Could Vitamin D Help Save Our Veterans?
Could vitamin D help save our veterans? This question has gained increasing attention as research reveals the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among veterans and its potential link to various health concerns. From physical ailments to mental well-being, the impact of vitamin D deficiency on veterans is a serious issue that deserves further investigation.
This blog post explores the complexities of vitamin D deficiency in veterans, examining the potential benefits of supplementation and highlighting the importance of comprehensive healthcare for this deserving population. Join us as we delve into the science behind vitamin D and its potential role in improving the lives of our veterans.
Vitamin D Deficiency in Veterans
Vitamin D deficiency is a common health concern, particularly among veterans. Several factors contribute to this, and it’s crucial to understand these factors to address the issue effectively.
Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency
Veterans are at a higher risk of vitamin D deficiency compared to the general population. This is due to several factors, including their increased likelihood of being exposed to sunlight, their potential for spending more time indoors, and their higher prevalence of certain health conditions.
It’s fascinating to think about how vitamin D could potentially improve the lives of our veterans, but it’s important to remember that there are other crucial issues affecting our nation. For example, the recent article about young black voters not being excited about the Biden-Harris ticket highlights the need to address systemic inequalities that impact communities across the country.
While vitamin D research is promising, it’s essential to consider a holistic approach to supporting our veterans and ensuring a brighter future for all Americans.
Factors Contributing to Vitamin D Deficiency in Veterans
Several factors can contribute to vitamin D deficiency in veterans. These include:
- Limited Sunlight Exposure:Veterans who have served in combat zones or have been deployed to areas with limited sunlight may experience vitamin D deficiency due to prolonged periods of indoor confinement.
- Skin Pigmentation:Individuals with darker skin pigmentation require more sunlight exposure to produce the same amount of vitamin D as those with lighter skin. This can make veterans of color more susceptible to vitamin D deficiency.
- Age:As individuals age, their skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight decreases. Veterans who have served for a significant period may be at increased risk of vitamin D deficiency due to their age.
- Health Conditions:Veterans are more likely to have certain health conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, which can affect vitamin D metabolism and increase the risk of deficiency.
- Medications:Some medications commonly used by veterans, such as anticonvulsants and corticosteroids, can interfere with vitamin D absorption and increase the risk of deficiency.
Statistics on Vitamin D Deficiency Rates
Studies have shown that vitamin D deficiency rates are significantly higher among veterans compared to the general population. For example, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that approximately 40% of veterans had vitamin D deficiency, compared to 25% of the general population.
“It is essential to recognize the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among veterans and implement strategies to address this issue.”
Health Concerns Linked to Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is a prevalent issue among veterans, potentially impacting their overall health and well-being. The lack of sufficient vitamin D can lead to a range of health problems, affecting both physical and mental health.
Impact on Physical Health
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health, regulating calcium absorption, and supporting muscle function. Its deficiency can have a significant impact on physical health, leading to various conditions.
- Bone Health:Vitamin D deficiency is directly linked to weakened bones, increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis. This is particularly concerning for veterans who may have experienced injuries or trauma during their service.
- Muscle Weakness:Insufficient vitamin D levels can impair muscle function, leading to weakness and fatigue. This can affect mobility and daily activities, making it challenging for veterans to maintain an active lifestyle.
- Cardiovascular Health:Studies suggest a link between vitamin D deficiency and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Low vitamin D levels may contribute to high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
- Immune Function:Vitamin D plays a vital role in immune system regulation, helping the body fight off infections. Deficiency can weaken the immune system, making veterans more susceptible to illnesses.
Impact on Mental Health
Emerging research suggests a potential connection between vitamin D deficiency and mental health conditions. While more research is needed, studies indicate that low vitamin D levels may be associated with:
- Depression:Vitamin D is known to influence mood regulation, and deficiency may contribute to depressive symptoms. This is particularly relevant for veterans who may experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or other mental health challenges.
- Cognitive Function:Some studies suggest that vitamin D deficiency may be linked to cognitive decline and an increased risk of dementia. This is a concern for veterans, as they may experience age-related cognitive changes.
Specific Health Conditions
Vitamin D deficiency can exacerbate or contribute to various health conditions, including:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS):Research suggests that low vitamin D levels may be associated with an increased risk of developing MS and may influence disease progression.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):Studies have indicated a potential link between vitamin D deficiency and the severity of RA symptoms. Maintaining adequate vitamin D levels may help manage RA pain and inflammation.
- Cancer:Some studies suggest a possible association between vitamin D deficiency and an increased risk of certain cancers, including colorectal, breast, and prostate cancer. However, more research is needed to confirm this link.
Potential Benefits of Vitamin D Supplementation
Vitamin D supplementation has gained significant attention as a potential therapeutic strategy for veterans, who are often susceptible to various health conditions. While further research is needed, existing evidence suggests that vitamin D supplementation might offer numerous benefits for veterans, particularly in addressing specific health concerns.
Improved Bone Health
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium absorption, which is essential for maintaining bone health. Studies have shown that veterans with low vitamin D levels are at increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Supplementation can help increase vitamin D levels, potentially reducing the risk of these conditions.
A 2017 study published in the journal “Osteoporosis International” found that vitamin D supplementation significantly improved bone mineral density in postmenopausal women, a population group at high risk of osteoporosis.
Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Research suggests that vitamin D supplementation may improve blood pressure, reduce inflammation, and improve cardiovascular function. A meta-analysis published in the “American Journal of Clinical Nutrition” found that vitamin D supplementation was associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals with low vitamin D levels.
Improved Muscle Function
Vitamin D deficiency can impair muscle function and increase the risk of falls. Supplementation has been shown to improve muscle strength and reduce the risk of falls in older adults. A 2018 study published in the “Journal of the American Geriatrics Society” found that vitamin D supplementation improved muscle function and reduced the risk of falls in older adults with vitamin D deficiency.
While we’re talking about the well-being of those who serve our country, it’s also important to remember the impact of natural disasters. The recent California storm that left a dozen dead and over 100,000 without power highlights the vulnerability of communities, and it’s a reminder that we need to support those in need, especially our veterans who may be disproportionately affected by such events.
Perhaps research into the potential benefits of Vitamin D for veterans’ health could also play a role in their resilience and overall well-being.
Reduced Risk of Depression
Studies have linked vitamin D deficiency to an increased risk of depression. Vitamin D supplementation has shown promise in improving mood and reducing depressive symptoms. A 2017 study published in the “Journal of Affective Disorders” found that vitamin D supplementation was associated with a significant reduction in depressive symptoms in individuals with low vitamin D levels.
It’s incredible to think that vitamin D could play such a vital role in the health of our veterans, especially considering the ongoing challenges they face. Speaking of challenges, it’s unsettling to hear about another train derailment in Springfield, Ohio , even if no hazardous materials were spilled this time.
Hopefully, research into vitamin D’s potential benefits for veterans will continue to shed light on ways to improve their overall well-being.
Improved Immune Function
Vitamin D plays a role in immune function. Supplementation may enhance immune responses and reduce the risk of infections. A 2019 study published in the “Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” found that vitamin D supplementation was associated with a lower risk of respiratory infections in individuals with low vitamin D levels.
Considerations for Vitamin D Supplementation
While vitamin D supplementation can be beneficial for many veterans, it’s crucial to approach it with caution and consider various factors.
Recommended Daily Intake
The recommended daily intake of vitamin D varies depending on age and health conditions.
| Age Group | Recommended Daily Intake (IU) |
|---|---|
| 0-12 months | 400 |
| 1-3 years | 600 |
| 4-8 years | 600 |
| 9-18 years | 600 |
| 19-70 years | 600 |
| 71 years and older | 800 |
Potential Risks and Side Effects, Could vitamin d help save our veterans
Although vitamin D is generally safe, excessive supplementation can lead to adverse effects.
- Hypercalcemia:High levels of calcium in the blood can cause nausea, vomiting, constipation, and kidney stones.
- Calcium Deposits:High doses of vitamin D can lead to the formation of calcium deposits in soft tissues, such as the kidneys and blood vessels.
- Interactions with Medications:Vitamin D can interact with certain medications, such as diuretics, heart medications, and antibiotics.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any vitamin D supplementation. They can:
- Assess your individual needs and determine the appropriate dosage.
- Monitor for any potential side effects or interactions with medications.
- Provide personalized advice based on your medical history and current health status.
Strategies for Increasing Vitamin D Levels Naturally
Boosting vitamin D levels naturally is crucial for overall well-being, especially for veterans who may be at higher risk for deficiency. Here’s a comprehensive guide to strategies that can help you achieve optimal vitamin D levels.
Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight is the most natural and efficient way to produce vitamin D. When your skin is exposed to sunlight, it triggers the production of vitamin D. However, it’s essential to optimize sun exposure for safe and effective vitamin D synthesis.
- Expose your skin to sunlight for short periods:Aim for 10-15 minutes of sun exposure on your face, arms, and legs during the midday hours (between 10 am and 3 pm) when the sun’s rays are strongest.
- Consider your skin tone and location:Individuals with darker skin tones require longer sun exposure to produce the same amount of vitamin D as those with lighter skin tones. Similarly, the intensity of sunlight varies based on geographical location.
- Use sunscreen strategically:While sunscreen is essential for protecting your skin from harmful UV rays, it can also block vitamin D production. Apply sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher after your initial sun exposure to prevent sunburn.
Dietary Intake
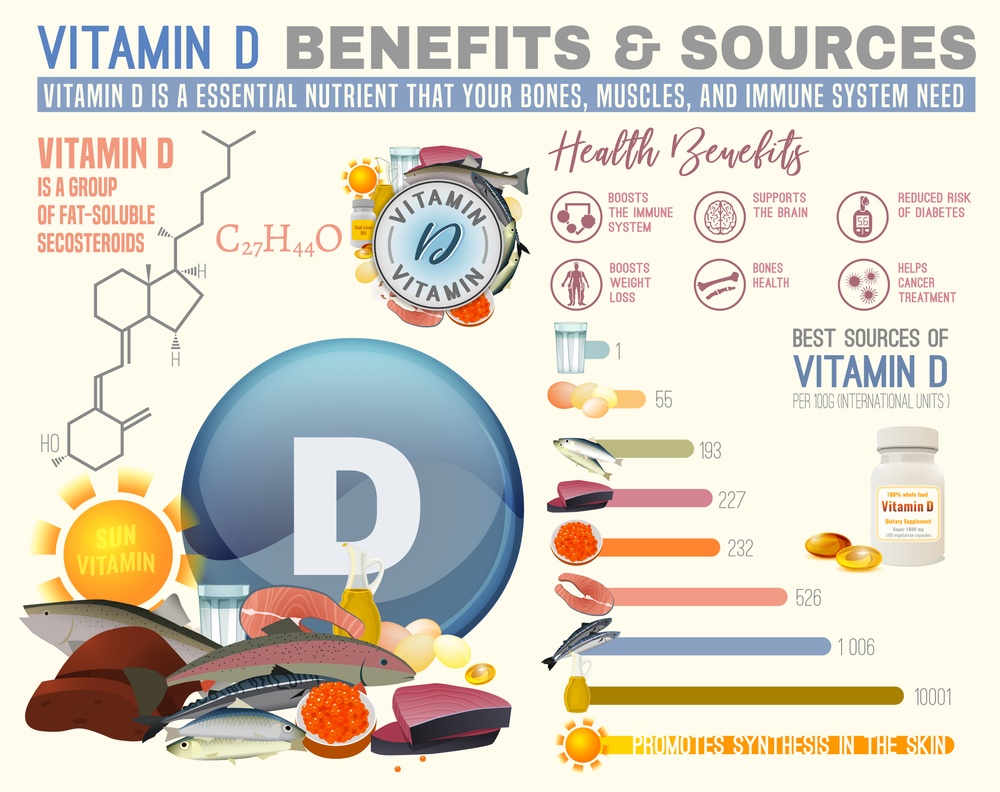
While sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D, certain foods can contribute to your daily intake.
- Fatty fish:Salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of vitamin D.
- Egg yolks:One large egg yolk contains approximately 40 IU of vitamin D.
- Fortified foods:Many dairy products, such as milk, yogurt, and cheese, are fortified with vitamin D. Look for products labeled “vitamin D fortified.”
- Mushrooms:Some varieties of mushrooms, like shiitake and oyster mushrooms, contain small amounts of vitamin D, especially when exposed to UV light.
The Importance of Comprehensive Healthcare for Veterans

Veterans face unique health challenges due to their service, and a comprehensive approach to healthcare is crucial for their well-being. This approach considers the physical, mental, and emotional needs of veterans, recognizing that their experiences may lead to a variety of health concerns.
Incorporating Vitamin D Supplementation into a Holistic Approach
Vitamin D supplementation can be a valuable component of a holistic approach to veteran health. While not a cure-all, vitamin D plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including bone health, immune function, and mood regulation. By addressing potential vitamin D deficiencies, veterans can potentially improve their overall health and well-being.
Resources and Support Systems for Veterans
Veterans have access to a range of resources and support systems designed to meet their specific needs. These resources can help veterans navigate the complexities of transitioning back to civilian life and address any health concerns they may face.
Government Resources
- The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA)offers a wide range of services, including healthcare, mental health support, and benefits. Veterans can access VA healthcare facilities nationwide, with specialized programs for conditions related to military service.
- The VA’s National Call Center for Homeless Veteransprovides information and resources for veterans experiencing homelessness. The call center offers a confidential and anonymous service, connecting veterans with local resources and support.
Non-Government Organizations
- The Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW)provides support and advocacy for veterans and their families. The VFW offers a variety of programs, including financial assistance, educational opportunities, and social activities.
- The American Legionis a non-profit organization dedicated to supporting veterans and their families. The American Legion provides a range of services, including job placement, legal assistance, and community outreach programs.
Community Support
- Many communities offer veteran support groupsthat provide a safe space for veterans to connect with others who understand their experiences. These groups offer peer support, social activities, and opportunities to share stories and build camaraderie.
- Local veteran service organizationscan provide guidance and support on a variety of issues, including employment, housing, and healthcare. These organizations often have close ties to local communities and can connect veterans with resources and services tailored to their specific needs.
Conclusion: Could Vitamin D Help Save Our Veterans
The health of our veterans is paramount, and understanding the role of vitamin D is a crucial step in providing comprehensive care. While vitamin D supplementation may offer potential benefits, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action.
By raising awareness and promoting healthy lifestyle choices, we can empower veterans to take charge of their well-being and live healthier, happier lives.