Researchers Find Ways to Limit Antipsychotic Drug Side Effects
Researchers Find Ways to Limit Metabolic Side Effects of Antipsychotic Drugs: A breakthrough in mental health treatment is on the horizon. Antipsychotic medications, while vital for managing severe mental health conditions, often come with a hefty price tag of metabolic side effects, impacting patients’ physical well-being.
Now, researchers are shedding light on strategies to minimize these unwanted consequences, potentially revolutionizing how we treat mental illness.
These side effects can range from weight gain and increased cholesterol to diabetes and cardiovascular issues, significantly impacting a patient’s quality of life and potentially hindering their recovery. This research, however, presents a glimmer of hope, suggesting that we may soon be able to effectively manage these metabolic risks, ensuring patients can access the treatment they need without compromising their overall health.
The Research Findings
The research on limiting metabolic side effects of antipsychotic drugs has yielded promising results, offering new avenues for improving patient care and reducing the burden of these adverse effects. Several innovative strategies have been explored, with varying degrees of success, focusing on understanding the underlying mechanisms of these side effects and developing targeted interventions.
Strategies to Limit Metabolic Side Effects
The research has focused on a range of strategies to mitigate metabolic side effects, each targeting different aspects of the complex interplay between antipsychotic medications and the body’s metabolic processes.
It’s encouraging to hear that researchers are finding ways to limit the metabolic side effects of antipsychotic drugs, especially considering the mental health challenges many face. It reminds me of the article ptsd isnt killing us the system is , which highlights the systemic failures that exacerbate mental health issues.
Hopefully, these advancements in antipsychotic treatment can contribute to a more comprehensive approach to mental health care, addressing both the biological and societal factors at play.
- Developing Novel Antipsychotic Drugs with Reduced Metabolic Side Effects: Researchers have been actively pursuing the development of new antipsychotic drugs with a lower propensity to induce metabolic side effects. This involves designing drugs with improved pharmacological profiles, aiming to minimize their impact on metabolic pathways while maintaining their therapeutic efficacy.
- Utilizing Existing Antipsychotic Drugs More Selectively: This strategy involves employing existing antipsychotic drugs more selectively, tailoring treatment plans to individual patients based on their risk factors for metabolic side effects. For instance, patients with a higher risk of metabolic issues might be prescribed lower doses or different antipsychotic medications altogether.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle modifications, such as regular physical activity, dietary changes, and weight management, have shown promise in reducing the metabolic side effects associated with antipsychotic drugs. These interventions aim to address the underlying metabolic imbalances that contribute to these adverse effects.
- Adjunctive Therapies: The use of adjunctive therapies, such as metformin, a medication commonly used for type 2 diabetes, has been investigated as a potential strategy to mitigate metabolic side effects. Metformin has shown some effectiveness in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing weight gain, but further research is needed to confirm its long-term efficacy and safety in this context.
Types of Antipsychotic Drugs: Researchers Find Ways To Limit Metabolic Side Effects Of Antipsychotic Drugs
Antipsychotic medications are a crucial part of treatment for various mental health conditions, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and severe anxiety. However, their use can be associated with metabolic side effects, which can significantly impact patients’ health and quality of life.
Understanding the different types of antipsychotics and their metabolic profiles is essential for clinicians to make informed decisions about treatment.
Categorization of Antipsychotic Drugs
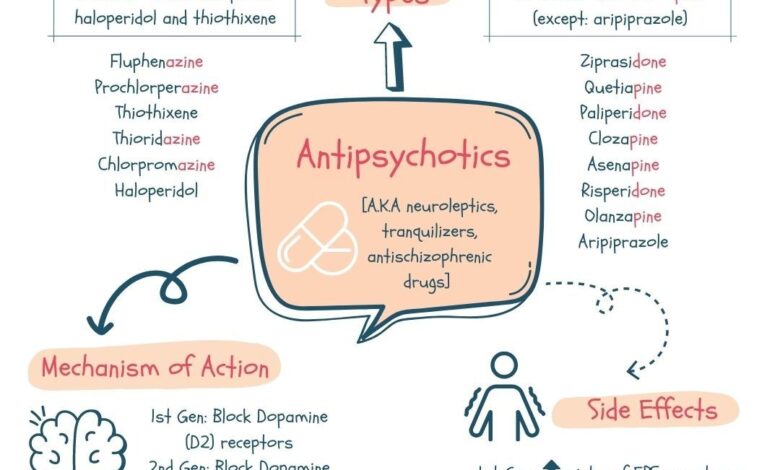
Antipsychotic drugs are broadly categorized into two main classes: typical and atypical. These classifications are based on their chemical structure, mechanism of action, and clinical effects.
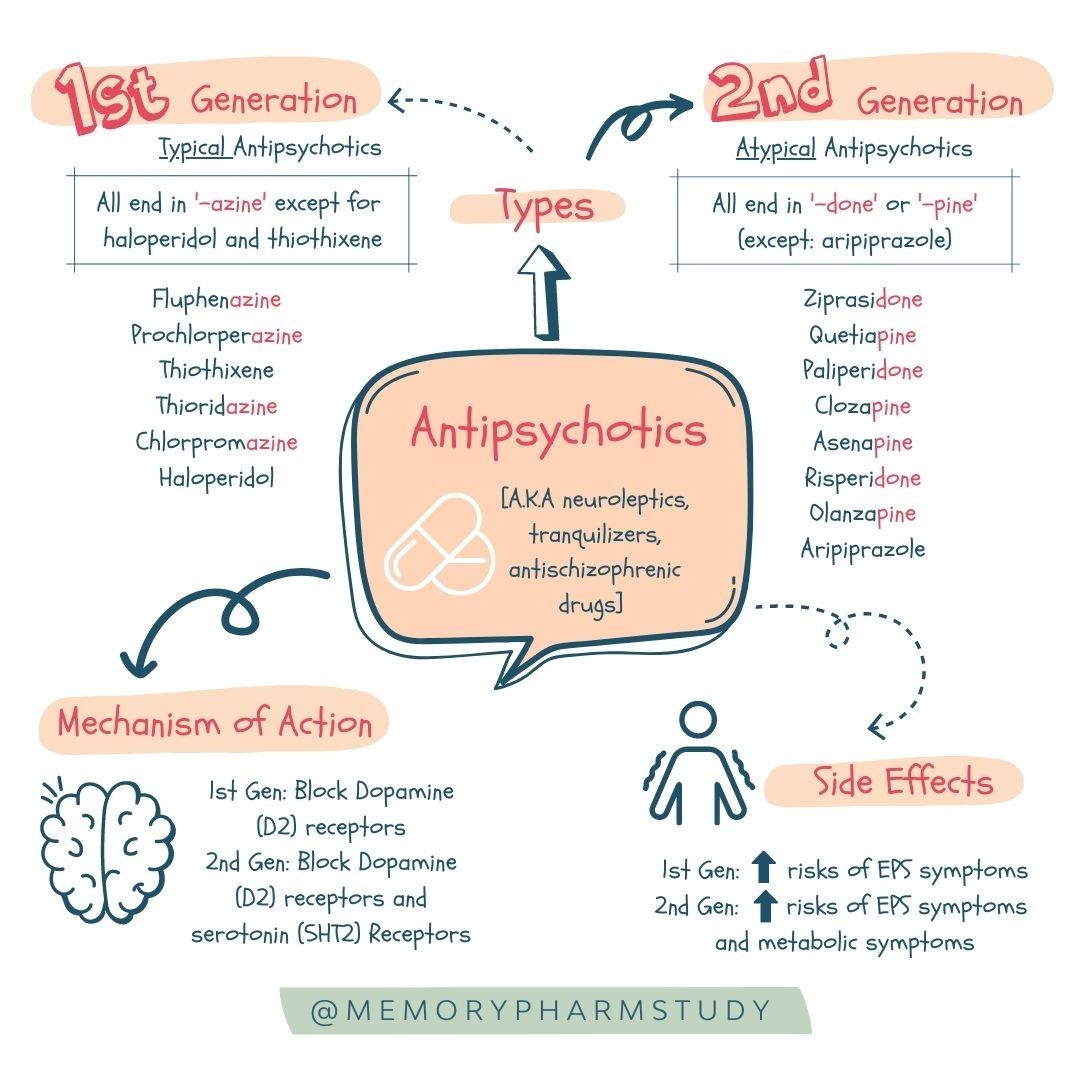
- Typical antipsychotics, also known as first-generation antipsychotics, were the first class of antipsychotics developed. They primarily block dopamine receptors in the brain, particularly the D2 receptor. These drugs are effective in treating positive symptoms of psychosis, such as hallucinations and delusions.
However, they can cause significant extrapyramidal side effects, including muscle stiffness, tremors, and involuntary movements.
- Atypical antipsychotics, also known as second-generation antipsychotics, were developed later and have a broader range of action, blocking both dopamine and serotonin receptors. These drugs are generally considered to have fewer extrapyramidal side effects than typical antipsychotics, but they are associated with a higher risk of metabolic side effects, such as weight gain, diabetes, and dyslipidemia.
It’s great news that researchers are finding ways to limit the metabolic side effects of antipsychotic drugs, but the cost of healthcare is still a major concern. This is especially true for those with mental health conditions, as they often face significant financial burdens.
It’s a bit ironic, then, that the cost of taking out federal student loans is about to go up, as outlined in this recent article , making it even harder for people to access the education and resources they need to manage their health.
Hopefully, these new developments in antipsychotic research will lead to more affordable treatment options in the future.
Metabolic Side Effects Across Different Drug Classes
The metabolic side effects associated with antipsychotics vary depending on the specific drug class and individual patient factors.
- Typical antipsychotics, while less likely to cause metabolic side effects, can still contribute to weight gain and lipid abnormalities in some patients.
- Atypical antipsychotics, particularly the newer agents, are known to have a higher risk of metabolic side effects. This is because they can affect the hypothalamus, a brain region involved in regulating appetite, energy expenditure, and glucose metabolism.
Examples of Antipsychotic Drugs and Their Associated Metabolic Risks
Here are some examples of antipsychotic drugs and their associated metabolic risks:
| Drug Class | Drug Name | Metabolic Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Antipsychotic | Haloperidol (Haldol) | Weight gain, lipid abnormalities |
| Typical Antipsychotic | Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) | Weight gain, lipid abnormalities |
| Atypical Antipsychotic | Olanzapine (Zyprexa) | Significant weight gain, increased risk of diabetes, dyslipidemia |
| Atypical Antipsychotic | Risperidone (Risperdal) | Moderate weight gain, increased risk of diabetes, dyslipidemia |
| Atypical Antipsychotic | Clozapine (Clozaril) | Significant weight gain, increased risk of diabetes, dyslipidemia, agranulocytosis (a serious blood disorder) |
Metabolic Side Effects
Antipsychotic medications are essential for managing mental health conditions like schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. However, they can also have significant metabolic side effects, which can negatively impact patients’ health and well-being. Understanding these side effects is crucial for optimizing treatment and minimizing potential complications.
Metabolic Side Effects of Antipsychotic Drugs
Metabolic side effects are common with antipsychotic medications, particularly atypical antipsychotics. These side effects can lead to various health issues, including:
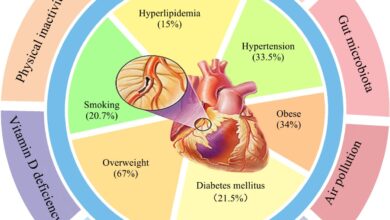
- Weight Gain:Antipsychotic medications can disrupt the body’s metabolism, leading to increased appetite and weight gain. This weight gain can be substantial and contribute to other health problems like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
- Hyperglycemia and Diabetes:Antipsychotic medications can interfere with insulin sensitivity, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Dyslipidemia:These medications can also affect lipid metabolism, leading to increased levels of triglycerides and cholesterol, contributing to cardiovascular disease.
- Metabolic Syndrome:The combination of weight gain, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and hypertension can lead to metabolic syndrome, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other chronic conditions.
Impact of Metabolic Side Effects on Patient Health and Well-being
The metabolic side effects of antipsychotic medications can have a significant impact on patients’ health and well-being:
- Physical Health:These side effects can contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome, significantly impacting patients’ physical health.
- Mental Health:The weight gain and other physical health issues associated with these side effects can negatively impact patients’ self-esteem and body image, potentially exacerbating mental health symptoms.
- Quality of Life:Metabolic side effects can reduce patients’ quality of life by impacting their physical health, mobility, and overall well-being.
- Adherence to Treatment:Patients experiencing significant side effects may be less likely to adhere to their medication regimen, leading to potential relapse of their mental health condition.
Examples of Metabolic Side Effects, Researchers find ways to limit metabolic side effects of antipsychotic drugs
Here are some real-life examples of how metabolic side effects can manifest in patients:
- A patient taking olanzapine experiences significant weight gain, leading to obesity and the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Another patient taking risperidone develops high cholesterol and triglycerides, increasing their risk of heart disease.
- A patient taking clozapine experiences weight gain, hyperglycemia, and hypertension, leading to a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome.
Potential Benefits of Limiting Side Effects
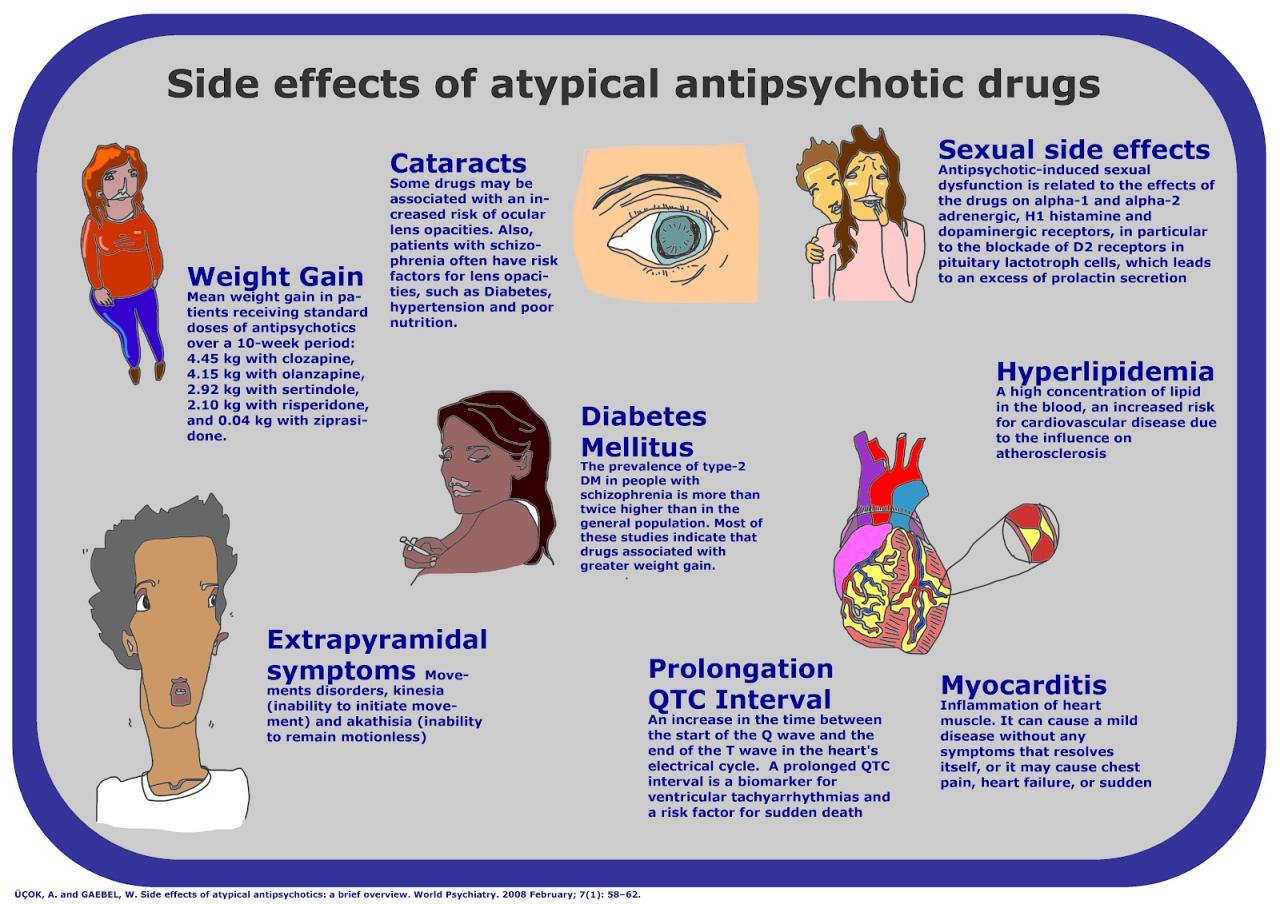
The potential benefits of reducing metabolic side effects from antipsychotic drugs are significant for both patients and the healthcare system. By minimizing these adverse effects, patients can experience improved physical health, enhanced well-being, and greater adherence to their prescribed treatment.
Improved Physical Health
Reducing metabolic side effects can directly contribute to improved physical health for patients taking antipsychotic medications. This is particularly important for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those at risk for developing metabolic complications.
- Weight Management:Antipsychotic-induced weight gain can contribute to obesity, increasing the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other chronic conditions. Limiting weight gain can help patients maintain a healthy weight and reduce their risk of developing these serious health problems.
- Cardiovascular Health:Antipsychotics can also negatively impact cardiovascular health by raising cholesterol levels and blood pressure. By reducing these metabolic side effects, patients can lower their risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
- Blood Sugar Control:Antipsychotics can interfere with blood sugar regulation, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Minimizing these effects can help patients maintain better blood sugar control and reduce their risk of developing diabetes.
Enhanced Adherence to Treatment
Metabolic side effects can be a significant barrier to patient adherence to antipsychotic medication. When patients experience unwanted weight gain, increased cholesterol, or other metabolic complications, they may be less likely to continue taking their medication as prescribed. This can lead to a relapse of their mental health condition and negatively impact their overall well-being.
By limiting these side effects, patients are more likely to adhere to their treatment plan, leading to better management of their mental health condition.
Enhanced Quality of Life
The impact of metabolic side effects extends beyond physical health and medication adherence. These side effects can negatively impact a patient’s overall quality of life.
- Body Image and Self-Esteem:Weight gain and other physical changes associated with antipsychotic use can negatively impact a patient’s body image and self-esteem, leading to feelings of shame, embarrassment, and social isolation. Reducing these side effects can help patients feel more comfortable in their own bodies and improve their self-esteem.
- Social Participation:Metabolic side effects can limit a patient’s ability to engage in social activities and enjoy life to the fullest. For example, weight gain may make it difficult to participate in physical activities or social gatherings, while increased cholesterol or blood pressure may limit a patient’s ability to engage in certain hobbies or travel.
By minimizing these side effects, patients can enjoy greater social participation and overall quality of life.
- Cognitive Function:Metabolic side effects can also impact cognitive function, making it difficult for patients to concentrate, learn, and remember information. This can negatively affect their ability to work, study, and manage their daily lives. By reducing these side effects, patients can experience improved cognitive function and greater independence.
Future Research Directions
The quest to minimize metabolic side effects associated with antipsychotic drugs is a dynamic field with numerous avenues for exploration. Ongoing research efforts aim to refine existing drugs and develop novel approaches to mitigate these adverse effects.
Exploring Personalized Medicine Approaches
Personalized medicine holds immense promise for tailoring antipsychotic treatment to individual patients. Research is focusing on identifying genetic markers that predict an individual’s susceptibility to metabolic side effects. This knowledge can guide the selection of antipsychotics and dosage, potentially minimizing metabolic risks.
For instance, studies are investigating the role of genetic variants in the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system, which plays a crucial role in drug metabolism.
This personalized approach could lead to more effective and safer treatment strategies.
Investigating Novel Drug Delivery Systems
Innovative drug delivery systems are being explored to optimize drug bioavailability and minimize metabolic side effects. Research is investigating the use of nanoparticles, liposomes, and other carriers to deliver antipsychotics directly to the brain, bypassing the systemic circulation and reducing potential metabolic complications.
For example, studies are evaluating the use of nanocarriers to deliver antipsychotic drugs to the brain, potentially reducing systemic exposure and associated metabolic risks.
These novel delivery systems could offer a more targeted and efficient approach to antipsychotic treatment.
Developing Antipsychotics with Reduced Metabolic Liability
The development of new antipsychotic drugs with reduced metabolic liability is a major focus of ongoing research. Scientists are exploring alternative drug targets and mechanisms of action that minimize metabolic side effects.
For example, research is exploring the potential of drugs that target specific neuronal circuits involved in psychosis, potentially reducing the need for high doses and associated metabolic risks.
These efforts aim to create a new generation of antipsychotics with improved safety profiles.
Utilizing Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Non-pharmacological interventions, such as lifestyle modifications and exercise, are being investigated as complementary strategies to manage metabolic side effects. Research is exploring the impact of dietary changes, regular physical activity, and behavioral interventions on metabolic health in patients receiving antipsychotic treatment.
For example, studies are examining the effectiveness of weight management programs and exercise interventions in reducing metabolic risks associated with antipsychotic use.
These non-pharmacological approaches can play a significant role in mitigating metabolic side effects and improving overall health outcomes.
It’s encouraging to hear that researchers are finding ways to limit the metabolic side effects of antipsychotic drugs, especially given the ongoing mental health challenges facing many communities. The recent tragedy in Buffalo, as reported in this article , highlights the need for accessible and effective mental health care, particularly for marginalized groups.
With these advancements in medication, hopefully, more people can access the treatment they need without worrying about the potential for adverse metabolic effects.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The research findings on limiting metabolic side effects of antipsychotic drugs have significant implications for clinical practice. These findings provide valuable insights for healthcare professionals on how to manage these side effects and improve patient outcomes.
Strategies for Managing Metabolic Side Effects
The research findings highlight the importance of a multi-pronged approach to managing metabolic side effects. This involves a combination of medication choices, lifestyle modifications, and close patient monitoring.
- Medication Choice:Healthcare professionals should consider the metabolic profiles of different antipsychotic drugs when making treatment decisions. For example, choosing atypical antipsychotics with lower metabolic side effect profiles, such as aripiprazole or ziprasidone, may be preferable in patients at higher risk for metabolic complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications:Encouraging healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and weight management, can significantly reduce the risk of developing metabolic side effects.
- Regular Monitoring:Close monitoring of patients’ weight, blood sugar levels, lipid profiles, and blood pressure is crucial. This allows early detection of metabolic complications and timely interventions.
Patient Education and Monitoring
Patient education is vital in managing metabolic side effects.
- Understanding Risks:Patients should be informed about the potential metabolic risks associated with antipsychotic medications and the importance of lifestyle modifications.
- Active Participation:Encouraging patients to actively participate in their treatment by adhering to prescribed medications, following lifestyle recommendations, and reporting any changes in their health can significantly improve outcomes.
- Regular Check-ups:Regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider allow for monitoring of metabolic parameters and adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
Summary
The implications of this research are far-reaching. By finding ways to limit metabolic side effects, we can improve patient adherence to treatment, enhance their overall well-being, and potentially even develop new antipsychotic drugs with fewer metabolic risks. This is a testament to the ongoing commitment of researchers to finding innovative solutions for mental health challenges, ultimately paving the way for a brighter future for those living with mental illness.