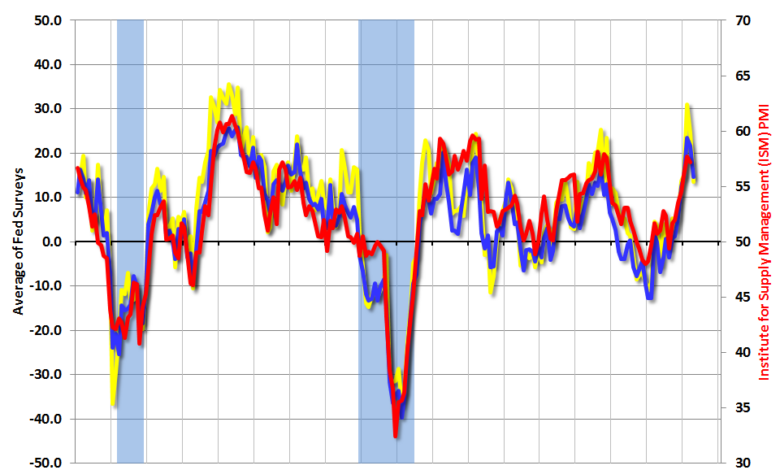
Stagflation Signs Mount as Fed Manufacturing Index Shows Activity Slump, Inflation Higher
Stagflation signs mount as fed manufacturing index shows activity slump inflation higher – Stagflation Signs Mount as Fed Manufacturing Index Shows Activity Slump, Inflation Higher: The recent Fed Manufacturing Index report paints a concerning picture of the U.S. economy, raising serious concerns about the potential for stagflation. The index, which tracks activity in the manufacturing sector, revealed a significant decline in production and a surge in inflationary pressures. This data aligns with other economic indicators, suggesting that the economy may be entering a period of stagflation – a combination of high inflation and stagnant economic growth.
This scenario is particularly troubling, as it could lead to a prolonged period of economic uncertainty and hardship for businesses and consumers alike.
The Fed Manufacturing Index is a key indicator of economic health, providing valuable insights into the manufacturing sector’s performance. The index is compiled based on surveys of manufacturing executives, capturing their views on current economic conditions, production levels, new orders, and employment. Recent data from the index has highlighted a significant decline in manufacturing activity, coupled with rising inflationary pressures.
This suggests that businesses are struggling to cope with rising input costs and weakening demand, leading to reduced production and job losses. This dynamic is a hallmark of stagflation, where the economy is simultaneously grappling with high inflation and stagnant economic growth.
Economic Implications of Stagflation
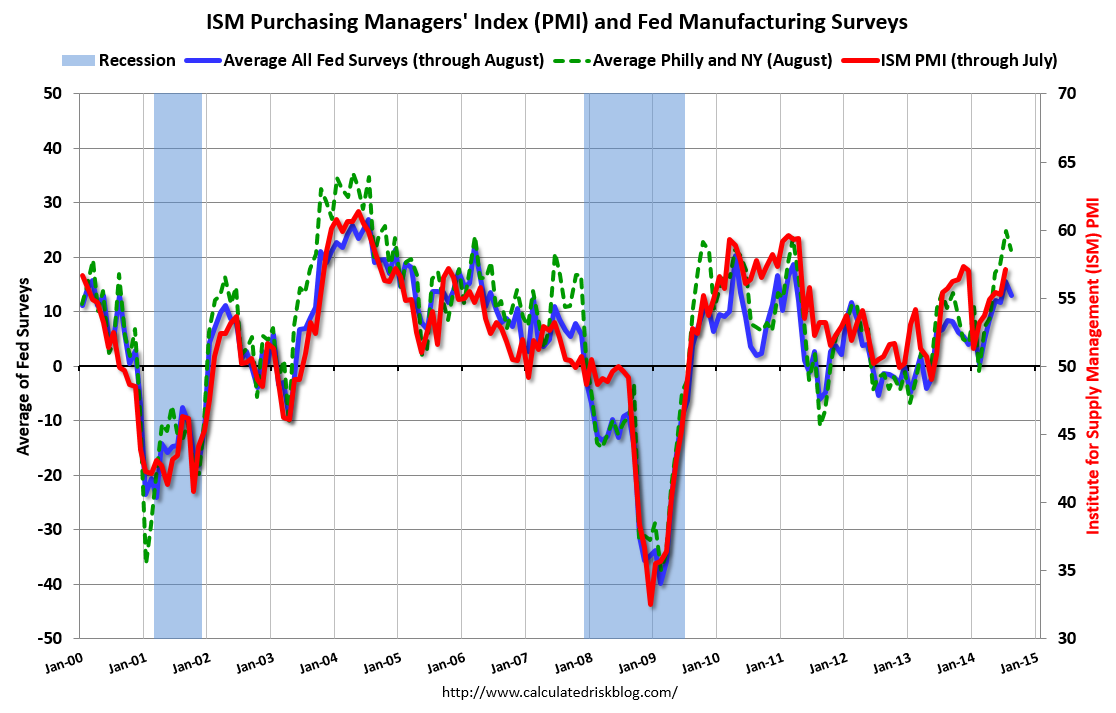
Stagflation, a dreaded economic condition characterized by a simultaneous rise in inflation and a decline in economic growth, presents significant challenges to businesses, consumers, and the overall economy. It disrupts the delicate balance of economic stability, leading to uncertainty, reduced investment, and a decline in living standards. Understanding the potential consequences of stagflation is crucial for navigating these turbulent economic waters.
Potential Consequences of Stagflation
Stagflation can have far-reaching consequences for various stakeholders in the economy. Businesses face a challenging environment with rising input costs, decreasing demand, and reduced profits. Consumers struggle with higher prices for goods and services, eroding their purchasing power and leading to reduced spending. The overall economy experiences a slowdown in growth, accompanied by increased unemployment and a decline in investment.
Impact on Investment, Employment, and Consumer Spending
Stagflation has a profound impact on investment, employment, and consumer spending. Businesses, facing rising costs and uncertainty, are likely to postpone or cancel investment projects, leading to reduced job creation and economic activity. The decline in consumer spending, driven by eroding purchasing power, further exacerbates the economic slowdown. The combination of rising inflation and stagnant economic growth creates a vicious cycle, perpetuating the negative effects of stagflation.
Historical Examples of Stagflation, Stagflation signs mount as fed manufacturing index shows activity slump inflation higher
History provides numerous examples of stagflation, each with its own unique set of circumstances and consequences. The stagflation of the 1970s, triggered by the oil crisis and excessive government spending, led to high inflation, unemployment, and economic stagnation in many developed countries. The Great Recession of 2008-2009, while not a classic case of stagflation, exhibited elements of both high inflation and economic slowdown, highlighting the complex interplay of economic forces.
Examining these historical examples provides valuable insights into the potential outcomes of stagflation and the challenges it poses for economic policymakers.
Strategies for Addressing Stagflation: Stagflation Signs Mount As Fed Manufacturing Index Shows Activity Slump Inflation Higher
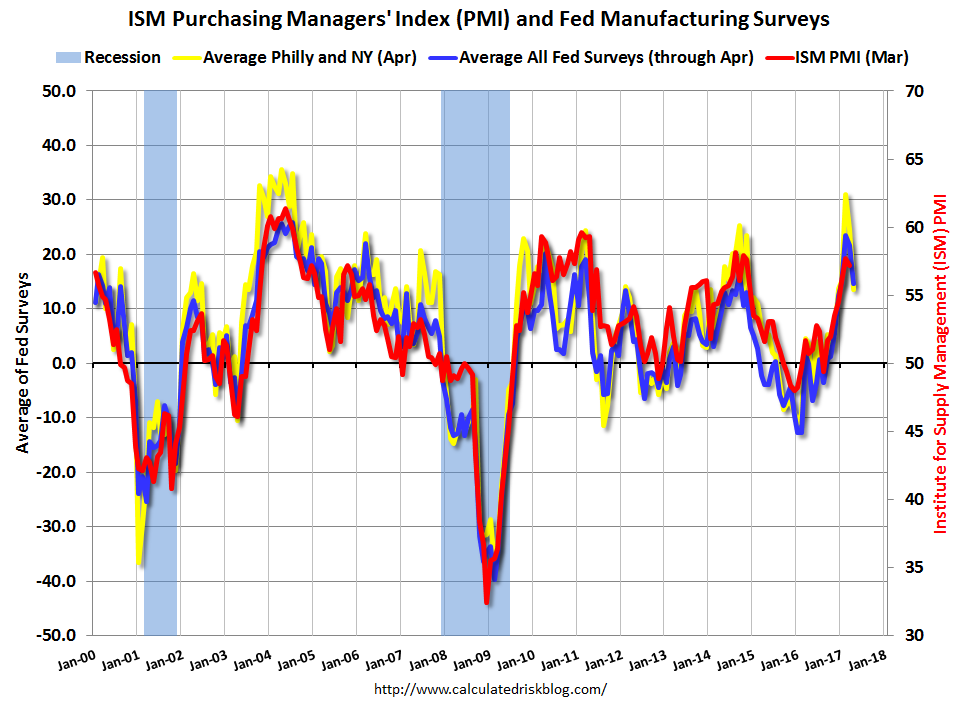
Stagflation, a confluence of stagnant economic growth and rising inflation, presents a formidable challenge for policymakers. Addressing this complex economic phenomenon requires a multifaceted approach that aims to stimulate growth, curb inflation, and maintain employment levels. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, several strategies can be employed to mitigate the adverse effects of stagflation.
Policy Options for Addressing Stagflation
Policymakers have a range of tools at their disposal to combat stagflation. These tools can be broadly categorized into monetary policy, fiscal policy, and supply-side policies.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks can use monetary policy tools to influence the money supply and interest rates. In the context of stagflation, central banks face a delicate balancing act. Raising interest rates can help curb inflation but may also stifle economic growth. Conversely, lowering interest rates can boost economic activity but could exacerbate inflationary pressures.
- Fiscal Policy: Governments can utilize fiscal policy tools, such as government spending and taxation, to influence aggregate demand. During stagflation, governments may consider increasing spending on infrastructure projects or providing tax breaks to stimulate economic growth. However, such measures could lead to higher budget deficits and contribute to inflation.
- Supply-Side Policies: Supply-side policies aim to increase the productive capacity of the economy. Examples include deregulation, tax cuts for businesses, and investments in education and training. These policies can help reduce costs and increase output, ultimately mitigating inflationary pressures. However, supply-side policies often take time to yield results.
Evaluating Policy Options
The effectiveness of different policy options in addressing stagflation depends on the specific economic circumstances and the nature of the stagflationary pressures.
| Policy Option | Potential Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Monetary Policy (Raising Interest Rates) |
|
|
| Fiscal Policy (Increased Government Spending) |
|
|
| Supply-Side Policies (Deregulation) |
|
|
Importance of a Comprehensive Approach
Addressing stagflation requires a coordinated approach that combines monetary, fiscal, and supply-side policies. Policymakers must carefully consider the potential trade-offs and adjust their strategies as needed.
“The optimal policy response to stagflation is likely to involve a combination of measures that address both demand-side and supply-side factors.”
[Source
International Monetary Fund]
The recent Fed Manufacturing Index report, with its stark depiction of declining activity and surging inflation, has ignited serious concerns about the potential for stagflation. The index, a crucial gauge of economic health, reveals a concerning trend that aligns with other economic indicators, suggesting a potential entry into a period of stagflation. This scenario poses significant challenges for businesses and consumers alike, as it could lead to prolonged economic uncertainty and hardship.
While the future remains uncertain, understanding the dynamics at play and the potential consequences of stagflation is essential for navigating the economic landscape ahead.
The latest economic indicators are painting a mixed picture, with signs of stagflation mounting as the Fed manufacturing index shows activity slumping and inflation remaining stubbornly high. Adding to the uncertainty, continuing unemployment claims have risen to their highest level in five months , while initial claims have fallen. This suggests that while some sectors are experiencing layoffs, others are still hiring, contributing to a complex economic landscape.
The combination of these factors reinforces the concerns about stagflation and the challenges policymakers face in navigating this delicate economic terrain.
The economic storm clouds are gathering, with the Fed’s manufacturing index revealing a worrying slump in activity coupled with rising inflation. This is a recipe for stagflation, a dangerous combination of economic stagnation and rising prices. While we grapple with these economic challenges, a separate political storm is brewing with the news that a top FBI official accused of shutting down the Hunter Biden probe must testify before Congress.
This revelation could further inflame the political climate, adding another layer of uncertainty to an already volatile situation. In the midst of this, the economy remains vulnerable, with stagflation looming large on the horizon.
The recent economic news paints a bleak picture, with the Fed manufacturing index showing a slump in activity while inflation remains high, raising concerns about stagflation. Amidst this economic uncertainty, news of the US government transporting dozens of unaccompanied minor illegal immigrants to New York adds another layer of complexity, highlighting the challenges facing policymakers as they navigate these turbulent times.
It remains to be seen how these developments will impact the economy in the long run, but it’s clear that we’re in for a bumpy ride.






