
Interest Rates Will Go Higher What You Need to Know
Interest rates will go higher, and this is a topic that has everyone talking. Whether you’re a homeowner, a borrower, an investor, or simply someone who wants to understand the economy, it’s important to know what this means for you. The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, is raising interest rates to combat inflation. This has a ripple effect throughout the economy, impacting everything from the cost of borrowing to the value of your investments.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the implications of higher interest rates across various aspects of our lives. We’ll discuss how rising rates affect consumers, businesses, and the economy as a whole. We’ll also look at investment strategies for navigating this new landscape and delve into the historical context of interest rate hikes.
Impact on Consumers
Higher interest rates have a significant impact on consumers, affecting their spending habits, borrowing costs, and overall financial well-being. As interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing money increases, making it more expensive for consumers to finance purchases, such as homes, cars, and other big-ticket items. This can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, potentially slowing down economic growth.
With interest rates on the rise, it’s tough to see where the economy is headed. It’s hard to focus on the future when you’re dealing with the present, like the news that the New York Attorney General has filed a civil lawsuit against former President Trump, which has him responding with his usual fiery rhetoric. I guess that’s one thing that’s staying consistent – regardless of interest rates, the drama seems to keep going.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Rising interest rates directly impact consumer spending by making it more expensive to borrow money. When interest rates go up, the cost of financing purchases like cars, homes, and appliances increases. This discourages consumers from taking on new debt, leading to a reduction in spending. For example, if a consumer is considering purchasing a new car, they may decide to postpone the purchase if the interest rate on a car loan is significantly higher.
This can lead to a decline in demand for goods and services, potentially affecting businesses and the overall economy.
Impact on Affordability for Mortgages and Loans
Higher interest rates make it more expensive to obtain mortgages and other loans. This is particularly impactful for first-time homebuyers who are already facing affordability challenges. The higher interest rates increase monthly mortgage payments, making it harder for potential homebuyers to qualify for a loan or afford the desired property. This can lead to a decrease in home sales and a slowdown in the housing market.
Similarly, rising interest rates increase the cost of personal loans, credit card debt, and student loans, putting a strain on consumers’ budgets.
Impact on Different Consumer Segments
Higher interest rates can affect different consumer segments in varying ways. For example, young adults who are just starting their careers and may be looking to purchase their first home or car are particularly vulnerable to rising interest rates. The increased borrowing costs can make it challenging for them to achieve their financial goals. Retirees, on the other hand, may see their savings grow at a faster rate as interest rates rise, but they may also face higher costs for borrowing if they need to access credit for unexpected expenses.
Economic Implications: Interest Rates Will Go Higher
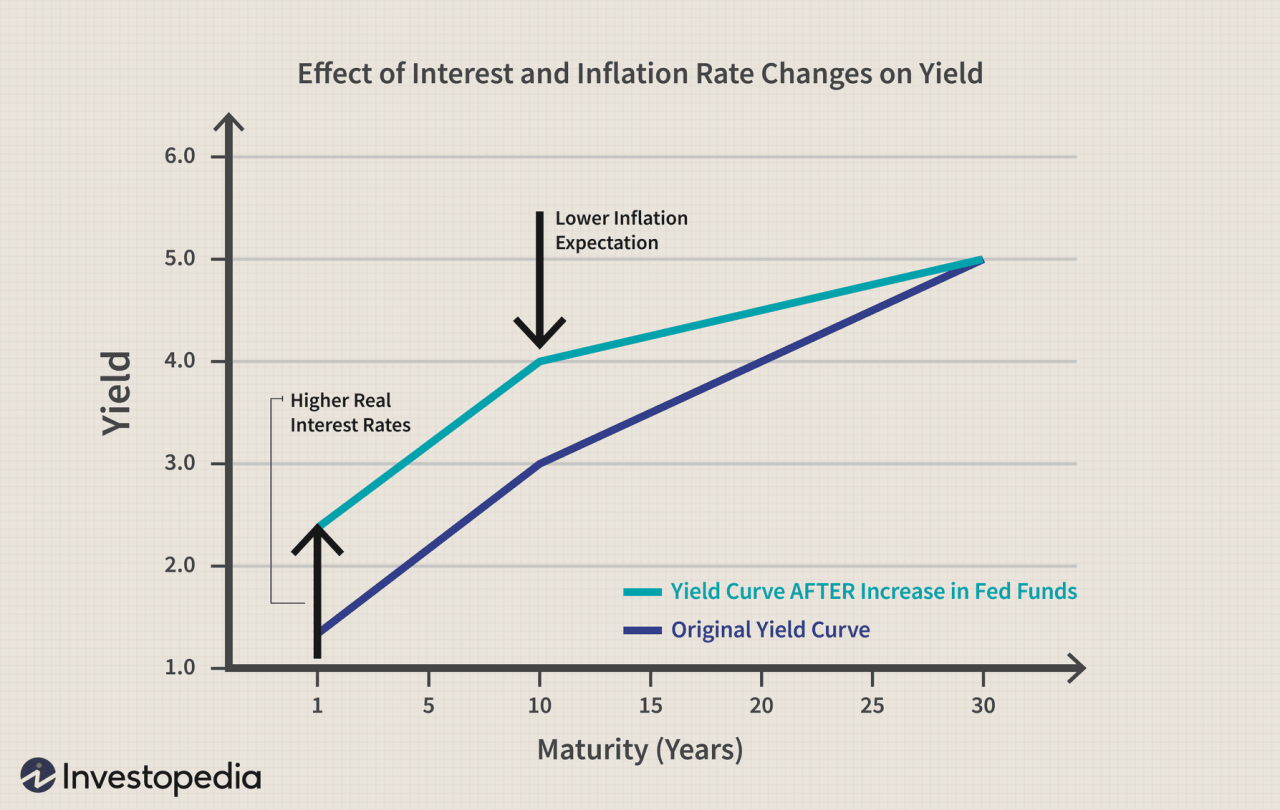
Higher interest rates are a powerful tool used by central banks to manage economic conditions. While they can help curb inflation, they also have significant implications for economic growth and the value of a currency. Understanding these implications is crucial for businesses and individuals alike, as they can impact investment decisions, spending habits, and overall economic well-being.
With interest rates on the rise, it’s hard to ignore the growing economic uncertainty. It’s a reminder that even as we grapple with the complexities of a changing world, there are other forces at play, like the alarming revelations of over 50 Biden administration employees from 12 US agencies involved in social media censorship. This level of government intervention in free speech is concerning, and its implications for the future of our democracy are worth considering, especially as we navigate the challenges of rising interest rates.
Impact of Higher Interest Rates on Inflation
Higher interest rates act as a brake on inflation by reducing borrowing and spending. When interest rates rise, it becomes more expensive for businesses and individuals to borrow money. This can lead to:
- Reduced investment: Businesses may postpone or cancel investment projects, leading to slower economic growth and job creation.
- Lower consumer spending: Individuals may delay major purchases, such as cars or homes, due to higher borrowing costs.
- Reduced demand: A decrease in investment and consumer spending can lead to lower overall demand for goods and services, which can put downward pressure on prices.
For example, the US Federal Reserve raised interest rates aggressively in 2022 and 2023 to combat high inflation. This move resulted in slower economic growth, but it also helped to bring inflation down from its peak.
Impact of Higher Interest Rates on Economic Growth
Higher interest rates can have a mixed impact on economic growth. While they can help control inflation, they can also stifle economic activity.
With interest rates on the rise, it’s more important than ever to be mindful of your spending. And speaking of spending, the news that credit card giants are categorizing gun-related sales separately has sparked controversy. This move, while intended to promote transparency, has raised concerns about potential discrimination and erosion of rights. But regardless of the ongoing debate, the reality is that higher interest rates will make managing debt even more challenging, so it’s essential to be proactive and find ways to reduce your reliance on credit.
- Reduced investment: As mentioned earlier, higher interest rates can discourage businesses from investing, leading to slower economic growth.
- Increased borrowing costs: Businesses may face higher costs for borrowing money to finance operations, which can reduce profitability and hinder expansion.
- Slower job creation: With reduced investment and business activity, job creation can slow down, leading to higher unemployment rates.
However, higher interest rates can also encourage saving, which can provide businesses with more capital for investment. The overall impact of higher interest rates on economic growth depends on various factors, including the starting level of interest rates, the rate of inflation, and the health of the economy.
Relationship Between Interest Rates and Currency Value
Interest rates play a significant role in determining the value of a currency. When interest rates rise, a country’s currency tends to appreciate in value. This is because higher interest rates make it more attractive for foreign investors to invest in that country’s assets, leading to an increase in demand for the currency.
- Increased demand for currency: Foreign investors are attracted to higher interest rates, as they can earn a better return on their investments. This leads to increased demand for the currency, which drives up its value.
- Stronger currency: A stronger currency can make imports cheaper, which can benefit consumers. However, it can also make exports more expensive, which can hurt businesses that sell their products abroad.
For instance, the US dollar has strengthened significantly against other currencies in recent years due to the Federal Reserve’s aggressive interest rate hikes. This has made it more expensive for US businesses to export goods, but it has also made it cheaper for US consumers to buy imported goods.
Investment Strategies
Rising interest rates can significantly impact investment portfolios, creating both challenges and opportunities. Understanding how different asset classes perform in such an environment and adopting appropriate strategies is crucial for investors seeking to navigate this dynamic landscape.
Asset Class Performance in a Rising Rate Environment
The performance of various investment classes can vary significantly in a rising interest rate environment. Here’s a comparison of how some common asset classes might fare:
| Asset Class | Performance in Rising Rates | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Bonds | Generally negative | As interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds with lower coupon rates declines, as investors demand higher yields for new bonds. |
| Equities (Stocks) | Potentially mixed | Higher interest rates can impact corporate profitability and valuation, leading to stock market volatility. However, some sectors, such as value stocks, may benefit from rising rates. |
| Real Estate | Potentially negative | Rising interest rates increase borrowing costs, making it more expensive to finance real estate investments, potentially dampening demand and prices. |
| Commodities | Potentially mixed | Commodities, such as gold, can act as a hedge against inflation, which often accompanies rising interest rates. However, the performance of other commodities, such as oil, can be influenced by various factors. |
Strategies to Mitigate Risks of Higher Interest Rates, Interest rates will go higher
Investors can employ several strategies to mitigate the risks associated with rising interest rates:
- Shorten Duration in Fixed Income Portfolios: Reducing the average maturity of bonds in a portfolio can lessen the impact of rising interest rates on bond prices. Shorter-duration bonds are less sensitive to interest rate changes.
- Diversify Investments: Spreading investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities, can help reduce overall portfolio volatility.
- Consider Value Stocks: Value stocks, which are companies trading at a discount to their intrinsic value, may benefit from rising interest rates as their earnings are less sensitive to economic cycles.
- Increase Cash Holdings: Holding a larger portion of cash in a portfolio provides flexibility to invest in opportunities that emerge in a rising rate environment.
Adjusting Investment Portfolios
Adjusting investment portfolios in response to rising interest rates involves a careful analysis of existing holdings and potential adjustments:
- Review Bond Portfolio: Assess the duration of bond holdings and consider shortening the average maturity to reduce interest rate sensitivity.
- Rebalance Equity Exposure: Evaluate the proportion of stocks in the portfolio and consider shifting towards value stocks or sectors that may benefit from rising rates.
- Consider Inflation Hedges: Include assets, such as gold or real estate, that can potentially provide protection against inflation, which often accompanies rising interest rates.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a financial advisor to discuss specific strategies tailored to individual circumstances and risk tolerance.
Business Perspectives
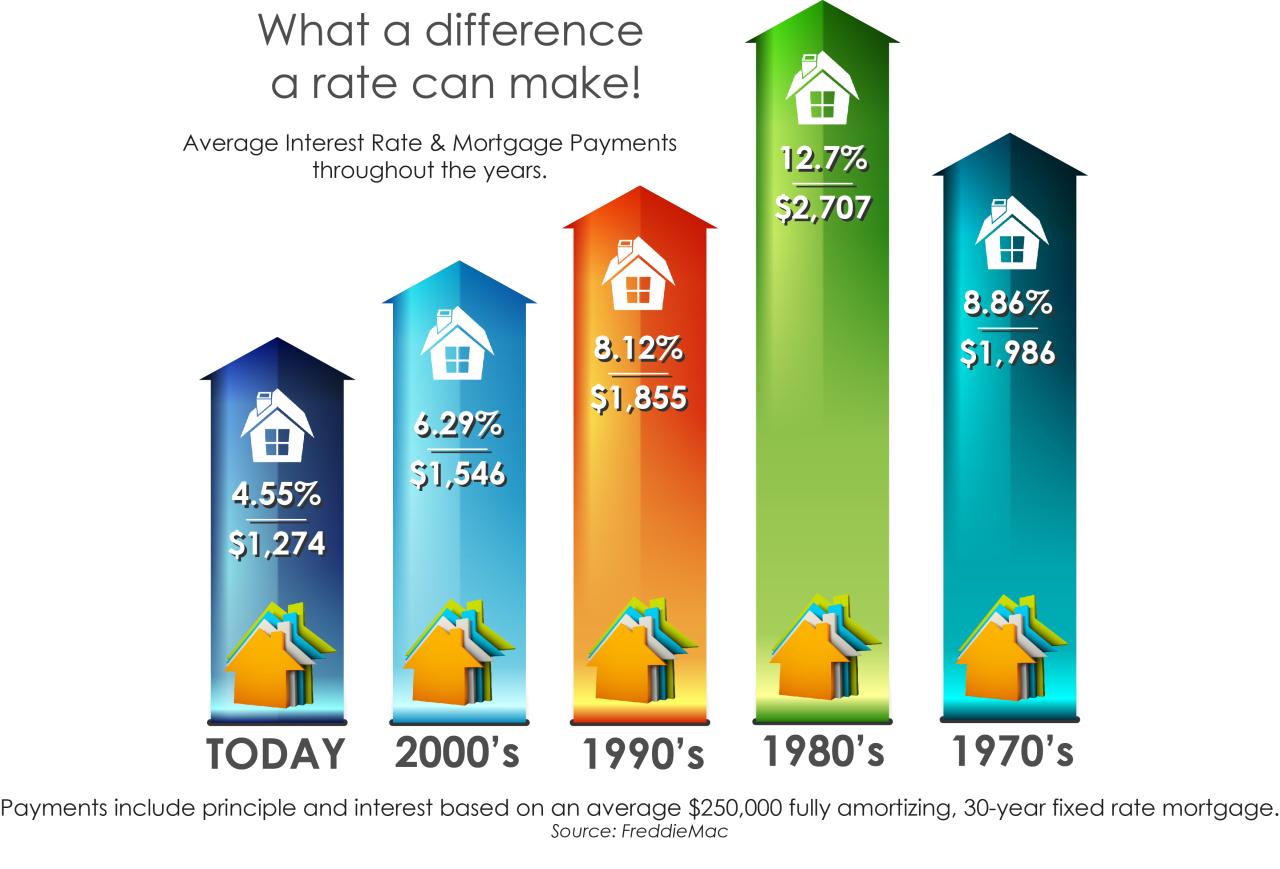
Higher interest rates pose a significant challenge to businesses, particularly those heavily reliant on debt financing. Rising borrowing costs can directly impact their financial health and ability to invest and expand.
Impact on Corporate Borrowing Costs
The cost of borrowing money for businesses increases when interest rates rise. This can lead to:
- Higher debt servicing costs: Businesses with existing loans will experience increased interest payments, reducing their profitability and cash flow.
- Reduced access to credit: Lenders may become more cautious in extending credit, particularly to businesses with high debt levels or weak financial performance. This can limit their ability to secure loans for expansion or working capital.
- Increased cost of capital: The cost of capital, which reflects the cost of funding operations, rises with higher interest rates. This can make it more expensive for businesses to invest in new projects or expand their operations.
For example, a company with a $10 million loan at a fixed interest rate of 5% would face an annual interest expense of $500,000. If interest rates rise to 7%, their annual interest expense would increase to $700,000, a significant financial burden.
Impact on Business Investment and Expansion
Rising interest rates can discourage business investment and expansion in several ways:
- Reduced profitability of projects: Higher borrowing costs make projects less profitable, as the return on investment needs to exceed the cost of financing.
- Increased uncertainty: Economic uncertainty associated with rising interest rates can lead to businesses delaying investment decisions, waiting for a clearer economic outlook.
- Shift in focus to cost-cutting: Businesses may prioritize cost-cutting measures over expansion, as they seek to preserve cash flow and manage rising expenses.
A company considering a new factory expansion may decide to postpone the project if the cost of borrowing money becomes too high, making the investment less attractive.
Historical Context

Understanding the current interest rate environment requires looking back at historical periods of rising rates. Examining past rate hikes helps us grasp their potential impact on the economy and markets. By analyzing these historical patterns, we can better anticipate how the current situation might unfold.
Interest Rate Hikes Throughout History
Past interest rate hikes have often been driven by factors like inflation, economic growth, and government policy. The Federal Reserve, responsible for setting interest rates in the US, typically raises rates to control inflation and prevent the economy from overheating.
- The Volcker Era (1979-1987): During this period, Federal Reserve Chairman Paul Volcker aggressively raised interest rates to combat rampant inflation, reaching a peak of 20% in 1980. This move successfully curbed inflation, but also led to a severe recession in 1981-1982.
- The Dot-Com Bubble (1999-2000): The Federal Reserve raised interest rates eleven times between 1999 and 2000 to cool down the booming tech sector and prevent excessive inflation. This contributed to the bursting of the dot-com bubble, leading to a sharp decline in the stock market.
- The Great Recession (2007-2009): The Federal Reserve lowered interest rates to near zero in the wake of the financial crisis. As the economy recovered, rates began to rise again. However, the rate increases were gradual and the economic recovery was relatively slow.
Factors Influencing Interest Rate Decisions
The Federal Reserve considers a range of factors when deciding whether to raise interest rates. These include:
- Inflation: The Fed aims to maintain inflation at a target rate of 2%. If inflation rises above this level, the Fed may raise rates to cool down the economy and prevent inflation from spiraling out of control.
- Economic Growth: The Fed monitors economic growth to ensure it remains at a sustainable pace. If the economy is growing too quickly, the Fed may raise rates to prevent overheating.
- Unemployment: The Fed considers the unemployment rate when making interest rate decisions. If unemployment is low, the Fed may raise rates to prevent the labor market from becoming too tight.
- Global Economic Conditions: The Fed also takes into account global economic conditions, such as exchange rates and international trade.
As interest rates climb, it’s crucial to stay informed and adapt your financial strategies accordingly. Understanding the potential impacts of rising rates allows you to make informed decisions and potentially navigate this period with greater confidence. Whether you’re adjusting your spending habits, re-evaluating your investment portfolio, or simply staying up-to-date on economic trends, having a clear grasp of this topic is essential.
Remember, knowledge is power, and in the world of finance, staying informed is key.






