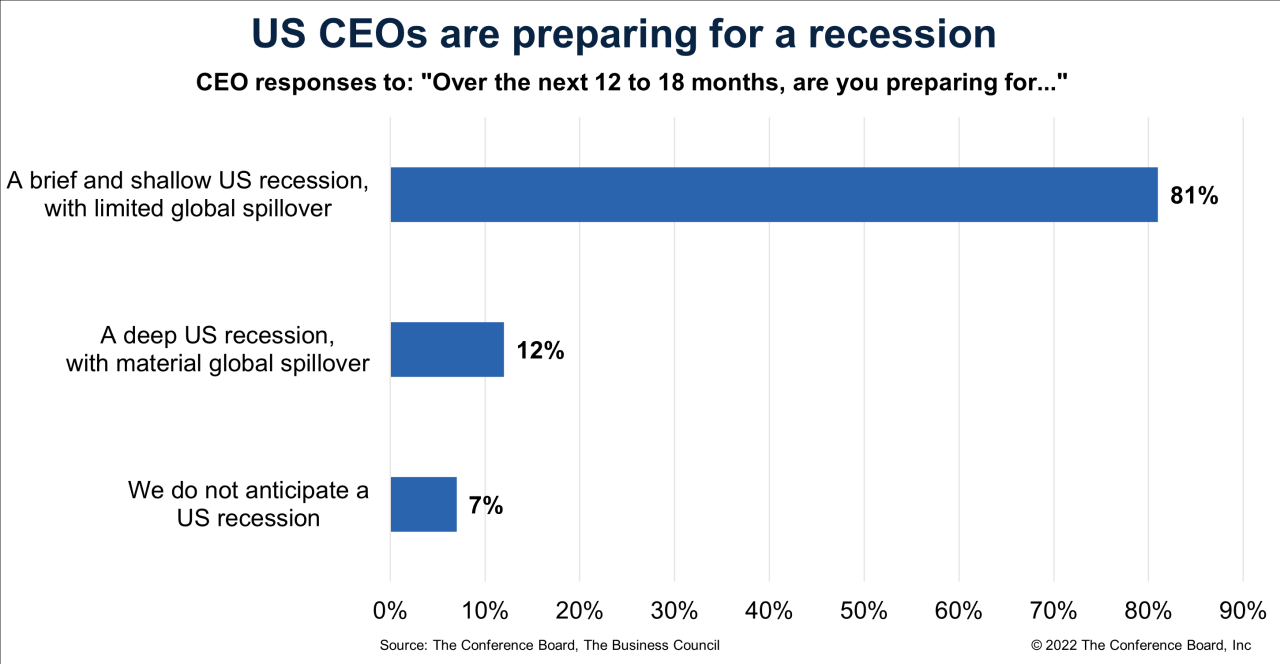
CEOs Brace for Recession Overwhelming Majority Prepare
Overwhelming majority of ceos say theyre preparing for recession – As “overwhelming majority of CEOs say they’re preparing for recession” takes center stage, it’s clear that the business world is bracing for a potential economic downturn. This sentiment isn’t just a fleeting fear; it’s a tangible shift in strategy and mindset. The implications are vast, reaching from boardrooms to everyday consumers. This article delves into the reasons behind this widespread preparation, the strategies CEOs are implementing, and the potential impact on various sectors.
The economic landscape is constantly evolving, and CEOs are acutely aware of the shifting tides. This heightened sense of recessionary preparedness isn’t a knee-jerk reaction; it’s a calculated response to a complex set of economic indicators. From rising inflation and interest rates to geopolitical uncertainties, a confluence of factors is driving this cautious approach.
Economic Indicators and Recessionary Signals
The possibility of a recession is a topic that often sparks anxieties and concerns. While economists and financial experts may have differing opinions on the timing and severity of an economic downturn, they all agree that monitoring key economic indicators is crucial in understanding the health of the economy.
Key Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into the state of the economy and can signal potential risks or opportunities. They can be broadly categorized into leading, lagging, and coincident indicators.
- Leading Indicators: These indicators tend to precede changes in economic activity, providing early warning signals of potential shifts. Some prominent leading indicators include:
- New Orders for Consumer Goods: A surge in orders suggests increased consumer confidence and potential future economic growth.
- Building Permits: A rise in building permits indicates future construction activity, which can boost economic growth.
- Stock Market Performance: A strong stock market often reflects investor confidence and a healthy economy.
- Interest Rate Spreads: The difference between short-term and long-term interest rates can indicate investor sentiment and potential economic changes.
- Consumer Confidence Index: This index measures consumer sentiment and spending intentions, which can impact economic activity.
- Lagging Indicators: These indicators tend to follow economic changes, confirming trends that have already occurred. Examples include:
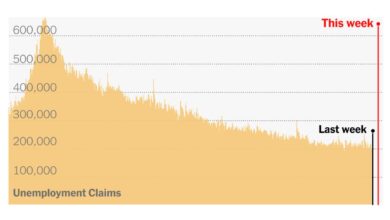
- Unemployment Rate: A rising unemployment rate signals a weakening economy.
- Inflation Rate: A persistently high inflation rate can erode purchasing power and stifle economic growth.
- Average Duration of Unemployment: A prolonged period of unemployment suggests a sluggish labor market.
- Coincident Indicators: These indicators tend to move in sync with economic activity, providing a snapshot of the current economic situation. Examples include:
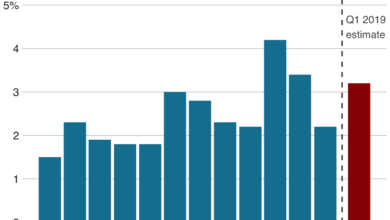
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced in an economy, providing a comprehensive gauge of economic activity.
- Personal Income: A rise in personal income indicates increased consumer spending and economic growth.
- Industrial Production: This indicator measures the output of factories and mines, reflecting manufacturing activity.
Consumer Behavior and Spending Patterns

Recessions can significantly impact consumer behavior and spending patterns, leading to a shift in priorities and a focus on essential goods and services. Understanding these shifts is crucial for businesses to adapt and navigate the economic downturn successfully.
Impact of Recessionary Conditions on Consumer Confidence and Discretionary Spending
Recessions often lead to a decline in consumer confidence, as individuals become more cautious about their financial situation. This decline in confidence can lead to a reduction in discretionary spending, as consumers prioritize essential needs over non-essential items. The impact of recessionary conditions on consumer confidence and discretionary spending can be observed through various economic indicators, such as the Consumer Confidence Index, which measures consumer sentiment and spending intentions.
A decline in this index can signal a decrease in consumer spending and an increase in saving, which can negatively impact businesses reliant on discretionary spending.
With the overwhelming majority of CEOs saying they’re preparing for a recession, it’s more important than ever to have open and honest conversations about the economic landscape. This is especially true in the online sphere, where platforms like Facebook and Twitter are often used to share information and opinions. A recent court ruling court rules against social media companies in free speech censorship fight could have a significant impact on how these platforms moderate content, potentially allowing for a more open and transparent exchange of ideas.
As we navigate the challenges of a potential recession, it’s crucial to ensure that we have access to a wide range of perspectives and information, allowing us to make informed decisions about our businesses and our lives.
Strategies Businesses Can Adopt to Mitigate the Impact of Declining Consumer Demand
Businesses can adopt various strategies to mitigate the impact of declining consumer demand during a recession. These strategies focus on adjusting their operations, pricing, and marketing efforts to cater to the changing consumer needs and preferences.
It’s unsettling to hear that the overwhelming majority of CEOs are bracing for a recession, but perhaps even more concerning is the news that the FBI is being sued for withholding records related to Facebook’s censorship of the Hunter Biden laptop story. This lawsuit raises serious questions about the extent of government involvement in shaping public discourse, and it’s a reminder that economic uncertainty can often be amplified by political turmoil.
- Price Optimization: Businesses can adjust their pricing strategies to remain competitive and attract price-sensitive consumers. This can involve offering discounts, promotions, or value bundles to incentivize purchases.
- Value-Oriented Product Development: Focusing on developing value-oriented products that cater to consumers’ essential needs can be a successful strategy. This could involve offering basic versions of existing products or developing new products that meet specific needs at a lower price point.
- Targeted Marketing: Businesses can refine their marketing strategies to target specific consumer segments that are less affected by the recession. This could involve focusing on value-conscious consumers or highlighting the value proposition of their products and services.
- Cost Optimization: Businesses can identify areas where they can reduce costs without compromising quality or customer service. This can involve streamlining operations, negotiating better deals with suppliers, or exploring alternative channels for distribution.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Building strong customer relationships and loyalty can be crucial during a recession. Businesses can implement customer loyalty programs that reward repeat purchases and encourage customer retention.
Examples of Successful Strategies Used by Businesses to Navigate Consumer Downturns
Numerous businesses have successfully navigated consumer downturns by implementing effective strategies. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, discount retailers like Walmart and Dollar General thrived by offering low prices on essential goods, attracting value-conscious consumers. Additionally, companies like Netflix and Amazon capitalized on the increased demand for entertainment and online shopping, expanding their services and customer base.
With the overwhelming majority of CEOs saying they’re preparing for a recession, it’s clear that uncertainty is high. This sense of unease extends beyond the corporate world, as evidenced by the recent FBI whistleblower coming forward to allege that many agents disagree with the bureau’s direction. This internal discord, coupled with economic anxieties, paints a picture of a nation grappling with significant challenges on multiple fronts.
It remains to be seen how these pressures will ultimately impact the economy and the future of the country.
Government Policies and Recessionary Response: Overwhelming Majority Of Ceos Say Theyre Preparing For Recession
Governments play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of recessions by employing a range of fiscal and monetary policies. These interventions aim to stabilize the economy, stimulate growth, and protect vulnerable populations. However, the effectiveness of these policies and the potential risks associated with government intervention are subject to ongoing debate.
Effectiveness of Fiscal and Monetary Policies
Fiscal policies, such as tax cuts and increased government spending, aim to stimulate demand and boost economic activity. Monetary policies, such as lowering interest rates and expanding the money supply, aim to encourage borrowing and investment. The effectiveness of these policies depends on various factors, including the severity of the recession, the structure of the economy, and the timing and implementation of the policies.
For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, the US government implemented a significant fiscal stimulus package, including tax cuts and increased spending on infrastructure and social programs. This intervention helped to stabilize the economy and prevent a deeper recession. However, the effectiveness of such policies is often debated, with some arguing that they can lead to increased government debt and inflation.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Government intervention during recessions can also pose risks and challenges. One concern is the potential for moral hazard, where businesses and individuals may take on more risk knowing that the government will intervene to bail them out. Another concern is the potential for government policies to distort market signals and discourage private investment. Additionally, the effectiveness of government policies can be hampered by political considerations, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and the time lag between policy implementation and its impact on the economy.
Government Response to Previous Recessions
Governments have responded to past recessions with a mix of fiscal and monetary policies. For example, during the 1981-82 recession, the US government implemented a combination of tax cuts and tight monetary policy. In contrast, during the 2008 financial crisis, the government adopted a more expansive fiscal policy and a highly accommodative monetary policy. The choice of policy tools and their effectiveness depend on the specific economic circumstances of each recession.
Comparison with the Current Economic Environment, Overwhelming majority of ceos say theyre preparing for recession
The current economic environment presents unique challenges for policymakers. The COVID-19 pandemic has led to significant disruptions in supply chains, labor markets, and consumer behavior. Inflation has surged to multi-decade highs, fueled by supply chain bottlenecks, strong consumer demand, and government stimulus measures. In this context, policymakers face a delicate balancing act between stimulating economic growth and controlling inflation.
The Federal Reserve, for example, is currently raising interest rates to combat inflation, but this could slow economic growth. The government is also considering measures to address supply chain disruptions and reduce energy prices.
The Impact of Recession on the Labor Market

Recessions are periods of significant economic decline, and their impact on the labor market is often profound. As businesses struggle to maintain profitability, they may reduce their workforce, leading to job losses and increased unemployment. This section will delve into the effects of a recession on unemployment rates and labor market dynamics, explore the challenges faced by workers and employers during an economic downturn, and examine strategies for businesses to effectively manage their workforce during such periods.
Unemployment Rates and Labor Market Dynamics
Recessions typically result in a surge in unemployment rates. When economic activity slows down, businesses reduce production, leading to layoffs. This rise in unemployment can have a significant impact on individuals and families, as they lose their income and face financial difficulties. The labor market dynamics also change during a recession. Job openings decrease, and competition for available positions intensifies.
This can make it challenging for individuals to find new employment opportunities, especially for those in industries heavily affected by the economic downturn.
Challenges Faced by Workers and Employers
Workers face numerous challenges during a recession. They may experience job loss, wage reductions, or reduced hours. This can lead to financial stress, difficulty making ends meet, and a decline in their overall well-being. Employers also face significant challenges. They must navigate reduced demand, lower profits, and the need to make difficult decisions regarding their workforce.
These decisions often involve layoffs, salary cuts, or other cost-saving measures, which can impact employee morale and productivity.
Strategies for Managing Workforce During a Recession
Businesses can implement various strategies to manage their workforce effectively during a recession. Some of these strategies include:
- Reducing Hiring: This can help businesses conserve resources and avoid unnecessary expenditures.
- Implementing Salary Cuts: While a difficult decision, this can help businesses maintain profitability and avoid layoffs.
- Reducing Working Hours: This can help businesses reduce labor costs while still retaining their workforce.
- Offering Early Retirement Packages: This can help businesses reduce their workforce while offering attractive incentives to long-term employees.
- Implementing Training and Development Programs: This can help employees acquire new skills and enhance their competitiveness in the job market, making them more valuable to the business.
Initiatives to Support Workers and Mitigate Job Losses
Governments and organizations often implement initiatives to support workers and mitigate job losses during economic downturns. These initiatives can include:
- Unemployment Benefits: Providing financial assistance to unemployed individuals can help them maintain a basic standard of living and support their families.
- Job Training Programs: These programs can help individuals acquire new skills and enhance their employability, increasing their chances of finding new employment.
- Wage Subsidies: These subsidies can help businesses offset the cost of hiring new employees, encouraging them to create jobs during a recession.
- Job Creation Programs: These programs can create new employment opportunities in sectors less affected by the economic downturn.
The overwhelming majority of CEOs preparing for a recession is a significant signal. It underscores the importance of staying informed about economic trends and being prepared for potential challenges. While the future remains uncertain, proactive measures and strategic planning can help businesses navigate potential economic downturns. By understanding the underlying causes, potential impact, and available strategies, we can better prepare for the future, whatever it may hold.