AI Jobs: Obsolete or Enhanced? Not Crying Wolf
Artificial intelligence could make these jobs obsolete not crying wolf, but the reality is far more nuanced. The fear of AI replacing humans in the workplace is a recurring theme throughout history, from the Luddites to the rise of automation.
While AI undoubtedly disrupts industries, it’s not about wholesale job elimination. Instead, it’s about reshaping the workforce and creating new opportunities.
This post explores the potential impact of AI on various jobs, examining both the risks and rewards. We’ll delve into the specific roles most susceptible to automation, but also highlight how AI can augment and enhance existing jobs, creating new roles and demanding new skills.
The Hype and Reality of AI Automation: Artificial Intelligence Could Make These Jobs Obsolete Not Crying Wolf

The prospect of artificial intelligence (AI) automating jobs has sparked intense debate, with some predicting widespread unemployment and others heralding a new era of prosperity. While AI’s potential impact on the workforce is undeniable, understanding the hype and reality of AI automation requires a nuanced perspective, considering both its limitations and its transformative power.
Historical Evolution of Automation Fears
The fear of technology replacing human labor is not new. Throughout history, each wave of technological advancement has been met with similar anxieties. The Industrial Revolution, for example, saw widespread concerns about the rise of machines displacing manual labor. The introduction of the personal computer in the 20th century also led to predictions of mass unemployment.
However, these fears have often proven unfounded. While certain jobs have indeed been automated, new opportunities have emerged in fields that require higher skills and creativity.
AI and Job Displacement: Common Misconceptions
The current discourse surrounding AI and job displacement is often characterized by exaggeration and misconceptions. One common misconception is that AI will soon replace all human workers. This is an overly simplistic view that fails to account for the complexities of human work.
While AI can excel at performing specific tasks, it lacks the adaptability, creativity, and emotional intelligence that are essential for many jobs. Another misconception is that AI will only benefit large corporations, leaving workers behind. In reality, AI has the potential to empower workers by automating mundane tasks and freeing up time for more fulfilling work.
Industries and Tasks Where AI is Automating Processes
AI is already automating processes across a wide range of industries. In manufacturing, robots are being used to perform repetitive tasks with greater precision and efficiency. In finance, AI algorithms are being used to analyze market trends and make investment decisions.
In healthcare, AI is being used to diagnose diseases and personalize treatment plans.
Benefits of AI Automation
AI automation offers several benefits, including:
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Improved accuracy and consistency
- Reduced costs and waste
- Enhanced decision-making
- Creation of new jobs in AI-related fields
Challenges of AI Automation
Despite its potential benefits, AI automation also presents challenges:
- Job displacement in certain sectors
- Ethical concerns regarding bias and transparency
- Need for reskilling and upskilling of workers
- Potential for social inequality if benefits are not distributed equitably
Jobs at Risk vs. Jobs Enhanced by AI
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) is undeniably transforming the job market, sparking concerns about potential job displacement while simultaneously opening doors to new opportunities. Understanding the interplay between AI and jobs is crucial for navigating this evolving landscape.
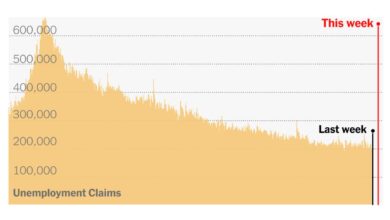
While the prospect of artificial intelligence making jobs obsolete might seem like a distant threat, the current economic climate adds another layer of uncertainty. The fact that a key economic indicator has fallen for the 10th straight month, as reported in this article , is a stark reminder that economic shifts can happen quickly.
This makes the potential impact of AI on employment all the more relevant, as we might be facing a double whammy of automation and economic downturn.
Jobs at Risk of Automation
AI’s ability to automate tasks, analyze data, and make decisions has the potential to disrupt certain job categories.
- Data Entry and Processing:AI-powered systems can efficiently extract data from documents, forms, and databases, automating tasks traditionally performed by data entry clerks.
- Customer Service Representatives:Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues.
- Truck Drivers:Self-driving trucks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, potentially replacing human drivers in long-haul transportation.
- Factory Workers:Robots and automated systems are being implemented in manufacturing, automating tasks like assembly, welding, and painting.
- Financial Analysts:AI algorithms can analyze financial data, identify trends, and generate investment recommendations, potentially reducing the need for human analysts.
Jobs Enhanced by AI
While some jobs may be at risk, AI can also enhance existing roles, empowering employees to perform their tasks more efficiently and effectively.
- Doctors and Nurses:AI can assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images, and providing personalized treatment plans, improving patient care and outcomes.
- Teachers:AI-powered tools can personalize learning experiences, provide real-time feedback, and automate grading, allowing teachers to focus on individual student needs.
- Sales Representatives:AI can analyze customer data, identify sales opportunities, and generate personalized marketing campaigns, enhancing sales effectiveness.
- Marketing Professionals:AI can automate tasks like content creation, social media management, and campaign optimization, freeing up marketers to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Software Developers:AI tools can assist developers in coding, debugging, and testing, streamlining the development process and increasing productivity.
Emerging Jobs in AI
The development and implementation of AI technologies are creating new job roles that were previously nonexistent.
- AI Engineers:These professionals design, develop, and implement AI systems, ensuring their performance and reliability.
- AI Data Scientists:Data scientists with expertise in AI algorithms and machine learning are in high demand to analyze and interpret large datasets.
- AI Ethics Specialists:As AI becomes more prevalent, there is a growing need for professionals who can address ethical considerations and ensure responsible AI development.
- AI Trainers:These individuals are responsible for training and fine-tuning AI models, ensuring they perform accurately and effectively.
- AI Product Managers:These professionals oversee the development and launch of AI-powered products, ensuring they meet market needs and user expectations.
The Human Element

While AI is revolutionizing many industries, it’s crucial to remember that it’s a tool, not a replacement for human ingenuity and collaboration. In this era of rapid technological advancement, human skills like emotional intelligence, creativity, and adaptability are becoming increasingly valuable.
It’s easy to dismiss warnings about AI replacing jobs as “crying wolf,” but the reality is that automation is already changing the landscape. While some argue that new jobs will emerge, the stark truth is that many of us are already struggling with declining living standards.
This economic pressure makes the potential for AI-driven job displacement even more concerning, and it’s a conversation we need to have before it’s too late.
These qualities, often referred to as “soft skills,” are essential for navigating the complex and ever-evolving landscape of the future workplace.
The Importance of Soft Skills and Emotional Intelligence, Artificial intelligence could make these jobs obsolete not crying wolf
Soft skills are interpersonal and social skills that are critical for success in any field. These skills, such as communication, collaboration, empathy, and problem-solving, are essential for building relationships, motivating teams, and navigating complex situations. Emotional intelligence, a key aspect of soft skills, involves understanding and managing one’s own emotions and those of others.
It enables individuals to build strong connections, foster trust, and navigate interpersonal challenges effectively. In the age of AI, these abilities are becoming increasingly important, as they enable humans to work effectively alongside intelligent machines and leverage their unique strengths.
Skills for the Future
In the future of work, humans will need to adapt and thrive alongside AI. This requires a focus on developing skills that complement and enhance the capabilities of AI.
- Critical Thinking: AI can process vast amounts of data, but it lacks the ability to critically analyze information, identify biases, and draw meaningful conclusions. Humans will need to be skilled in critical thinking to interpret AI-generated insights, make informed decisions, and solve complex problems.
- Creativity: AI excels at automation and optimization, but it struggles with originality and innovation. Humans will need to cultivate their creativity to develop new ideas, solve problems in unconventional ways, and adapt to changing circumstances.
- Adaptability: The pace of technological change is accelerating, and the skills required for success in the future are constantly evolving. Individuals will need to be adaptable, embracing new technologies and learning new skills throughout their careers.
- Complex Problem-Solving: AI can assist with specific tasks, but it often lacks the capacity to understand the broader context of a problem. Humans will need to be skilled in complex problem-solving, drawing on their critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence to identify root causes, develop comprehensive solutions, and implement them effectively.
Educational Programs and Initiatives
Recognizing the importance of these skills, educational institutions and organizations are developing programs and initiatives to prepare individuals for the future of work.
- Interdisciplinary Education: Many universities are incorporating interdisciplinary courses and programs that combine technical skills with soft skills, enabling students to develop a well-rounded skill set that is valuable in the age of AI. For example, the University of Oxford offers a master’s degree in “Data Science and AI for Business,” which integrates technical skills in data analysis and AI with business acumen and communication skills.
- Upskilling and Reskilling Programs: Organizations are offering upskilling and reskilling programs to help employees adapt to the changing demands of the workplace. These programs often focus on developing skills in data analysis, AI, and soft skills, enabling employees to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving job market.
While the recent news that the US economy added 223,000 new jobs might seem reassuring, it’s crucial to remember that this growth could be temporary. The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence continues to threaten certain jobs, and we can’t afford to be complacent.
We need to focus on retraining and upskilling our workforce to adapt to the changing landscape of the future.
For example, Google offers a “Digital Skills for Africa” program that provides free online training in digital marketing, data analysis, and other skills that are in high demand in the African market.
- Focus on Emotional Intelligence: Many schools and workplaces are incorporating programs that emphasize emotional intelligence, teaching students and employees how to understand and manage their own emotions and those of others. For example, the “EQi-2.0” is a widely used emotional intelligence assessment tool that helps individuals identify their strengths and weaknesses in emotional intelligence and develop strategies for improvement.
The Role of Policy and Education

The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges, particularly in the realm of employment. While AI can automate tasks and create new opportunities, it also raises concerns about job displacement, social inequality, and data privacy.
This necessitates a proactive approach involving government policies, regulations, and investments in education and training to mitigate potential negative impacts and ensure a fair and equitable transition to an AI-driven future.
Ethical Considerations in AI Automation
The ethical considerations surrounding AI automation are complex and multifaceted. Job displacement is a primary concern, as AI systems can automate tasks previously performed by humans, potentially leading to unemployment in certain sectors. This can exacerbate existing social inequalities, as individuals with lower skill levels or limited access to education and training may be disproportionately affected.
Additionally, the use of AI in decision-making processes raises concerns about bias and fairness, as algorithms can perpetuate existing societal biases if not carefully designed and monitored. Data privacy is another crucial concern, as the collection and use of personal data for AI applications raise questions about individual rights and the potential for misuse.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the development and deployment of AI technologies. Policies aimed at mitigating the negative impacts of AI on the workforce include:
- Upskilling and Reskilling Programs:Governments can invest in programs that provide workers with the skills needed to adapt to an AI-driven economy. This could involve funding training programs, apprenticeships, and educational initiatives that focus on in-demand skills such as data analysis, programming, and AI literacy.
- Job Transition Support:Policies can be implemented to support workers who are displaced by AI automation. This could include unemployment benefits, retraining programs, and job placement services.
- Regulation of AI Systems:Regulations can be put in place to ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed responsibly. This could include standards for data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and bias mitigation.
- Investment in Research and Development:Governments can invest in research and development to foster innovation in AI technologies that benefit society as a whole. This includes supporting research on AI safety, ethical considerations, and the development of AI applications that create new jobs and industries.
Investing in Education and Training
Investing in education and training programs is crucial for equipping individuals with the skills needed to thrive in an AI-driven economy. This includes:
- STEM Education:Emphasis should be placed on STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education at all levels, from primary school to higher education. This will provide individuals with the foundational knowledge and skills needed to understand and work with AI technologies.
- AI Literacy:Programs that promote AI literacy for the general public are essential. This includes educating individuals about the potential benefits and risks of AI, as well as the ethical considerations surrounding its use.
- Lifelong Learning:Individuals need to be encouraged to engage in lifelong learning, as the skills needed for success in the future will likely evolve rapidly. This could involve online courses, boot camps, and other flexible learning opportunities.
- Focus on Soft Skills:While technical skills are important, soft skills such as critical thinking, creativity, communication, and collaboration will be increasingly valuable in an AI-driven world. Education and training programs should emphasize these skills to prepare individuals for the future of work.
Outcome Summary
The future of work in an AI-driven world isn’t about robots taking over; it’s about humans and AI working together. By understanding the potential of AI and adapting our skills, we can embrace the opportunities it presents. It’s not about fearing the unknown, but about shaping the future by collaborating with technology to create a more productive, innovative, and fulfilling work environment.