Biden Budget Proposal: National Debt Interest Payments Balloon
National debt interest payments balloon under latest Biden budget proposal, a trend that has experts and policymakers concerned about the long-term fiscal sustainability of the United States. This proposal, aiming to address critical social and economic issues, has inadvertently set the stage for a significant increase in the nation’s debt burden, with projections showing a substantial rise in interest payments.
This escalation is driven by a combination of factors, including rising interest rates and a growing national debt, both of which are putting immense pressure on the federal budget.
The Biden administration’s approach to debt management, while prioritizing social programs and infrastructure investments, has sparked debate about the potential consequences of these fiscal policies. Critics argue that the proposed spending increases, coupled with a lack of concrete plans to address the rising debt, could lead to economic instability and undermine long-term growth.
However, supporters maintain that the proposed investments are crucial for boosting the economy and addressing pressing societal needs, and that the administration is committed to responsible fiscal management.
The Biden Budget Proposal and National Debt Interest Payments
The Biden administration’s budget proposal for fiscal year 2024 has generated significant discussion, particularly concerning its approach to managing the national debt. A central focus of the proposal is addressing the rising cost of interest payments on the national debt, a trend that has been steadily increasing in recent years.
This blog post will delve into the key provisions of the Biden budget proposal related to national debt interest payments, examining their potential impact on the federal budget deficit and the national debt. Additionally, we will compare the Biden administration’s approach to debt management with those of previous administrations.
The Biden Budget Proposal’s Provisions on National Debt Interest Payments
The Biden budget proposal seeks to address the rising cost of national debt interest payments through a combination of strategies. The proposal emphasizes the need for responsible fiscal policies that prioritize deficit reduction while also supporting economic growth. The administration argues that a strong economy is essential for reducing the national debt, as it generates higher tax revenues and lowers the cost of borrowing.
“The Biden administration’s budget proposal for fiscal year 2024 emphasizes the need for responsible fiscal policies that prioritize deficit reduction while also supporting economic growth.”
The proposal Artikels several specific measures aimed at reducing the national debt. These include:
- Increased Tax Revenue:The proposal calls for increasing tax revenue through a combination of measures, such as closing tax loopholes and raising tax rates on corporations and high-income earners. This strategy is intended to generate additional funds to help offset the cost of interest payments on the national debt.
- Reduced Spending:The proposal also calls for reducing federal spending in certain areas, such as defense and entitlement programs. The administration argues that these cuts are necessary to ensure fiscal sustainability and to reduce the strain on the national debt. However, these proposed reductions have faced significant opposition from both Democrats and Republicans.
- Economic Growth:The Biden administration believes that strong economic growth is essential for reducing the national debt. The proposal includes measures designed to stimulate economic growth, such as investments in infrastructure, education, and clean energy. The administration argues that these investments will create jobs, boost productivity, and ultimately lead to higher tax revenues that can help reduce the national debt.
Projected Impact of the Biden Budget Proposal on the Federal Budget Deficit and the National Debt
The Biden administration’s budget proposal projects that its proposed policies will lead to a significant reduction in the federal budget deficit over the next decade. The administration argues that these measures will help to stabilize the national debt and prevent it from spiraling out of control.
However, these projections have been met with skepticism from some economists and policymakers who argue that the administration’s proposed policies are not sufficient to address the long-term challenges facing the national debt.
“The Biden administration’s budget proposal projects that its proposed policies will lead to a significant reduction in the federal budget deficit over the next decade.”
Comparison of the Biden Administration’s Approach to Debt Management with Previous Administrations
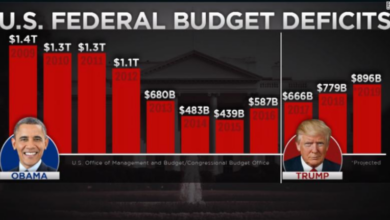
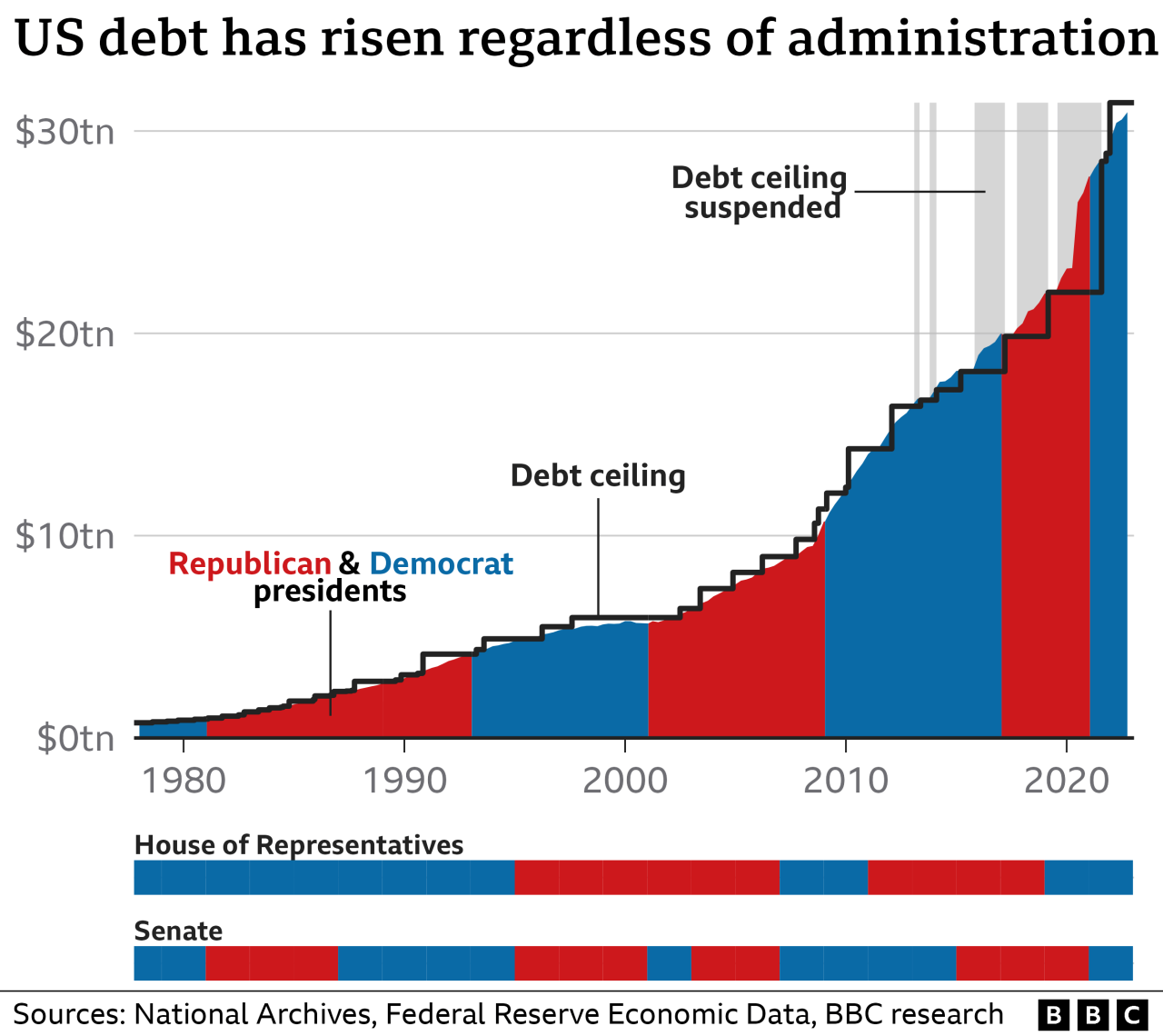
The Biden administration’s approach to debt management differs significantly from those of previous administrations. The Trump administration, for example, implemented significant tax cuts that led to a substantial increase in the federal budget deficit. The Obama administration, on the other hand, focused on reducing the deficit through a combination of spending cuts and tax increases.
The Biden administration’s approach is more nuanced, seeking to balance deficit reduction with economic growth.
“The Biden administration’s approach to debt management differs significantly from those of previous administrations.”
The Biden administration’s budget proposal is a complex document that Artikels a wide range of policy priorities. The proposal’s approach to national debt interest payments is just one aspect of a larger strategy for addressing the federal budget deficit.
The effectiveness of these proposals will depend on a variety of factors, including the state of the economy, the political climate, and the willingness of policymakers to make difficult decisions.
Factors Contributing to Rising Interest Payments
The Biden administration’s budget proposal has highlighted a concerning trend: the ballooning cost of interest payments on the national debt. This trend is driven by a combination of factors, including rising interest rates and the ever-growing national debt. Understanding these factors is crucial to grasp the economic implications of this issue.
Rising Interest Rates
Interest rates are a key factor influencing the cost of borrowing. When interest rates rise, the government has to pay more to service its existing debt. This is because the interest payments on Treasury bonds and other debt instruments are tied to prevailing market interest rates.
The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, sets the benchmark interest rate, known as the federal funds rate. This rate influences other interest rates in the economy, including those on government debt. The Fed has been raising interest rates in recent months to combat inflation, which has led to higher borrowing costs for the government.
Growing National Debt
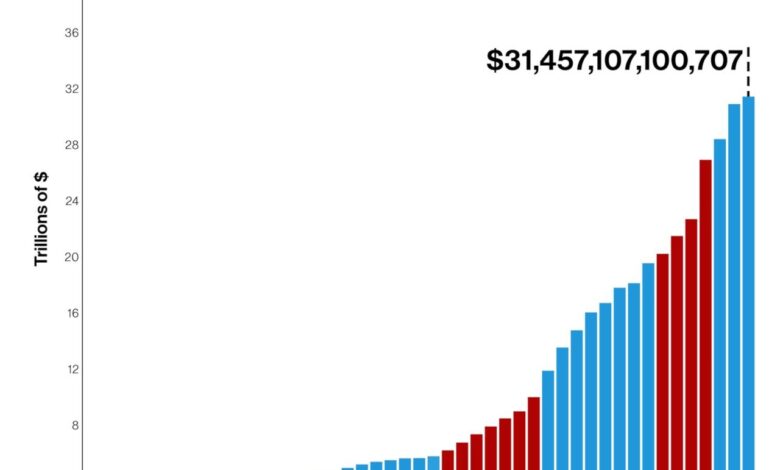
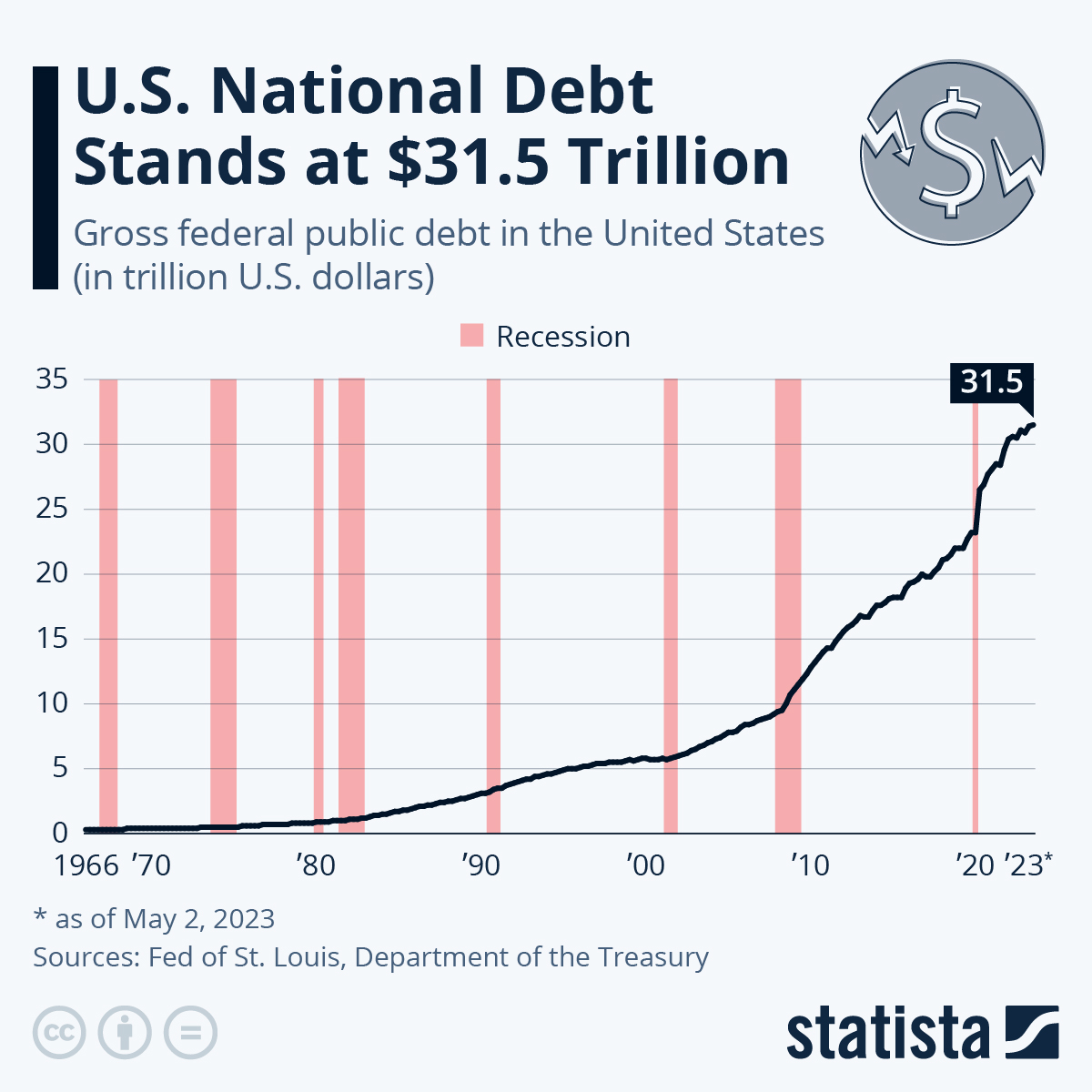
The national debt is the total amount of money that the U.S. government owes to its creditors, including individuals, businesses, and foreign governments. As the debt grows, the amount of interest payments the government needs to make also increases.The national debt has been steadily rising for decades, fueled by factors such as tax cuts, wars, and economic downturns.
In recent years, the COVID-19 pandemic has also contributed to a significant increase in the debt.
The Biden administration’s latest budget proposal is causing a stir, with projected national debt interest payments ballooning to unprecedented levels. This comes at a time when the Koch Industries, a major player in the American economy, continues to operate in Russia and even backs groups that oppose US sanctions.
This move by Koch Industries raises concerns about the company’s priorities and the potential impact on US foreign policy, particularly as the national debt continues to grow. The implications of these developments for the US economy and global relations remain to be seen.
Historical Trends in Interest Payments
Interest payments have historically been a relatively small portion of the federal budget. However, they have been rising steadily in recent decades.
- In the 1960s, interest payments accounted for less than 1% of the federal budget.
- By the 1990s, this figure had risen to around 5%.
- In recent years, interest payments have surpassed 10% of the federal budget.
This trend is projected to continue in the coming years, as the national debt is expected to continue growing.
Economic and Political Factors
Several economic and political factors influence the trend of rising interest payments.
- Economic Growth:A strong economy typically leads to higher interest rates, as investors demand a higher return on their investments. However, slower economic growth can also lead to higher interest payments if the government needs to borrow more money to stimulate the economy.
- Inflation:High inflation can lead to higher interest rates as the Federal Reserve tries to control price increases. This can further increase the cost of borrowing for the government.
- Fiscal Policy:Government spending and tax policies can also influence interest rates. For example, large deficits can lead to higher interest rates as investors become concerned about the government’s ability to repay its debts.
- Political Uncertainty:Political instability and uncertainty can also lead to higher interest rates, as investors demand a risk premium for holding government debt.
Economic Implications of Rising Interest Payments
The ballooning interest payments on the national debt pose significant economic implications, potentially hindering economic growth, increasing inflation, and crowding out private investment. Understanding these implications is crucial for navigating the complex interplay between government finances and the broader economy.
Impact on Economic Growth
Rising interest payments can negatively impact economic growth. As the government allocates a larger portion of its budget to debt servicing, it has fewer resources available for other critical areas such as infrastructure development, education, and healthcare. This can lead to reduced public investment, slowing economic growth, and limiting opportunities for job creation.
Additionally, increased interest payments can raise borrowing costs for businesses, making it more expensive for them to invest and expand operations.
Crowding Out Private Investment, National debt interest payments balloon under latest biden budget proposal
As the government borrows more money to finance its debt, it increases demand for loanable funds, pushing interest rates higher. This rise in interest rates can make it more expensive for businesses and individuals to borrow money for investment and consumption.
As a result, private investment may decline, as businesses find it less attractive to borrow and invest at higher interest rates. This phenomenon is known as crowding out, where government borrowing crowds out private investment.
The latest Biden budget proposal has sparked concern as it projects a significant increase in national debt interest payments. This rise in interest payments, coupled with the news that Zovio is exploring selling parts of its business as net losses continue , highlights the financial challenges facing both the government and private sector.
With growing debt obligations and shrinking revenue streams, it’s crucial to find sustainable solutions to ensure long-term financial stability.
Impact on Inflation
Rising interest payments can contribute to inflation in several ways. When the government borrows more money, it increases the money supply, which can lead to inflation. Additionally, higher interest rates can increase borrowing costs for businesses, leading them to raise prices to maintain profitability.
This can further contribute to inflationary pressures.
Impact on Employment
Rising interest payments can have a negative impact on employment. As economic growth slows due to reduced public investment and crowding out of private investment, businesses may be less likely to hire new workers. Furthermore, increased borrowing costs can lead to job losses in sectors that rely heavily on borrowing, such as construction and manufacturing.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Higher interest rates can also impact consumer spending. As borrowing costs rise, consumers may reduce their spending on durable goods, such as cars and appliances. This can lead to a decline in overall economic activity.
Relationship Between National Debt Interest Payments and Key Economic Indicators
The following table illustrates the relationship between national debt interest payments and key economic indicators:
| Economic Indicator | Relationship with National Debt Interest Payments | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Growth | Negative | Higher interest payments can lead to reduced public investment, slowing economic growth. |
| Private Investment | Negative | Rising interest rates can crowd out private investment, as businesses find it less attractive to borrow and invest. |
| Inflation | Positive | Increased government borrowing can lead to higher inflation through an increase in the money supply. |
| Unemployment Rate | Positive | Slower economic growth due to rising interest payments can lead to higher unemployment. |
| Consumer Spending | Negative | Higher interest rates can discourage consumer spending on durable goods, leading to a decline in overall economic activity. |
Policy Options for Addressing Rising Interest Payments
The escalating cost of servicing the national debt poses a significant challenge to the U.S. government. This rising burden necessitates a comprehensive approach to address the issue and ensure long-term fiscal sustainability. Various policy options are available, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Tax Increases
Tax increases represent a direct approach to generating revenue to offset the rising interest payments. This can be achieved through various means, including raising income tax rates, imposing new taxes on corporations or individuals, or broadening the tax base.
- Pros:
- Directly increases government revenue, contributing to debt reduction.
- Can be targeted to specific income groups or sectors, ensuring a fair distribution of the burden.
- Provides a sustainable source of funding for debt service.
- Cons:
- May stifle economic growth by reducing disposable income and investment.
- Could lead to tax avoidance and evasion, undermining revenue generation.
- May be politically unpopular and difficult to implement.
Spending Cuts
Reducing government spending is another way to address rising interest payments. This can involve trimming discretionary programs, reducing entitlement benefits, or reforming government agencies to improve efficiency.
- Pros:
- Reduces the government’s overall debt burden, lowering interest payments.
- Can improve fiscal discipline and encourage responsible budgeting practices.
- May free up resources for other priorities, such as infrastructure or education.
- Cons:
- Can lead to cuts in essential services and programs, impacting vulnerable populations.
- May result in job losses and economic slowdown.
- Difficult to implement due to political resistance and public opposition.
Debt Restructuring
Debt restructuring involves modifying the terms of existing debt obligations to reduce interest payments or extend the repayment period. This could involve refinancing outstanding debt at lower interest rates or extending the maturity dates.
The latest Biden budget proposal paints a bleak picture for our nation’s finances, with interest payments on the national debt set to skyrocket. This comes at a time when the Biden family is facing a barrage of subpoenas, as reported by Molnewsnet , which could further complicate the already challenging economic landscape.
The combination of mounting debt and potential political turmoil creates a volatile environment for our nation’s financial future.
- Pros:
- Can lower immediate interest payments, providing temporary relief.
- May allow for a more manageable debt repayment schedule.
- Can improve the government’s credit rating and borrowing costs in the long term.
- Cons:
- May signal financial distress and undermine investor confidence.
- Could lead to higher interest rates on future borrowing.
- May only provide a temporary solution and not address the underlying fiscal imbalances.
Economic Impact of Policy Options
| Policy Option | Potential Economic Impact ||—|—|| Tax Increases | May slow economic growth by reducing disposable income and investment. || Spending Cuts | Can lead to job losses and economic slowdown, particularly in sectors reliant on government spending.
|| Debt Restructuring | May initially provide temporary relief but could lead to higher interest rates on future borrowing. |
Long-Term Implications for Fiscal Sustainability: National Debt Interest Payments Balloon Under Latest Biden Budget Proposal
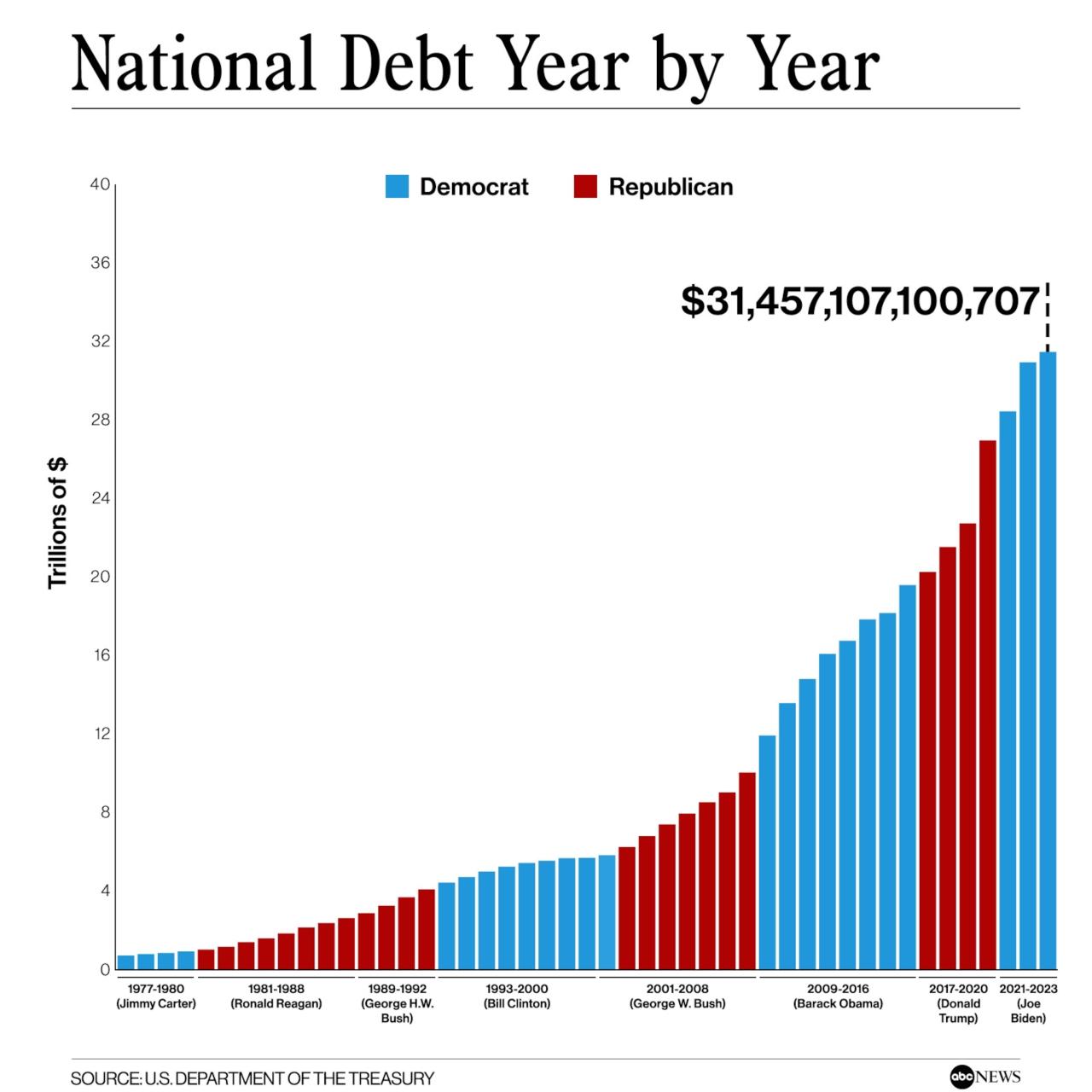
The ballooning national debt interest payments under the latest Biden budget proposal raise significant concerns about the long-term fiscal sustainability of the United States. While the government can continue to borrow money in the short term, a consistently growing debt burden poses serious risks to the nation’s economic future.
Potential Risks Associated with a Growing National Debt
A growing national debt can have several negative consequences for the US economy. One of the most significant risks is a loss of investor confidence. As the debt burden increases, investors may become less willing to lend money to the US government, leading to higher interest rates and making it more expensive for the government to borrow.
This can further exacerbate the debt problem and create a vicious cycle.Another risk is a sovereign debt crisis. If the US government is unable to meet its debt obligations, it could default on its debt, which would have catastrophic consequences for the economy.
A sovereign debt crisis could lead to a loss of confidence in the US dollar, higher inflation, and a recession.
Views of Economists and Policymakers
Economists and policymakers have differing views on the long-term outlook for the US national debt. Some argue that the debt is unsustainable and will eventually lead to a crisis. They point to the fact that the debt is growing faster than the economy and that interest payments are consuming an increasing share of government revenue.
Others argue that the debt is manageable and that the US economy is resilient enough to handle it. They point to the fact that the US has a strong economy and a long history of paying its debts.
“The long-term outlook for the US national debt is uncertain, but it is clear that the current trajectory is unsustainable.”
The Congressional Budget Office
The long-term implications of the national debt are complex and subject to debate. However, it is clear that the current trajectory of rising debt and interest payments poses significant risks to the US economy. Addressing this issue will require a combination of policies to reduce spending, increase revenue, and promote economic growth.
Ending Remarks
The prospect of ballooning national debt interest payments under the latest Biden budget proposal presents a complex challenge for the US economy. The potential economic consequences of this trend, including crowding out private investment and inflation risks, are serious concerns that require careful consideration and proactive policy responses.
The administration faces the difficult task of balancing its commitment to social and economic progress with the need to ensure long-term fiscal sustainability. This will require a comprehensive strategy that addresses both the immediate pressures on the budget and the underlying factors driving the growth of the national debt.
The path forward will likely involve a combination of policy options, including spending cuts, tax increases, and debt restructuring, all of which will require careful consideration and broad political consensus.