Elon Musks Neuralink Gets FDA Approval for Brain Implants
Elon musks neuralink gets fda approval to study brain implants in humans – Elon Musk’s Neuralink has received FDA approval to begin human trials of its brain-computer interface technology. This groundbreaking development marks a significant step forward in the field of neurotechnology, potentially revolutionizing how we interact with the world and even our own minds.
Neuralink’s device, a tiny chip implanted in the brain, aims to restore lost functions, enhance human abilities, and even treat neurological disorders. The implications of this technology are vast, raising both excitement and ethical concerns about the future of humanity.
Neuralink’s journey began with a mission to create a seamless connection between the human brain and computers, paving the way for a future where thoughts and actions are directly controlled through technology. The device, designed to be implanted in the brain through a minimally invasive procedure, is equipped with thousands of electrodes that can record and stimulate brain activity.
This intricate system has the potential to treat a wide range of conditions, from paralysis to blindness, and even enhance cognitive functions. The FDA’s approval of Neuralink’s clinical trial is a testament to the potential of this technology, but it also raises important questions about safety, ethics, and the potential consequences of merging human biology with artificial intelligence.
Neuralink’s History and Mission
Neuralink is a neurotechnology company founded by Elon Musk in 2016, aiming to develop brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) for medical and consumer applications. The company’s ambition is to create a future where humans can seamlessly interact with technology through their thoughts.
Neuralink’s Origins and Evolution
Neuralink’s origins can be traced back to Musk’s interest in artificial intelligence (AI). He has repeatedly expressed concerns about the potential risks of unchecked AI development and believes that BCIs could help humans keep pace with advancing technology. Neuralink’s early focus was on developing a high-bandwidth BCI capable of transmitting data between the brain and a computer.
The company initially explored various approaches, including using lasers to create tiny holes in the skull and inserting electrodes into the brain.
Neuralink’s Mission and Goals
Neuralink’s stated mission is to “create a future where humans can seamlessly interact with technology through their thoughts.” This ambitious goal encompasses a range of applications, including:
- Restoring lost functions:Neuralink aims to help individuals with paralysis, blindness, and other neurological conditions regain lost abilities by providing them with a direct connection to their brains.
- Treating neurological diseases:Neuralink believes that its technology could be used to treat conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy.
- Enhancing human capabilities:In the long term, Neuralink envisions a future where BCIs can enhance human cognitive abilities, allowing individuals to learn faster, remember more, and even access information directly from the internet.
Key Milestones in Neuralink’s Development
Neuralink has achieved several significant milestones in its development:
- 2016:Neuralink was founded by Elon Musk.
- 2017:Neuralink publicly announced its existence and began recruiting engineers and scientists.
- 2019:Neuralink unveiled its first prototype BCI, a device called “N1” designed to be implanted in the brain. The company also released a video demonstrating the device’s ability to record and transmit neural signals from a pig’s brain.
- 2020:Neuralink conducted its first demonstration of the N1 device in a monkey, showing that the device could control a computer cursor with the monkey’s thoughts.
- 2021:Neuralink received FDA approval to study its brain implants in humans.
The Technology Behind Neuralink Implants
Neuralink’s brain-computer interface (BCI) is a revolutionary technology that aims to connect the human brain to computers, opening up a world of possibilities for treating neurological conditions and enhancing human capabilities. The implant, designed to be surgically inserted into the brain, consists of a series of tiny electrodes that record and stimulate neural activity.
Design and Functionality, Elon musks neuralink gets fda approval to study brain implants in humans
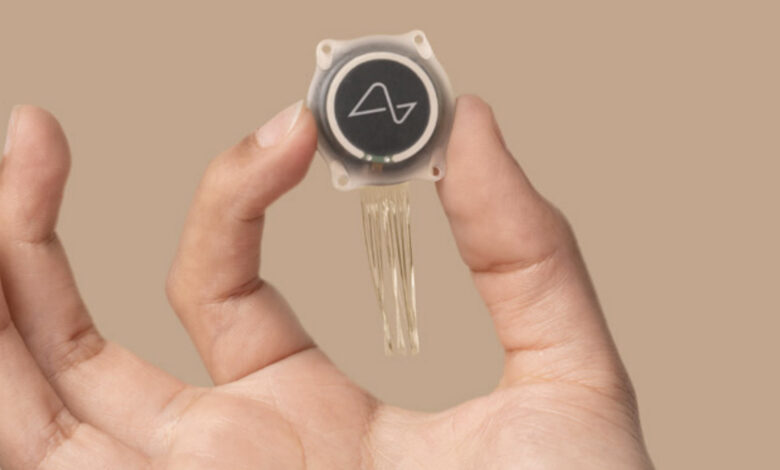
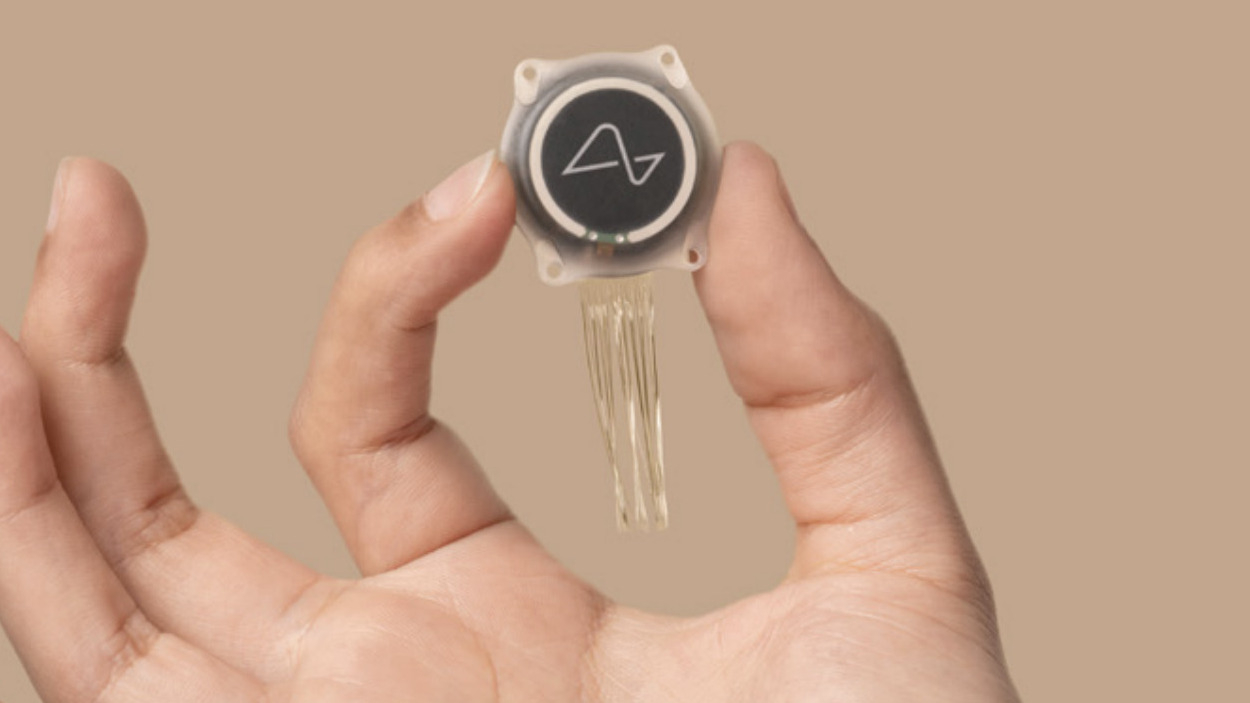
The Neuralink implant, dubbed the “N1 Link,” is a small, coin-sized device that is implanted in the skull. It contains thousands of flexible electrodes that are thinner than a human hair. These electrodes are connected to a chip called the “N1,” which processes the signals received from the brain.
The N1 chip is then wirelessly connected to an external device, such as a smartphone or computer, allowing users to control various functions.
Implantation Process
The implantation process is a surgical procedure that requires a specialized robotic system developed by Neuralink. The robot precisely inserts the electrodes into the brain using a minimally invasive technique. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, and the recovery time is relatively short.
Potential Applications and Benefits
Neuralink’s technology holds immense potential for various applications, including:
- Treating neurological conditions: The implant could potentially help treat conditions like Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, and spinal cord injuries by stimulating specific brain regions or bypassing damaged pathways.
- Restoring lost senses: For individuals with blindness or deafness, Neuralink could potentially restore lost sensory functions by transmitting visual or auditory information directly to the brain.
- Enhancing cognitive abilities: The technology could potentially enhance memory, focus, and learning abilities by stimulating specific brain regions associated with these functions.
- Controlling external devices: Neuralink could allow users to control external devices, such as prosthetic limbs, computers, and smartphones, using their thoughts.
“The potential of Neuralink is vast, and it could revolutionize how we treat neurological conditions and interact with the world around us.”
Elon Musk
FDA Approval and Ethical Considerations: Elon Musks Neuralink Gets Fda Approval To Study Brain Implants In Humans
The FDA’s decision to allow Neuralink to proceed with human trials marks a significant step in the field of brain-computer interfaces. While the potential benefits are vast, the technology also raises significant ethical concerns that require careful consideration.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations surrounding brain-computer interfaces are complex and multifaceted. The potential for these technologies to enhance human capabilities is undeniable, but it also raises questions about privacy, autonomy, and the very definition of what it means to be human.
Elon Musk’s Neuralink just received FDA approval to test brain implants in humans, a monumental leap in neurotechnology. This news comes at a time when the economy is facing turbulent times, with a key economic indicator falling for the tenth straight month, suggesting a recession could be on the horizon.
Read more about the economic downturn here. While the economic outlook might be uncertain, Neuralink’s progress offers a glimmer of hope for the future, potentially paving the way for revolutionary medical advancements and even new frontiers in human potential.
- Privacy:Brain-computer interfaces could provide unprecedented access to our thoughts and feelings, raising concerns about data security and potential misuse. Who will have access to this information, and how will it be protected?
- Autonomy:Brain-computer interfaces could potentially influence our decisions and actions, blurring the lines between our own will and external control. How do we ensure that individuals retain control over their own thoughts and actions?
- Equality:Access to these technologies could be limited by cost and availability, potentially creating new forms of inequality. How do we ensure that these technologies are available to all, regardless of their financial status or social background?
- Safety:The long-term effects of brain-computer interfaces are still unknown. What are the potential risks associated with implanting devices in the brain, and how can we mitigate them?
Potential Risks and Concerns
While Neuralink promises a future of enhanced human capabilities, there are significant risks and concerns associated with the technology. These risks range from the immediate to the long-term, and require careful consideration before widespread adoption.
- Surgical Complications:Brain surgery is inherently risky, and implanting a device in the brain carries the potential for infection, bleeding, and other complications.
- Device Malfunction:Like any electronic device, Neuralink implants could malfunction, potentially leading to harm or loss of function.
- Long-Term Effects:The long-term effects of brain-computer interfaces are still unknown. Could these devices alter brain function or lead to unforeseen consequences?
- Ethical Concerns:As discussed earlier, brain-computer interfaces raise ethical concerns about privacy, autonomy, and equality. These concerns must be addressed before the technology can be widely adopted.
Potential Applications and Future Directions

The FDA’s approval of Neuralink’s clinical trial marks a significant milestone in the development of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). This technology holds immense potential to revolutionize medicine and human capabilities.
Potential Applications in Medicine
Neuralink’s technology could have transformative applications in various medical fields.
- Treating Neurological Disorders:BCIs could potentially restore motor function in individuals with paralysis, spinal cord injuries, or neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuralink’s implants could bypass damaged neural pathways and allow patients to control prosthetic limbs or devices directly with their thoughts.
- Restoring Sensory Functions:BCIs could help restore lost sensory functions, such as vision or hearing, by providing direct stimulation to the brain. For example, blind individuals could potentially regain some vision through a BCI that translates visual information into electrical signals interpreted by the brain.
Elon Musk’s Neuralink getting FDA approval to study brain implants in humans is a big deal, but it’s also got me thinking about the potential for free speech issues. Just imagine if the same technology could be used to censor our thoughts or control our behavior! It’s a chilling thought, especially considering the recent case of a man facing trial for creating a meme about Hillary Clinton, which an attorney says could chill free speech for all Americans.
We need to be vigilant about the ethical implications of these powerful technologies, and ensure they are used responsibly for the benefit of all.
- Treating Mental Health Conditions:BCIs could potentially provide new avenues for treating mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. By monitoring and modulating brain activity, BCIs could help regulate mood and reduce symptoms.
- Improving Cognitive Function:BCIs could potentially enhance cognitive function in individuals with cognitive impairments or age-related decline. By stimulating specific brain regions, BCIs could potentially improve memory, attention, and focus.
Impact on Human Abilities and Limitations
The development of BCIs like Neuralink raises important questions about the potential impact on human abilities and limitations.
- Augmented Capabilities:BCIs could potentially enhance human capabilities beyond what is currently possible. Individuals could potentially learn new skills more quickly, access information more easily, or even communicate telepathically.
- Ethical Considerations:The potential for enhancing human abilities raises ethical concerns about fairness, accessibility, and the potential for creating a divide between those with and without access to BCI technology.
- Privacy and Security:The ability to read and write information to the brain raises concerns about privacy and security. Who will have access to this information, and how will it be protected from unauthorized access?
Future Developments and Advancements
The field of brain-computer interfaces is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research and development focused on advancing the technology and expanding its potential applications.
Elon Musk’s Neuralink getting FDA approval to study brain implants in humans is definitely a big deal, but I can’t help but feel like we’re living in a world where reality is stranger than fiction. It’s almost as if we’re in a parallel universe where news about brain implants is just as commonplace as the latest court rulings, like the recent decision by the Arizona Supreme Court on Kari Lake’s second election petition.
The implications of Neuralink are mind-blowing, and I’m curious to see how this technology will evolve in the years to come.
- Miniaturization and Integration:Future BCIs are likely to become smaller and more seamlessly integrated with the brain, reducing the need for external devices and improving comfort for users.
- Wireless Communication:Wireless communication between the BCI and external devices will likely become more sophisticated, allowing for more natural and intuitive interactions.
- Artificial Intelligence Integration:Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) with BCIs could enhance their capabilities, enabling them to learn and adapt to individual users’ needs and preferences.
- Enhanced Data Processing:Advances in data processing and analysis will enable BCIs to collect and interpret more complex and nuanced brain signals, leading to more accurate and effective applications.
Public Perception and Debate

The FDA’s approval of Neuralink’s clinical trial sparked a wave of mixed reactions from the public, ranging from cautious optimism to outright skepticism. This approval signifies a crucial step towards the development of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and their potential applications in healthcare and beyond.
However, the ethical and societal implications of this technology have also raised significant concerns.
Public Reactions to Neuralink’s FDA Approval
The public’s reaction to Neuralink’s FDA approval has been diverse, reflecting a range of perspectives on the potential benefits and risks associated with brain-computer interfaces.
- Supporters:Many individuals expressed excitement and hope for the potential of Neuralink’s technology to address neurological conditions like paralysis, blindness, and epilepsy. They believe that BCIs could revolutionize healthcare by offering new treatment options and improving quality of life for millions.
- Skeptics:Others remain apprehensive about the safety and ethical implications of implanting devices directly into the brain. They raise concerns about potential risks, including brain damage, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and the possibility of unintended consequences.
- Cautious Optimists:A significant portion of the public holds a more nuanced view, recognizing both the potential benefits and risks of BCIs.
They advocate for careful research, stringent safety protocols, and transparent communication about the technology’s development and application.
Arguments for and Against the Development of Brain-Computer Interfaces
The debate surrounding brain-computer interfaces centers on a fundamental tension between the potential benefits and the ethical and societal challenges they pose.
- Arguments in Favor:
- Medical Advancement:Proponents argue that BCIs have the potential to revolutionize healthcare by offering new treatment options for a wide range of neurological conditions. They cite examples like restoring mobility to paralyzed individuals, providing vision to the blind, and treating debilitating neurological disorders like epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.
- Enhanced Human Capabilities:Some believe that BCIs could enhance human capabilities beyond the realm of medicine, potentially leading to improved cognitive function, communication, and even telepathic communication.
- Technological Innovation:The development of BCIs is seen as a major driver of technological innovation, potentially leading to breakthroughs in fields like artificial intelligence, robotics, and neuroscience.
- Arguments Against:
- Safety Concerns:Critics raise concerns about the potential risks associated with implanting devices directly into the brain. They point to the possibility of brain damage, infection, and the long-term effects of chronic brain stimulation.
- Ethical Implications:Ethical concerns surround the potential for BCIs to be used for non-medical purposes, such as enhancing human performance, manipulating behavior, or even controlling people’s thoughts.
There are also concerns about the potential for misuse, such as hacking into BCIs or using them for surveillance.
- Social Inequality:There are concerns that BCIs could exacerbate existing social inequalities by creating a divide between those who have access to this technology and those who do not.
Potential Societal Implications of Widespread Neuralink Adoption
The widespread adoption of BCIs could have profound societal implications, affecting various aspects of human life.
- Healthcare Transformation:BCIs could fundamentally transform healthcare by offering new treatment options for a wide range of conditions, potentially leading to improved health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
- Human Enhancement:The potential for BCIs to enhance human capabilities raises questions about the definition of “human” and the implications for our understanding of human nature.
- Social and Economic Disparity:The availability and affordability of BCIs could exacerbate existing social and economic disparities, potentially creating a new class of “enhanced” individuals.
- Privacy and Security Concerns:The potential for BCIs to access and control sensitive personal data raises significant privacy and security concerns.
- Ethical and Legal Frameworks:The development of BCIs necessitates the development of robust ethical and legal frameworks to guide their use and address potential risks.
Closure
The approval of Neuralink’s clinical trial marks a pivotal moment in the development of brain-computer interfaces. While the potential benefits are immense, it’s crucial to address the ethical considerations and potential risks associated with this technology. As we move forward, open dialogue and responsible research are essential to ensure that the development of brain-computer interfaces benefits humanity while safeguarding our values and rights.