Russia Doubles Interest Rate to Boost Crashing Ruble as Sanctions Bite
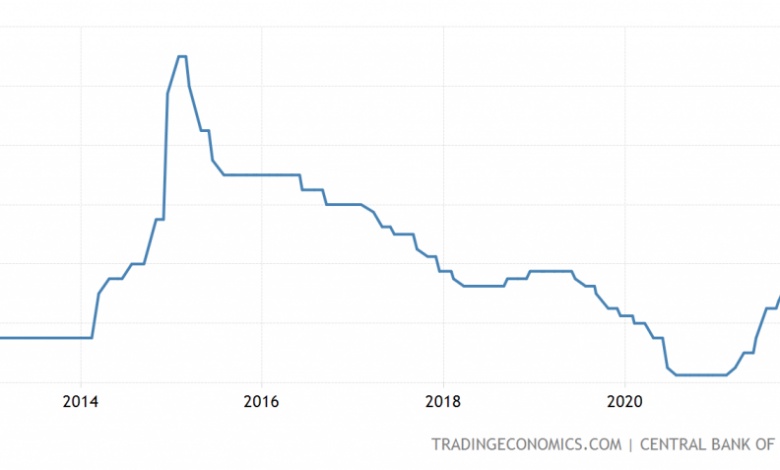
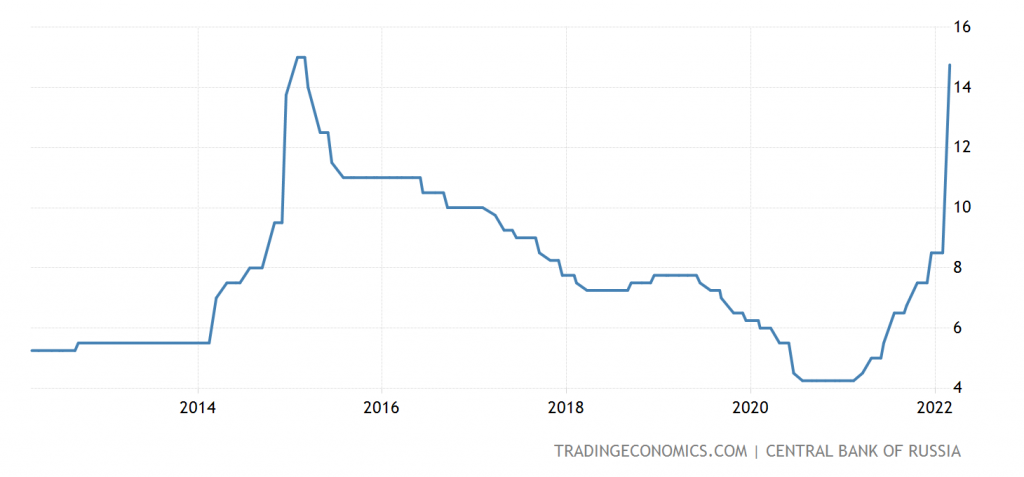
Russia Doubles Interest Rate to Boost Crashing Ruble as Sanctions Bite. The world watched in shock as the ruble plummeted to record lows, a direct consequence of sweeping international sanctions imposed on Russia following its invasion of Ukraine. In a desperate attempt to stem the bleeding, the Bank of Russia made a drastic move: doubling the key interest rate to a staggering 20%.
This unprecedented action sent shockwaves through the global financial system, raising questions about the effectiveness of such a drastic measure and the potential consequences for the Russian economy and beyond.
This bold move was intended to bolster the ruble, attract foreign investment, and control runaway inflation. The question remains, however, whether this drastic measure will be enough to stabilize the Russian economy in the face of mounting sanctions and a global backlash against the invasion of Ukraine.
The impact of this interest rate hike on inflation and economic growth remains to be seen, and the long-term effects on the ruble’s value are still uncertain. The world watches with bated breath as the economic fallout from the conflict continues to unfold.
The Interest Rate Hike
In a dramatic move aimed at stemming the rapid decline of the ruble, the Bank of Russia doubled its key interest rate to 20% on February 28, 2022. This unprecedented move, the largest single-day increase in the country’s history, reflects the urgency of the situation as Russia faces unprecedented economic pressure from international sanctions imposed following its invasion of Ukraine.
Rationale Behind the Interest Rate Hike
The Bank of Russia’s decision to drastically raise interest rates was driven by a need to stabilize the ruble, which had plummeted to record lows against the US dollar and euro in the days following the imposition of sanctions. The rationale behind this move can be summarized as follows:
- Curbing Inflation:A higher interest rate makes borrowing more expensive, discouraging spending and investment. This, in turn, helps to curb inflation, which has been rising rapidly due to the sanctions and the war in Ukraine.
- Attracting Foreign Investment:A higher interest rate makes Russian assets more attractive to foreign investors, potentially boosting demand for the ruble and helping to stabilize its value.
- Supporting the Ruble:By making it more expensive to borrow, the central bank aims to reduce the demand for foreign currency, potentially slowing down the ruble’s decline.
Impact of the Interest Rate Hike, Russia doubles interest rate to boost crashing ruble as sanctions bite
The dramatic increase in interest rates is likely to have significant implications for the Russian economy.
- Inflation:While the interest rate hike aims to curb inflation, it could also have a paradoxical effect. By making borrowing more expensive, it could lead to higher prices for goods and services, potentially exacerbating inflationary pressures.
- Economic Growth:The higher interest rates are expected to stifle economic growth, as businesses are less likely to invest and consumers are more likely to cut back on spending. This could lead to a recession, further compounding the economic challenges facing Russia.
Comparison with Previous Monetary Policy Decisions
The 20% interest rate hike represents a stark departure from the Bank of Russia’s previous monetary policy decisions. In the years leading up to the invasion of Ukraine, the central bank had been gradually lowering interest rates in an effort to stimulate economic growth.
This recent move underscores the severity of the current economic crisis and the drastic measures the central bank is willing to take to address it.
The Ruble’s Performance
The recent decline of the ruble is a direct result of the economic sanctions imposed by Western countries in response to the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. These sanctions have targeted Russia’s financial system, energy exports, and key industries, leading to a decrease in foreign investment, a reduction in trade, and a decline in the value of the ruble.
The ruble’s performance is closely tied to the overall health of the Russian economy, and the current situation has created a challenging environment for the currency.
The Impact of the Interest Rate Hike on the Ruble
The Central Bank of Russia’s decision to raise interest rates is a significant move aimed at stabilizing the ruble and mitigating the impact of sanctions. The increased interest rates make it more attractive for investors to hold rubles, potentially increasing demand for the currency and boosting its value.
The short-term effects of the interest rate hike are likely to be positive, as the higher interest rates could help to attract foreign investment and curb inflation. This could lead to a temporary appreciation of the ruble. However, the long-term effects of the interest rate hike are less clear.
It’s a tough time to be a Russian ruble, plummeting as the West tightens the screws with sanctions. The desperate move to double interest rates is a clear sign of the pressure, and it’s hard not to see echoes of the economic chaos that can come from such drastic measures.
All this while the political scene in the US is seeing a shift, with the democrats only now discovering that their culture wars are unpopular. Perhaps the focus on global issues like the Russian economic crisis will force a refocus on domestic matters.
Only time will tell, but it’s clear that the world is changing, and with it, the priorities of its citizens.
The sanctions imposed on Russia have created a complex economic environment, and the effectiveness of the interest rate hike in stabilizing the ruble will depend on a range of factors, including the duration and severity of the sanctions, the global economic outlook, and the response of the Russian government.
Historical Examples of Currency Interventions
Throughout history, central banks have intervened in currency markets to stabilize their currencies. These interventions can take various forms, including buying or selling foreign currencies, adjusting interest rates, and implementing capital controls. The effectiveness of these interventions depends on a range of factors, including the size of the intervention, the underlying economic conditions, and the credibility of the central bank.For example, in 1998, the Russian government intervened in the currency market to support the ruble following the Asian financial crisis.
The intervention involved selling foreign currency reserves and raising interest rates. However, the intervention was ultimately unsuccessful, and the ruble depreciated sharply. This example highlights the challenges of currency interventions, particularly in times of economic stress.Another example is the intervention by the Bank of Japan in the 1990s to weaken the yen.
This intervention involved buying foreign currencies and lowering interest rates. The intervention was successful in weakening the yen, but it also led to concerns about the long-term impact on the Japanese economy.These examples illustrate the complex and often unpredictable nature of currency interventions.
While they can be effective in stabilizing a currency in the short term, they can also have unintended consequences in the long term. The effectiveness of currency interventions ultimately depends on a range of factors, including the underlying economic conditions, the credibility of the central bank, and the overall global economic environment.
The Russian central bank’s desperate move to double interest rates in an attempt to prop up the plummeting ruble highlights the severe economic pressure the country is facing due to international sanctions. It’s a stark reminder of how global events can have far-reaching consequences, and it also raises questions about the influence of corporate funding on institutions like medical associations, as seen in this recent article corporate funding raises ethical concerns about medical associations.
The impact of these sanctions on the Russian economy will likely be felt for years to come, and it’s a situation that demands careful monitoring and analysis.
Global Economic Implications
The Russian economic crisis, triggered by the war in Ukraine and subsequent international sanctions, has far-reaching implications for the global economy. The depreciation of the ruble, coupled with disruptions in energy supplies and trade, has created a complex and uncertain landscape for businesses and investors worldwide.
It’s fascinating to see how the world is reacting to the crisis in Russia. While the country is desperately trying to prop up its currency with a massive interest rate hike, the US is taking a different approach by investing in the future with a $2 billion loan to an electric vehicle battery component maker.
It’s a reminder that even amidst global turmoil, there are opportunities for growth and innovation.
Impact on Global Markets
The Russian economic crisis has already sent shockwaves through global markets. The war and sanctions have led to increased volatility in energy prices, with oil and gas prices surging to multi-year highs. This has contributed to inflation globally, as businesses pass on higher input costs to consumers.
Additionally, the crisis has disrupted supply chains, leading to shortages of key commodities, such as wheat and fertilizers. The uncertainty surrounding the situation has also dampened investor sentiment, leading to stock market declines in many countries.
Implications for International Trade and Investment
The depreciation of the ruble has made Russian exports more competitive, potentially benefiting some sectors. However, the sanctions have significantly hindered Russian imports, leading to shortages of essential goods and services. This has also made it more difficult for foreign businesses to operate in Russia.
Furthermore, the crisis has reduced investor confidence in Russia, leading to a decline in foreign direct investment.
Economic Risks and Opportunities
The Russian economic crisis presents both risks and opportunities for countries and businesses globally.
Risks
- Increased Inflation:The rise in energy prices and supply chain disruptions have contributed to inflation globally, putting pressure on central banks to raise interest rates.
- Economic Slowdown:The crisis could lead to a global economic slowdown as businesses face higher costs and reduced demand.
- Financial Instability:The crisis could lead to financial instability, particularly in countries with close economic ties to Russia.
- Geopolitical Tensions:The crisis has heightened geopolitical tensions, leading to increased military spending and potential conflicts.
Opportunities
- Diversification of Supply Chains:The crisis has highlighted the importance of diversifying supply chains to reduce reliance on single countries or regions.
- Growth in Alternative Energy Sources:The crisis has accelerated the transition to renewable energy sources as countries seek to reduce their dependence on Russian fossil fuels.
- Increased Trade with Other Countries:The crisis has created opportunities for businesses to expand their trade with other countries, particularly in Asia and Africa.
Russia’s Response
Facing a severe economic crisis triggered by Western sanctions and the depreciation of the ruble, the Russian government has implemented a series of measures to stabilize the situation. These actions aim to mitigate the impact of sanctions, control inflation, and bolster the ruble’s value.
Measures Implemented by the Russian Government
The Russian government has taken several steps to address the economic crisis. These include:
- Interest Rate Hikes:The Central Bank of Russia (CBR) has significantly raised interest rates to curb inflation and attract foreign investment. The CBR’s aggressive interest rate hikes have proven effective in slowing down inflation and attracting capital back into the ruble, helping to stabilize the currency.
- Capital Controls:The Russian government has imposed restrictions on capital outflows to prevent a mass exodus of funds and further weaken the ruble. These measures have helped to control the outflow of capital and prevent a further decline in the ruble’s value.
- Currency Interventions:The CBR has intervened in the foreign exchange market to buy rubles and sell foreign currencies, supporting the ruble’s value. These interventions have helped to stabilize the ruble’s exchange rate and reduce volatility.
- Fiscal Stimulus:The Russian government has announced a series of fiscal measures to support businesses and individuals, including tax breaks and subsidies. These measures aim to stimulate economic activity and mitigate the impact of sanctions.
- Import Substitution:The Russian government has encouraged domestic production and import substitution to reduce reliance on foreign goods and services. This strategy aims to strengthen the Russian economy and reduce its vulnerability to sanctions.
Effectiveness of Measures
The effectiveness of the Russian government’s measures in mitigating the impact of sanctions and currency depreciation is a subject of debate. Some argue that the measures have been successful in stabilizing the ruble and preventing a deeper economic crisis. Others point to the significant economic contraction and the ongoing challenges faced by the Russian economy.
- Stabilization of the Ruble:The ruble has recovered significantly from its initial plunge after the imposition of sanctions. This recovery can be attributed to the CBR’s aggressive interest rate hikes, capital controls, and currency interventions.
- Inflation Control:Inflation in Russia has remained relatively low, despite the economic challenges. This can be attributed to the CBR’s tight monetary policy and the government’s efforts to control prices.
- Economic Contraction:Despite the measures taken by the government, the Russian economy has contracted significantly. This contraction is primarily due to the impact of sanctions, which have disrupted trade and investment.
- Long-Term Sustainability:The long-term sustainability of the Russian economy remains uncertain. The impact of sanctions and the ongoing conflict in Ukraine continue to pose significant challenges.
Comparison with Past Responses
The Russian government’s response to the current economic crisis shares similarities with its responses to previous economic challenges. In the past, the government has relied on similar measures, such as interest rate hikes, capital controls, and currency interventions, to stabilize the economy.
However, the current crisis is unprecedented in its scale and complexity.
- 1998 Financial Crisis:During the 1998 financial crisis, the Russian government also implemented capital controls and currency interventions to stabilize the ruble. However, the current crisis is more severe, as it involves widespread sanctions and a prolonged conflict.
- 2008 Global Financial Crisis:During the 2008 global financial crisis, the Russian government used fiscal stimulus and currency interventions to mitigate the impact of the crisis. However, the current crisis is more challenging due to the severity of sanctions and the ongoing conflict.
Ending Remarks: Russia Doubles Interest Rate To Boost Crashing Ruble As Sanctions Bite
The Russian economic crisis is a complex and evolving situation, and the impact of the interest rate hike on the ruble and the overall economy is still unfolding. While the immediate goal of the interest rate hike was to stabilize the ruble and control inflation, the long-term consequences remain uncertain.
The global economic implications of this crisis are far-reaching, and the world is watching closely to see how Russia navigates this turbulent period. The future of the Russian economy, and its relationship with the global financial system, hangs in the balance.