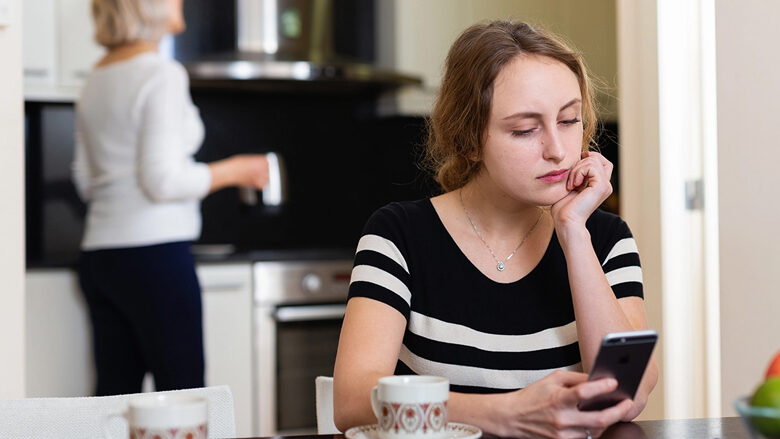

Inflation and Economic Woes Lead 54% of Gen Z to Live with Parents
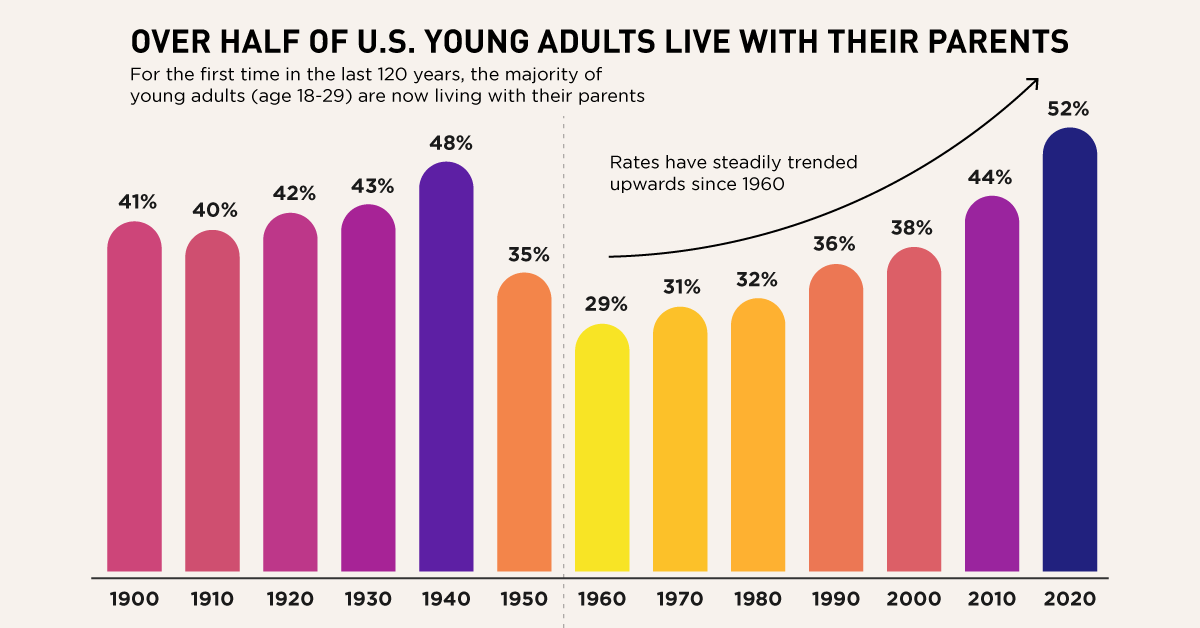
Inflation and economic woes lead 54 percent of Gen Z Americans to live with their parents, a stark reality for a generation facing a housing crisis and rising costs of living. This trend, fueled by a combination of historical economic shifts, limited job opportunities, and skyrocketing housing prices, highlights the immense financial challenges young adults are grappling with. While the allure of independence and self-sufficiency remains a strong motivator, the economic landscape has forced many to re-evaluate their living arrangements, leading to a significant increase in multi-generational households.
The impact of inflation on Gen Z’s finances is undeniable. With wages failing to keep pace with rising prices, their purchasing power has dwindled, making it increasingly difficult to save for a down payment on a home or even afford basic necessities. This financial strain, coupled with a competitive housing market characterized by limited inventory and rising interest rates, has created a perfect storm that has pushed many young adults back into their parents’ homes.
The Gen Z Housing Crisis: Inflation And Economic Woes Lead 54 Percent Of Gen Z Americans To Live With Their Parents
The housing market has always been a rollercoaster, but for Gen Z, it feels like a freefall. The dream of homeownership, once a cornerstone of the American Dream, seems increasingly out of reach for this generation, leaving many grappling with a housing crisis unlike any before.
It’s no surprise that with inflation and economic woes, 54 percent of Gen Z Americans are living with their parents. This financial strain is impacting consumer spending habits, as seen in Target’s recent profit decline due to consumers cutting back on discretionary spending. It’s a tough time for young adults trying to establish independence, and this trend highlights the real impact inflation is having on everyday lives.
Historical Context and Generational Shifts, Inflation and economic woes lead 54 percent of gen z americans to live with their parents
The affordability of housing in the US has been steadily declining for decades, but the current situation is particularly acute for Gen Z. This generation faces a perfect storm of economic trends that have made homeownership a distant aspiration for many. The rise of student loan debt, stagnant wages, and a rapidly escalating housing market have all conspired to create a formidable barrier to entry for young homebuyers.
Inflation’s Impact on Gen Z Finances
Inflation, the persistent rise in prices for goods and services, has significantly impacted Gen Z’s financial well-being. This generation, already burdened by student loan debt and a competitive job market, faces unique challenges in navigating an economy characterized by rising costs and a shrinking purchasing power.
It’s a tough time to be young, with inflation and economic woes making it nearly impossible for many Gen Zers to afford independent living. In fact, a recent study revealed that a staggering 54% of Gen Z Americans are living with their parents. It’s a stark reminder of the economic challenges facing our generation, and it’s a situation that has only been exacerbated by the recent influx of migrants, as seen in the Massachusetts governor’s decision to activate the National Guard and send migrants from Martha’s Vineyard to a military base.
This situation highlights the need for comprehensive solutions to address both economic hardship and the immigration crisis, ensuring a brighter future for all Americans.
The Impact of Inflation on Purchasing Power
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, meaning that the same amount of money buys fewer goods and services over time. This effect is particularly pronounced for Gen Z, who are just starting their careers and are likely to have lower incomes compared to older generations. As prices rise, Gen Z finds it increasingly difficult to afford essential items such as groceries, rent, and transportation, leaving less money available for savings, investments, and future financial goals.
It’s a tough time to be a young adult. Inflation and economic woes are forcing many Gen Zers to move back in with their parents. It’s a reality check that the American dream might be a little harder to achieve than we thought. Meanwhile, the FBI is asking a court to wait 66 years to release information from Seth Rich’s computer, a case that has been shrouded in conspiracy theories.
While we grapple with these complex issues, it’s important to remember that we’re not alone in facing these challenges. We need to support each other and find solutions that work for everyone.
The Psychological and Social Implications
Living with parents due to economic hardship can have a significant impact on Gen Z’s mental well-being and social interactions. While it offers financial relief, it also presents unique challenges that can affect their sense of independence, relationships, and overall outlook.
The Psychological Impact
Living with parents can evoke a range of emotions, from feelings of dependence and pressure to contribute to the household to a sense of delayed independence. The constant reminder of financial reliance can lead to feelings of frustration, inadequacy, and even shame. The pressure to contribute financially, even when struggling themselves, can add to the stress and burden. Moreover, the inability to establish their own living space and forge their own identity can lead to feelings of stagnation and a sense of being stuck in a prolonged adolescence.
The Social Dynamics
Living with parents can also affect social dynamics, particularly with family members. While it offers the benefit of close family ties and support, it can also lead to conflicts and strained relationships. The need to navigate personal space, privacy, and differing expectations can create friction. Additionally, living with parents can impact relationships with friends and romantic partners. The lack of independence can make it difficult to maintain social lives and pursue romantic interests.
It can also create a sense of isolation and loneliness, especially if friends are living independently.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Living with Parents
The decision to live with parents is a complex one, with both advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a table comparing the potential benefits and drawbacks:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Financial relief | Limited privacy and personal space |
| Family support and closeness | Potential for conflict and strained relationships |
| Reduced living expenses | Delayed independence and self-reliance |
| Access to family resources | Social isolation and limited social opportunities |
Economic Solutions and Strategies

The Gen Z housing crisis and the broader economic challenges they face call for a multifaceted approach, involving both policy solutions and personal financial strategies. Addressing these issues requires a concerted effort from governments, policymakers, and individuals to create a more equitable and sustainable future for young adults.
Policy Solutions for Housing Affordability
Policy solutions play a crucial role in addressing the housing crisis and making homes more accessible for Gen Z. These policies can help increase the supply of affordable housing, regulate rental markets, and provide financial assistance to young homebuyers.
- Increased Funding for Affordable Housing Development: Government investment in affordable housing projects can significantly expand the supply of affordable units, easing the pressure on rental markets and making homeownership more attainable for Gen Z. This can include direct funding for new construction, rehabilitation of existing units, and support for community land trusts.
- Rent Control and Stabilization Measures: Rent control policies can help protect tenants from excessive rent increases and displacement. Implementing rent stabilization measures can create a more stable and predictable rental environment, providing greater security for young renters.
- Expanding Access to Down Payment Assistance: Programs that offer down payment assistance can help Gen Z overcome the significant financial barrier of entering the housing market. These programs can be tailored to specific needs, such as first-time homebuyers or those in specific geographic areas.
Financial Strategies for Gen Z
Navigating inflation and building financial security requires a proactive approach from Gen Z. These strategies can help them manage expenses, build savings, and plan for their financial future.
- Budgeting and Expense Tracking: Creating a detailed budget and tracking expenses can help Gen Z understand their spending patterns and identify areas where they can cut back. Budgeting apps and online tools can make this process easier and more efficient.
- Prioritizing Savings: Regularly saving a portion of income, even if it’s a small amount, is crucial for building financial security. Consider automating savings transfers to ensure consistency.
- Investing for the Future: Investing in the stock market or other assets can help grow wealth over time. Consider starting with index funds or robo-advisors for a low-cost and diversified approach.
- Debt Management: Managing debt responsibly is essential for financial stability. Prioritize paying down high-interest debt, such as credit card debt, and explore options for debt consolidation or refinancing.
Resources and Organizations for Young Adults
Several resources and organizations provide support and guidance to young adults facing economic challenges. These resources can offer financial literacy education, job training, and access to financial assistance.
- National Endowment for Financial Education (NEFE): NEFE offers a range of resources and programs, including financial literacy education, budgeting tools, and debt management advice. Their website provides a wealth of information and resources for young adults.
- The United Way: The United Way is a network of community-based organizations that provide a variety of services, including financial assistance, housing support, and job training. They can connect young adults with local resources and programs.
- The National Housing Conference: The National Housing Conference advocates for affordable housing policies and provides resources for individuals and families facing housing challenges. Their website offers information on housing affordability, rental assistance programs, and homeownership opportunities.
Living with parents, while not always ideal, offers a temporary solution to the economic realities facing Gen Z. However, it comes with its own set of challenges, including feelings of dependence, pressure to contribute, and delayed independence. It’s a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing both individual financial strategies and policy solutions to address the underlying economic and housing market imbalances.
The future of Gen Z’s financial well-being hinges on finding sustainable solutions that address these systemic issues and pave the way for a more equitable and affordable future.






