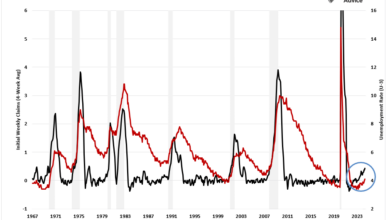
American Consumer Sentiment Plunges While Inflation Expectations Rise
American consumer sentiment plunges while inflation expectations rise – a stark reality that paints a picture of economic uncertainty. This trend, fueled by persistent inflation and rising interest rates, has cast a shadow over consumer confidence, impacting spending patterns and overall economic growth.
The decline in consumer sentiment is a significant indicator of the current economic climate. It reflects a growing sense of anxiety among American households about their financial well-being, particularly in the face of rising prices for essential goods and services. This unease is further compounded by concerns about job security and the potential for a recession.
Consumer Sentiment Plunge
American consumer sentiment has taken a nosedive, signaling a potential shift in economic prospects. This decline is a significant indicator of consumer confidence and spending habits, which are crucial drivers of the economy. Understanding the factors behind this plunge is crucial for gauging the future trajectory of economic growth.
Factors Driving the Decline
Several factors are contributing to the recent decline in consumer sentiment.
It’s a tough time to be a consumer in America, with plummeting sentiment and soaring inflation expectations. Perhaps reflecting this economic anxiety, Tulsi Gabbard’s decision to stump for a GOP candidate a day after leaving the Democratic party is another sign of the shifting political landscape. Whether this signals a broader trend remains to be seen, but one thing is certain: Americans are feeling the strain of inflation, and it’s impacting their views on everything from politics to their own financial futures.
- Inflation: The persistent rise in prices, particularly for essential goods and services, is eroding consumer purchasing power and leaving them feeling less optimistic about their financial well-being.
- Rising Interest Rates: The Federal Reserve’s aggressive interest rate hikes are increasing borrowing costs for consumers, making it more expensive to finance purchases like homes and cars.
- Economic Uncertainty: Concerns about a potential recession, rising unemployment, and geopolitical tensions are creating a sense of uncertainty and anxiety among consumers.
Historical Trends and Economic Indicators
Consumer sentiment has a long history of fluctuating in response to economic conditions. Historically, there has been a strong correlation between consumer sentiment and key economic indicators like GDP growth, employment, and inflation.
- Relationship with GDP: When consumer sentiment is high, consumers tend to spend more, leading to increased economic activity and GDP growth. Conversely, low consumer sentiment can signal a slowdown in spending and economic growth.
- Correlation with Employment: Consumer sentiment often tracks closely with employment trends. When unemployment is low and job security is high, consumers tend to feel more optimistic about their financial prospects, leading to higher sentiment.
The recent plunge in American consumer sentiment, coupled with rising inflation expectations, paints a bleak picture for the economy. This uncertainty is further complicated by the fact that GOP voters are now virtually impossible to poll accurately after Biden’s recent “MAGA Republicans” speech, as reported by a top pollster here. This makes it difficult to gauge the true sentiment of the electorate, which could have a significant impact on upcoming elections and economic policy decisions.
- Impact of Inflation: High inflation erodes consumer purchasing power and can lead to a decline in consumer sentiment. This is because consumers feel less confident about their ability to afford essential goods and services.
Comparison to Previous Periods of Uncertainty
The current decline in consumer sentiment is comparable to periods of economic uncertainty in the past. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, consumer sentiment plummeted as the economy faced a severe recession. Similarly, during the COVID-19 pandemic, sentiment took a hit due to widespread economic disruptions and job losses.
Inflation Expectations
The latest consumer sentiment survey revealed a concerning trend: while consumer confidence is plummeting, inflation expectations are on the rise. This suggests that consumers are increasingly worried about the future purchasing power of their money, and this anxiety is likely to impact their spending habits.
Current Levels of Inflation Expectations
Inflation expectations are a key indicator of future inflation. When consumers expect prices to rise, they are more likely to spend now, before prices increase further. This can lead to a self-fulfilling prophecy, where increased demand pushes prices up even more. According to the University of Michigan’s Consumer Sentiment Index, consumers expect inflation to average 5.4% over the next year, and 3.1% over the next five years.
These figures are significantly higher than they were just a few months ago, reflecting growing concerns about the persistence of inflation.
Sources of Inflation Concerns
American households are facing a number of factors that are contributing to their inflation concerns.
- Persistent High Inflation: The current rate of inflation, which is hovering around 4%, is well above the Federal Reserve’s target of 2%. This persistent high inflation has eroded purchasing power and made it more difficult for consumers to afford essential goods and services.
- Rising Energy Prices: Energy prices have been a major driver of inflation, particularly in recent months. The war in Ukraine has disrupted global energy markets, leading to higher prices for gasoline, natural gas, and electricity.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Supply chain disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic have contributed to higher prices for a wide range of goods. These disruptions have made it more difficult for businesses to obtain the materials and components they need to produce goods, leading to shortages and higher prices.
- Rising Interest Rates: The Federal Reserve has been raising interest rates in an attempt to cool inflation. These rate hikes have made it more expensive for consumers to borrow money, which could dampen consumer spending.
Impact of Rising Inflation Expectations on Consumer Spending
Rising inflation expectations can have a significant impact on consumer spending patterns.
- Delayed Purchases: Consumers may delay large purchases, such as cars or appliances, if they expect prices to rise further in the future.
- Increased Savings: Consumers may save more money to offset the impact of rising prices.
- Shifting Spending Priorities: Consumers may shift their spending priorities, focusing on essential goods and services rather than discretionary items.
Strategies to Cope with Inflation
Consumers are adopting a variety of strategies to cope with inflation.
- Budgeting and Saving: Consumers are becoming more mindful of their spending and are looking for ways to save money. This may involve creating a budget, cutting back on non-essential expenses, and looking for deals and discounts.
- Shopping Around: Consumers are comparing prices and looking for the best deals on goods and services. This may involve shopping at different stores, using coupons, and taking advantage of sales.
- Investing: Some consumers are investing their money to try to outpace inflation. This may involve investing in stocks, bonds, or real estate.
- Seeking Additional Income: Some consumers are seeking additional income to offset the impact of rising prices. This may involve taking on a second job, starting a side hustle, or selling unused items.
Economic Impact: American Consumer Sentiment Plunges While Inflation Expectations Rise
The plunge in consumer sentiment and the rise in inflation expectations have significant implications for the economy. When consumers are less confident about the future, they tend to spend less, which can lead to a slowdown in economic growth. Similarly, rising inflation expectations can prompt businesses to raise prices, further fueling inflation and eroding consumer purchasing power.
Impact on Business Investment
Declining consumer sentiment and rising inflation expectations can negatively impact business investment. Businesses are less likely to invest in expansion or new projects when they anticipate lower consumer demand and higher costs. This can lead to job losses and a further slowdown in economic growth. For example, a manufacturing company might delay investing in new equipment if it expects lower demand for its products due to rising inflation and consumer uncertainty.
The news that American consumer sentiment is plummeting while inflation expectations are rising is a double whammy for the economy. It’s a reminder that we’re living in turbulent times, where even the biggest news stories can feel distant from the everyday struggles of people trying to make ends meet. Meanwhile, the legal battle over classified documents in the Trump records case continues to unfold, with a judge blocking the special master from viewing materials with classified markings.
It’s a stark contrast to the economic anxieties facing many Americans, but it’s a reminder that even in these challenging times, the pursuit of justice and accountability continues.
Impact on Job Creation
Job creation is closely linked to consumer spending and business investment. When consumer sentiment is low, businesses are less likely to hire new workers, leading to a decrease in job creation. Rising inflation can also contribute to job losses as businesses struggle to cope with higher input costs and may be forced to lay off workers. For instance, a retail company might reduce its workforce if it anticipates a decline in consumer spending due to rising inflation and economic uncertainty.
Impact on Overall Economic Growth
Consumer spending accounts for a significant portion of economic activity. When consumers spend less, it can lead to a decrease in overall economic growth. Rising inflation can also have a negative impact on economic growth by eroding consumer purchasing power and making businesses less likely to invest. For example, a decline in consumer spending on durable goods, such as cars and appliances, can significantly impact economic growth.
Impact on Various Economic Sectors
The following table illustrates the potential impact of consumer sentiment and inflation on various economic sectors:| Sector | Impact of Declining Consumer Sentiment | Impact of Rising Inflation ||—|—|—|| Retail | Reduced consumer spending on discretionary items | Increased costs for retailers, potentially leading to price increases || Housing | Reduced demand for new homes and existing housing | Increased mortgage rates, making homeownership less affordable || Manufacturing | Reduced demand for manufactured goods | Increased costs for raw materials and labor || Services | Reduced demand for non-essential services | Increased costs for service providers, potentially leading to price increases || Tourism | Reduced travel and leisure spending | Increased costs for travel and accommodation |
Government Response
The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, is taking a leading role in combating inflation and supporting consumer confidence. Their primary tool is adjusting interest rates, which influence borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. The Fed has aggressively raised interest rates in recent months, aiming to cool down the economy and bring inflation under control.
Interest Rate Hikes and Their Impact
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes aim to curb inflation by making it more expensive to borrow money, potentially slowing down economic activity. However, these hikes can also have a dampening effect on consumer confidence, as higher borrowing costs make it more expensive to finance purchases like homes and cars.
“The Federal Reserve’s goal is to achieve a soft landing, where inflation is brought down without triggering a recession.”
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell
- Impact on Consumer Spending: Higher interest rates can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, as individuals become more cautious about taking on debt. This could contribute to a slowdown in economic growth.
- Impact on Housing Market: Rising interest rates make mortgages more expensive, which can slow down home sales and potentially lead to a decline in home prices.
- Impact on Business Investment: Businesses may be less inclined to invest in expansion or new projects when borrowing costs are high.
Fiscal Policy Measures
The government, through fiscal policy, can also influence consumer confidence and inflation. This involves managing government spending and taxation.
- Tax Cuts: The government may consider tax cuts to boost disposable income for consumers, potentially leading to increased spending and economic growth.
- Government Spending: Increased government spending on infrastructure projects or social programs can stimulate economic activity and create jobs, but it could also contribute to inflation if not carefully managed.
Consumer Behavior

Declining consumer sentiment and rising inflation are having a significant impact on how Americans spend and save their money. Consumers are becoming more cautious and are adjusting their spending habits to cope with the current economic environment. These changes are likely to have long-term implications for consumer demand and economic growth.
Changes in Spending Habits
The decline in consumer sentiment has led to a shift in spending priorities. Consumers are becoming more price-conscious and are seeking out value for their money. This has resulted in a decrease in discretionary spending, such as dining out, entertainment, and travel. Here are some examples of how consumers are adjusting their spending habits:
- Trading down: Consumers are switching to cheaper brands or generic products, particularly for non-essential items. For example, they might opt for store-brand cereal instead of a name-brand cereal.
- Delayed purchases: Consumers are delaying major purchases, such as new cars or appliances, due to concerns about rising prices and economic uncertainty.
- Increased use of coupons and discounts: Consumers are actively searching for deals and discounts to stretch their budgets further.
- Shifting towards necessities: Consumers are prioritizing essential spending on food, housing, and healthcare, while cutting back on discretionary items.
Changes in Saving Patterns, American consumer sentiment plunges while inflation expectations rise
Rising inflation is prompting consumers to prioritize saving more. They are concerned about the rising cost of living and are trying to build up their emergency funds to weather potential economic shocks. Here are some examples of how consumers are adjusting their saving patterns:
- Increasing savings: Consumers are increasing their savings rate to protect themselves from rising prices and potential economic downturns.
- Prioritizing debt repayment: Consumers are focusing on paying down high-interest debt, such as credit card debt, to reduce their financial burden.
- Investing for the future: Consumers are seeking out investment opportunities that can help them outpace inflation and secure their financial future.
Long-Term Implications
The changes in consumer behavior driven by declining sentiment and rising inflation have significant implications for consumer demand and economic growth.
- Reduced consumer spending: The shift towards value-oriented spending and delayed purchases could lead to a decline in consumer spending, which is a major driver of economic growth.
- Slower economic growth: Reduced consumer spending can lead to slower economic growth as businesses experience lower demand for their products and services.
- Shift in consumer preferences: The changes in spending habits could lead to a long-term shift in consumer preferences, with a greater emphasis on value and affordability.
Market Volatility
Declining consumer sentiment and rising inflation expectations create a perfect storm for market volatility. When consumers are pessimistic about the economy and anticipate higher prices, they tend to reduce spending, leading to slower economic growth and corporate earnings. This uncertainty, coupled with the Federal Reserve’s aggressive interest rate hikes, creates a challenging environment for investors.
Impact on Financial Assets
The impact of declining consumer sentiment and rising inflation expectations on financial assets is multifaceted.
Stock Prices
-
Rising inflation erodes corporate profits, leading to lower earnings expectations and potential stock price declines.
-
Increased interest rates make borrowing more expensive for businesses, potentially hindering growth and impacting stock valuations.
-
Higher inflation expectations can also lead to increased volatility in the stock market, as investors adjust their portfolios based on their perception of future economic conditions.
Bond Yields
-
As interest rates rise, bond yields also tend to increase. This is because investors demand higher returns on bonds to compensate for the increased risk of inflation eroding the value of their investment.
-
Higher bond yields can lead to capital losses for bond investors, particularly for those holding bonds with longer maturities.
-
The relationship between rising inflation expectations and bond yields is complex, as it depends on factors such as the perceived risk of inflation, the Fed’s monetary policy stance, and the overall economic outlook.
Other Financial Assets
-
Commodities such as gold and oil can be seen as inflation hedges, as their prices tend to rise during periods of high inflation. However, the relationship between commodity prices and inflation expectations is not always clear-cut.
-
Real estate can also be impacted by rising interest rates, as mortgage rates increase, making it more expensive to purchase homes.
-
The impact of declining consumer sentiment and rising inflation expectations on other financial assets depends on the specific asset class and the underlying economic factors.
Investor Strategies
Navigating market volatility during periods of declining consumer sentiment and rising inflation expectations requires a proactive approach. Investors can consider the following strategies:
-
Diversify your portfolio: Diversification across different asset classes, sectors, and geographies can help mitigate risk and potentially improve returns.
-
Focus on quality companies: During periods of economic uncertainty, companies with strong balance sheets, consistent earnings, and a history of resilience can provide a buffer against market volatility.
-
Consider value stocks: Value stocks, which are often undervalued by the market, can offer potential upside in a rising inflation environment.
-
Rebalance your portfolio regularly: Rebalancing ensures that your portfolio remains aligned with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
-
Consult with a financial advisor: A qualified financial advisor can provide personalized guidance based on your individual circumstances and investment objectives.
As consumer sentiment remains fragile and inflation expectations persist, the economic landscape appears complex and uncertain. The impact of these trends will likely continue to shape consumer behavior, business decisions, and government policies in the coming months. Understanding the interplay of these forces is crucial for navigating the current economic environment and preparing for the future.