available prevention strategies. Empower individuals to take control of their health and reduce their dementia risk.
- Advocate for Policy Change:Advocate for policies that support dementia prevention initiatives, such as access to healthy food options, safe environments for physical activity, and affordable healthcare services.
Research and Innovation
Dementia research is a rapidly evolving field with significant potential for developing new treatments and preventive strategies. Investing in research and innovation is crucial for tackling this global health challenge.
Emerging Technologies and Interventions
The advent of emerging technologies offers exciting possibilities for delaying or preventing dementia. For instance, artificial intelligence (AI) is being utilized to analyze large datasets of medical images, genetic information, and lifestyle factors to identify early signs of dementia and predict disease risk.
The Lancet Commission’s findings on dementia prevention are a powerful reminder that we can take proactive steps to protect our cognitive health. It’s a stark contrast to the ongoing debate surrounding the JFK assassination, where jfk assassination doctors break silence dispute key government claim , highlighting the importance of thorough investigation and truth-seeking in all areas of life.
The Lancet Commission’s call to action for preventing dementia underscores the need for comprehensive approaches to public health, including addressing modifiable risk factors and promoting healthy lifestyles.
AI-powered tools are also being developed to assist with diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs)are being explored as a potential therapeutic tool for cognitive decline. BCIs allow individuals to control external devices using brain signals, which could help improve cognitive function and compensate for cognitive deficits.
- Precision medicineapproaches are being implemented to tailor treatment strategies based on an individual’s genetic profile, lifestyle, and other factors. This personalized approach could lead to more effective and targeted interventions.
Understanding the Mechanisms of Dementia
Further research is essential to understand the complex mechanisms underlying dementia. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective preventive and therapeutic strategies.
The Lancet Commission’s report on dementia is a stark reminder that we need to prioritize preventative measures. It’s disheartening, however, to see such a critical health issue overshadowed by divisive rhetoric, like the recent comments from a GOP congressional candidate who believes abortion is a human sacrifice to demons.
While we grapple with these complex issues, let’s not lose sight of the urgent need to address the growing dementia crisis and invest in research and public health initiatives to protect our aging population.
- Identifying new targets for prevention: Research is ongoing to identify new targets for drug development that could prevent or delay the onset of dementia. This includes exploring the role of inflammation, oxidative stress, and other cellular processes in dementia development.
- Developing novel diagnostic tools: Early detection of dementia is crucial for timely intervention and maximizing treatment effectiveness. Research is focused on developing non-invasive diagnostic tools that can identify dementia at its earliest stages, potentially before symptoms are apparent.
Global Perspective
Dementia is a global health challenge, affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding the global distribution of dementia and the factors influencing its prevalence is crucial for developing effective prevention and management strategies. This section explores the global landscape of dementia, highlighting the disparities in prevalence across different regions and the unique challenges faced by low- and middle-income countries.
Prevalence of Dementia Across Regions
The prevalence of dementia varies significantly across different regions of the world. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the highest prevalence rates are observed in high-income countries, particularly in North America and Europe. For example, in the United States, approximately 1 in 9 people aged 65 and over have dementia, while in Europe, the prevalence rate is estimated to be around 1 in 6.
In contrast, lower prevalence rates are reported in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), although these estimates may be underestimated due to limited access to healthcare and diagnostic resources. The prevalence of dementia is expected to rise globally, with the number of people living with dementia projected to reach 152 million by 2050.
- High-income countries:These countries generally have higher prevalence rates due to factors such as aging populations, improved life expectancy, and better access to healthcare.
- Low- and middle-income countries:LMICs often face challenges in accurately assessing dementia prevalence due to limited diagnostic resources, healthcare infrastructure, and awareness.
- Regional disparities:Within regions, there can be significant variations in dementia prevalence due to factors such as socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, and lifestyle factors.
Challenges and Opportunities for Dementia Prevention in Low- and Middle-Income Countries
LMICs face unique challenges in addressing dementia, including:
- Limited resources:LMICs often have limited financial resources, healthcare infrastructure, and trained personnel to address the growing burden of dementia.
- Lack of awareness:There is often a lack of awareness about dementia, its causes, and available interventions, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Stigma:Dementia is often stigmatized in LMICs, leading to social isolation and reluctance to seek help.
- Aging populations:As populations age, the number of people living with dementia is expected to increase significantly in LMICs, putting further strain on already limited resources.
Despite these challenges, there are also opportunities for dementia prevention in LMICs:
- Focus on modifiable risk factors:Addressing modifiable risk factors, such as smoking, physical inactivity, and unhealthy diets, can have a significant impact on dementia prevention.
- Investing in healthcare infrastructure:Investing in healthcare infrastructure, training healthcare professionals, and developing community-based services can improve access to diagnosis and care.
- Promoting awareness:Raising awareness about dementia through public health campaigns, educational programs, and community outreach can help reduce stigma and encourage early diagnosis.
- Developing culturally appropriate interventions:Developing interventions that are culturally appropriate and tailored to the needs of LMICs can enhance their effectiveness.
Successful Initiatives for Dementia Prevention in Different Global Contexts
Several successful initiatives have been implemented globally to address dementia prevention:
- The Lancet Commission on Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care:This global initiative aims to reduce the incidence and impact of dementia by advocating for policies and interventions that promote brain health and well-being.
- The Global Alzheimer’s Association (GAA):The GAA works to advance research, provide education, and advocate for policies that support people living with dementia and their families worldwide.
- The World Health Organization (WHO):The WHO has developed global action plans for dementia, promoting prevention, diagnosis, and care.
- National Dementia Strategies:Many countries have developed national dementia strategies to address the growing burden of the disease, including policies for prevention, diagnosis, and care.
- Community-based initiatives:Community-based initiatives, such as support groups, educational programs, and home care services, can provide essential support to people living with dementia and their families.
Outcome Summary
The Lancet Commission’s report provides a compelling roadmap for preventing and delaying dementia. By embracing the recommendations Artikeld in the report, we can empower individuals to make informed choices about their health and contribute to a future where dementia is less prevalent.
The report serves as a call to action for governments, healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals alike to work together to create a world where dementia is not a foregone conclusion but a preventable condition.