US Inflation Slows to 6.5%, Food and Shelter Drive Prices Up
Us annual inflation rate slows to 6 5 percent food and shelter costs add to price pressures – US annual inflation rate slows to 6.5 percent food and shelter costs add to price pressures. This headline, though seemingly positive, tells a complex story. While the inflation rate has eased slightly, persistent price pressures in key sectors like food and housing continue to strain household budgets and impact the overall economy.
We’ll delve into the factors contributing to this slowdown, analyze the persistent price pressures, and explore the implications for both consumers and businesses.
The recent slowdown in the inflation rate is a welcome development for consumers and businesses alike. However, it’s important to note that the decline is primarily due to a decrease in energy prices, while core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy costs, remains stubbornly high.
This indicates that the underlying inflationary pressures are still present and could potentially re-emerge if energy prices rebound.
Inflation Rate Slowdown
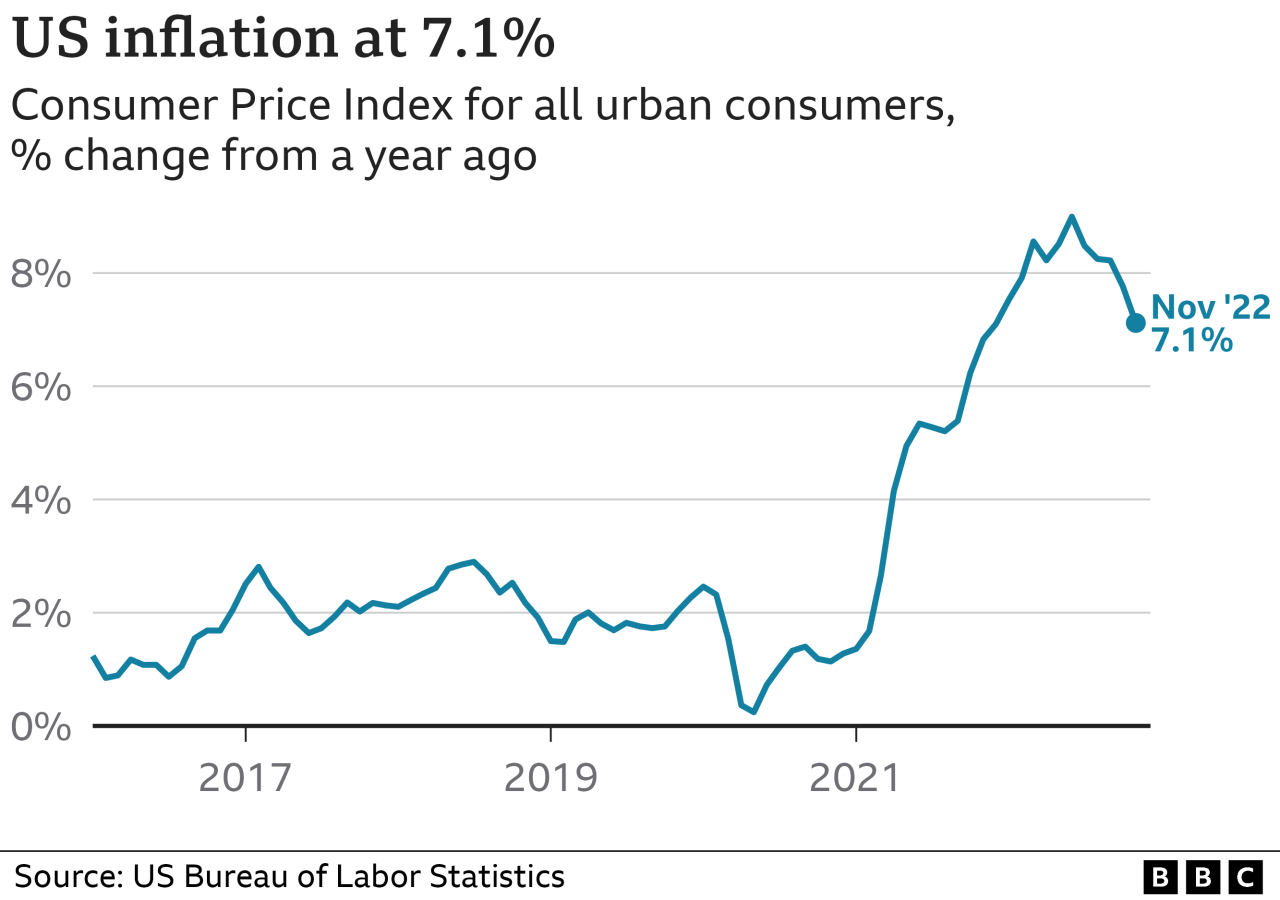
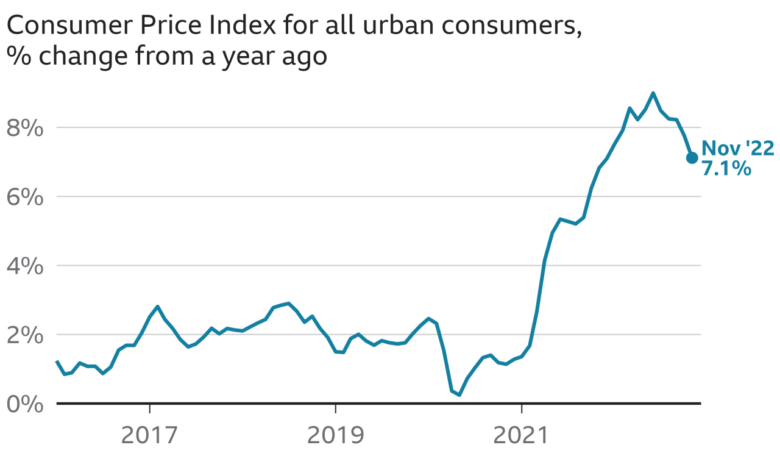
The US annual inflation rate has slowed to 6.5%, marking a significant step down from the peak of 9.1% in June 2022. This slowdown offers a glimmer of hope for consumers and businesses struggling with rising prices, but it remains to be seen whether this trend will continue.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
The slowdown in inflation brings some relief to consumers who have been burdened by rising prices for essential goods and services. Lower inflation means that their purchasing power is gradually recovering, allowing them to stretch their budgets further. Businesses, on the other hand, can benefit from lower input costs, potentially leading to improved profitability and increased investment.
Comparison with Previous Months and Years
The 6.5% inflation rate is a considerable decrease compared to the previous month’s rate of 7.1%. This slowdown is also evident when comparing it to the same period last year, where inflation stood at 7.5%. The trend suggests a gradual easing of inflationary pressures, but it’s important to note that the rate remains above the Federal Reserve’s target of 2%.
The US annual inflation rate has slowed to 6.5 percent, but that doesn’t mean we’re out of the woods yet. Food and shelter costs continue to drive up prices, putting a strain on household budgets. Meanwhile, Elon Musk, known for his chaotic leadership style, announced he will step down as Twitter CEO , though he’ll remain involved in key operations.
It’s unclear how this will impact the platform’s future, but it’s a reminder that even with inflation easing, we’re still navigating a volatile economic landscape.
Factors Contributing to the Slowdown
Several factors have contributed to the slowdown in inflation, including:
- Easing Supply Chain Bottlenecks:Supply chain disruptions, which had exacerbated inflation, have started to ease, leading to improved availability of goods and reduced price pressures.
- Declining Energy Prices:Energy prices, a major contributor to inflation, have declined in recent months due to factors such as increased oil production and reduced demand.
- Federal Reserve’s Interest Rate Hikes:The Federal Reserve’s aggressive interest rate hikes have aimed to curb inflation by slowing down economic growth and reducing consumer spending.
Persistent Price Pressures
While the headline-grabbing annual inflation rate has slowed, underlying price pressures remain a significant concern for the US economy. These persistent pressures are driven by a combination of factors, making it difficult to predict when they will subside.
Food and Shelter Costs
Food and shelter costs are key drivers of inflation, accounting for a significant portion of consumer spending. Food prices have been pushed up by a range of factors, including supply chain disruptions, increased demand, and rising energy costs for farmers.
Shelter costs, particularly rents, have also risen sharply due to strong demand and limited housing supply.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The ongoing global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine, have significantly impacted prices. These disruptions have led to shortages of key goods, increased transportation costs, and delays in production and delivery. As a result, businesses have been forced to raise prices to offset these added costs.
The impact of supply chain disruptions on inflation is significant, as it affects the prices of a wide range of goods and services.
Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions on Price Increases
The impact of supply chain disruptions on price increases is significant, as it affects the prices of a wide range of goods and services. For example, the shortage of semiconductor chips has led to higher prices for cars and other electronic devices.
It’s tough to see the US annual inflation rate slow to 6.5%, especially with food and shelter costs still climbing. It feels like everything is getting more expensive, and it’s hard to plan for the future when prices are so volatile.
But on a brighter note, it’s good to see operations resuming gradually after all flights were grounded across the US by a federal agency. This news brings a sense of normalcy back to our lives, which is always a welcome change.
Hopefully, with these disruptions behind us, we can start to see some stability in the economy, even if it’s just a little bit.
The war in Ukraine has disrupted global wheat and energy markets, driving up food and fuel prices.
Potential for Continued Price Pressures, Us annual inflation rate slows to 6 5 percent food and shelter costs add to price pressures
While the recent slowdown in inflation offers some hope, it is too early to declare victory. Persistent supply chain disruptions, coupled with ongoing geopolitical tensions, suggest that price pressures may continue for some time. Additionally, the Federal Reserve’s efforts to combat inflation through interest rate hikes could lead to slower economic growth, potentially impacting consumer spending and exacerbating price pressures.
Economic Outlook
The recent slowdown in the annual inflation rate to 6.5 percent provides a glimmer of hope for the economy. However, persistent price pressures, particularly in food and shelter, suggest that the battle against inflation is far from over. This development has significant implications for the overall economic outlook, particularly with regard to the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy and the impact on consumer spending and business investment.
Potential Adjustments to Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability and full employment. With inflation still above its target range, the Fed is likely to continue raising interest rates in the coming months to cool down the economy and curb inflation.
However, the recent slowdown in inflation could lead to a less aggressive approach, with smaller rate hikes or even a pause in rate increases depending on future economic data.
The Fed’s decisions on interest rates will be guided by a variety of factors, including the trajectory of inflation, the strength of the labor market, and the overall economic outlook.
Impact on Consumer Spending and Business Investment
Inflation has a significant impact on consumer spending and business investment. High inflation erodes purchasing power, leading to a decline in consumer spending. Businesses, on the other hand, face higher input costs, which can lead to reduced investment and hiring.
The recent slowdown in inflation could provide some relief to consumers and businesses, boosting spending and investment. However, the persistent price pressures in key sectors like food and shelter could continue to weigh on consumer and business sentiment.
Potential for Economic Growth
The economic outlook for the coming months is uncertain. While the recent slowdown in inflation provides some optimism, persistent price pressures and the potential for further interest rate hikes from the Federal Reserve could dampen economic growth.
The strength of the labor market, consumer confidence, and business investment will play a crucial role in determining the trajectory of economic growth.
The news about the US annual inflation rate slowing to 6.5 percent, while a positive sign, is still a concern for many Americans. Food and shelter costs continue to add pressure to household budgets, and it’s clear that the economic recovery is fragile.
It’s against this backdrop that the recent controversy surrounding CNN’s Jake Tapper, who has been accused of lying about GOP candidate Sean Parnell, critics blast cnns jake tapper for lying after claim about gop candidate sean parnell , is particularly troubling.
This incident highlights the importance of accurate reporting, especially when it comes to issues that directly impact people’s lives.
Consumer Impact
Inflation directly impacts household budgets and purchasing power, forcing consumers to adapt their spending habits. This section explores how inflation affects consumers, including strategies to manage rising prices and the potential for changes in consumer behavior.
Impact on Household Budgets and Purchasing Power
Inflation erodes the value of money, meaning that the same amount of money buys fewer goods and services over time. This decline in purchasing power can significantly impact household budgets, especially for those with fixed incomes or limited financial resources.
For instance, rising food and energy prices can disproportionately affect lower-income households, forcing them to make difficult choices between essential needs.
Strategies for Managing Rising Prices
Consumers can employ various strategies to manage rising prices and protect their purchasing power. These include:
- Budgeting and Financial Planning:Creating a detailed budget and tracking expenses can help consumers identify areas where they can cut back or find more affordable alternatives. This can involve prioritizing essential needs, reducing discretionary spending, and exploring cost-saving options like meal planning or using public transportation.
- Seeking Out Deals and Discounts:Taking advantage of sales, coupons, and loyalty programs can help consumers save money on everyday purchases. Online platforms and apps provide tools for comparing prices and finding the best deals on groceries, electronics, and other goods.
- Negotiating Prices:Consumers can try to negotiate lower prices on services like utilities, insurance, or even rent. This may require research and preparation, but it can lead to significant savings over time.
- Investing in Assets:Investing in assets that appreciate in value, such as real estate or stocks, can help hedge against inflation. However, it’s important to consult with a financial advisor and understand the risks involved before making any investment decisions.
Impact on Consumer Confidence and Spending Habits
High inflation can erode consumer confidence, leading to reduced spending and economic uncertainty. Consumers may delay major purchases like cars or appliances, opt for cheaper alternatives, or save more money due to concerns about future price increases. This can create a vicious cycle, where lower consumer spending further slows economic growth.
Changes in Consumer Behavior
In response to rising prices, consumers may adopt new behaviors to stretch their budgets and adapt to the changing economic landscape. These changes can include:
- Shifting to Cheaper Alternatives:Consumers may switch from brand-name products to generic brands or explore less expensive options for goods and services.
- Increased DIY Activities:With rising costs for services, consumers may choose to perform tasks like home repairs or landscaping themselves to save money.
- Emphasis on Sustainability:Rising prices for essential goods like food and energy can drive consumers to adopt more sustainable practices, such as growing their own food or reducing energy consumption.
- Increased Demand for Value:Consumers may prioritize value over brand recognition, seeking products that offer the best quality at the most affordable price.
Epilogue: Us Annual Inflation Rate Slows To 6 5 Percent Food And Shelter Costs Add To Price Pressures
The recent slowdown in inflation provides a glimmer of hope, but the persistent price pressures in food and shelter highlight the ongoing challenges facing the economy. Consumers continue to feel the strain of rising prices, and businesses are navigating a complex environment of rising costs and uncertain demand.
As the Federal Reserve grapples with the appropriate monetary policy response, the coming months will be crucial in determining the trajectory of inflation and its impact on the broader economy.