Economy Tops Voters Minds in Midterm Election
98 percent of voters say economy will be important in their midterm vote, according to a recent poll. This overwhelming sentiment highlights the central role that economic concerns are playing in the upcoming election. The state of the economy, with its fluctuating inflation, unemployment, and wage growth, is a dominant factor shaping voter behavior and the political landscape. This article delves into the intricacies of how economic factors are influencing voters’ decisions and the potential impact on the midterm elections.
From the rising cost of living to concerns about job security, voters are feeling the strain of economic uncertainty. This has led to a heightened focus on economic issues, prompting candidates to prioritize economic policies in their campaigns. The economic climate has become a key battleground, with political parties vying for voters’ support by outlining their respective economic plans and emphasizing their ability to address the challenges facing the nation.
Economic Factors Driving Voter Sentiment: 98 Percent Of Voters Say Economy Will Be Important In Their Midterm Vote
The upcoming midterm elections are shaping up to be a referendum on the economy, with voters expressing significant concern about rising prices, job security, and their financial well-being. These economic anxieties are likely to play a pivotal role in determining the outcome of the elections.
Key Economic Indicators Influencing Voter Concerns, 98 percent of voters say economy will be important in their midterm vote
The current economic climate is characterized by a number of factors that are likely to influence voter sentiment. These include:
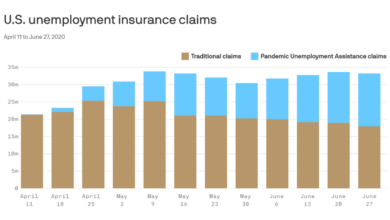
- Inflation: The Consumer Price Index (CPI), a key measure of inflation, has risen significantly in recent months, eroding purchasing power and putting pressure on household budgets. For example, the CPI rose by 8.5% in March 2023, marking the highest level in over 40 years.
- Unemployment: While unemployment rates have generally declined in recent years, concerns about job security remain. The Bureau of Labor Statistics reported an unemployment rate of 3.6% in March 2023, a relatively low level, but there are still concerns about potential job losses and wage stagnation.
- Wage Growth: Wage growth has not kept pace with inflation, leading to a decline in real wages. This means that workers are earning less in terms of purchasing power despite nominal wage increases.
Impact of Economic Factors on Voter Behavior
The economic factors discussed above are likely to have a significant impact on voter behavior in the upcoming midterm elections.
- Inflation: High inflation is likely to motivate voters to support candidates who promise to address rising prices and protect their purchasing power. This could lead to increased support for candidates who advocate for policies that aim to reduce inflation, such as fiscal restraint or supply chain reforms.
- Unemployment: Concerns about job security and potential job losses could lead voters to support candidates who promise to create jobs and support economic growth. This could translate into increased support for candidates who advocate for policies that promote job creation, such as infrastructure investments or tax cuts for businesses.
- Wage Growth: Stagnant wages and the decline in real wages could motivate voters to support candidates who promise to increase wages and improve the standard of living for working families. This could lead to increased support for candidates who advocate for policies that raise the minimum wage, strengthen unions, or provide tax breaks for low- and middle-income families.
Policies and Events Contributing to the Economic Climate
A number of policies and events have contributed to the current economic climate and are likely to influence voter sentiment. These include:
- The COVID-19 Pandemic: The pandemic had a significant impact on the economy, leading to widespread business closures, supply chain disruptions, and increased demand for goods and services. These factors contributed to the surge in inflation that we are currently experiencing.
- Government Spending: The government’s response to the pandemic included significant spending programs, such as the CARES Act, which provided economic relief to individuals and businesses. While these programs helped to mitigate the economic impact of the pandemic, they also contributed to the increase in inflation.
- The War in Ukraine: The war in Ukraine has further disrupted global supply chains and driven up energy prices, adding to inflationary pressures.
Political Implications of Economic Concerns

The economy is a dominant factor shaping the political landscape, particularly during midterm elections. Voter sentiment regarding economic conditions significantly influences their choices, often leading to shifts in political power. Understanding how economic concerns impact voters’ decisions is crucial for analyzing election outcomes and predicting future political trends.
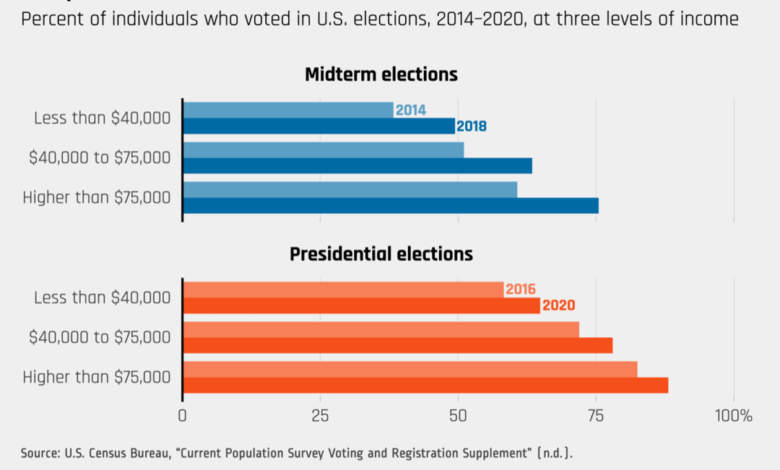
Impact of Economic Concerns on Voter Turnout
The level of economic anxiety directly affects voter turnout. When the economy is performing poorly, voters are more likely to feel motivated to participate in elections, hoping for a change in leadership or policy. Conversely, during periods of economic prosperity, voter turnout tends to be lower as people feel less urgency to participate in the political process. For instance, the 2010 midterm elections witnessed a surge in voter turnout, largely attributed to the ongoing economic recession and widespread dissatisfaction with the incumbent administration.
Similarly, the 2018 midterms saw a significant increase in voter participation, driven by concerns about economic inequality, healthcare costs, and immigration policies.
Impact of Economic Concerns on Election Results
Economic issues play a central role in shaping election outcomes. Voters often view elections as a referendum on the incumbent party’s economic performance. If the economy is struggling, voters may be more inclined to vote for the opposing party, hoping for a change in economic policies. A notable example is the 2008 presidential election, where the economic recession played a significant role in Barack Obama’s victory over John McCain.
It’s no surprise that 98 percent of voters say the economy will be a major factor in their midterm vote. After all, rising inflation and gas prices are impacting everyone’s wallets. But while voters are focused on their pocketbooks, it’s concerning to learn that over 50 Biden administration employees from 12 US agencies were involved in pushing documents related to social media censorship as reported here.
This raises serious questions about government overreach and the potential for manipulation of public discourse. It’s crucial for voters to be aware of these issues as they head to the polls, as they could have a significant impact on the future of our country.
Obama campaigned on a platform of economic change, promising to address the financial crisis and stimulate the economy.
It’s no surprise that 98 percent of voters say the economy will be a major factor in their midterm vote. With inflation soaring and the cost of living rising, people are understandably concerned about their financial futures. However, the news of Hurricane Ian strengthening to an extremely dangerous Category 4 as Florida braces for impact is a stark reminder that even the most pressing economic issues can be overshadowed by immediate, life-altering events.
It’s a tragic situation that will undoubtedly have a ripple effect on the economy, further complicating the issues voters are already facing.
Comparison of Political Party Positions on Economic Issues
The two major political parties in the United States, the Democrats and Republicans, often hold contrasting views on economic issues.
- Democrats generally advocate for government intervention in the economy, promoting policies like increased social programs, labor regulations, and tax increases on high earners. They argue that these measures create a fairer and more equitable society, providing a safety net for vulnerable populations and stimulating economic growth.
- Republicans, on the other hand, tend to favor a more hands-off approach to the economy, emphasizing free market principles, tax cuts, deregulation, and limited government spending. They believe that these policies promote economic growth and individual opportunity.
The positions of these parties on economic issues can significantly influence voter preferences. Voters who prioritize social welfare programs, government regulation, and income equality are more likely to support Democratic candidates. In contrast, voters who prioritize economic growth, individual liberty, and lower taxes may lean towards Republican candidates.
It’s no surprise that 98 percent of voters say the economy will be a major factor in their midterm vote. After all, rising inflation and gas prices are impacting everyone’s wallets. But amidst the economic concerns, senators are now demanding answers from Mark Zuckerberg about Facebook’s alleged suppression of information related to Hunter Biden’s laptop.
This revelation could have major implications for the election, potentially shifting the focus away from economic issues. It’s clear that the midterm elections will be a battleground for both economic and political agendas.
Historical Context and Trends
The influence of economic conditions on midterm elections is a well-documented phenomenon in American politics. Throughout history, voters have consistently demonstrated a tendency to hold the incumbent party accountable for the state of the economy, particularly during midterm elections. Understanding these historical trends can provide valuable insights into the current political landscape and the potential impact of economic factors on the upcoming midterm elections.
Historical Examples of Economic Influence
The historical record offers numerous examples of how economic conditions have swayed midterm election outcomes. For instance, the 1994 midterm elections saw Republicans gain control of both houses of Congress, a shift largely attributed to voter dissatisfaction with the economic performance under President Bill Clinton. Similarly, the 2010 midterm elections resulted in a Republican wave, fueled by concerns about the economic recession and the Affordable Care Act.
These examples highlight the potent influence of economic sentiment on voter behavior, particularly during midterm elections.
Patterns and Trends in Past Elections
Analysis of past midterm elections reveals recurring patterns and trends related to economic concerns. A consistent finding is that voters tend to punish the incumbent party when the economy is performing poorly. This “retrospective voting” phenomenon suggests that voters hold the party in power accountable for economic outcomes, regardless of external factors.
“Voters are more likely to vote against the incumbent party when they perceive the economy to be in poor shape.”
Political Science Research
Furthermore, specific economic indicators, such as unemployment rates, inflation, and consumer confidence, have been shown to correlate with midterm election outcomes. Studies have found that higher unemployment rates and inflation tend to favor the challenger party, while strong economic growth and low unemployment rates often benefit the incumbent party.
Comparison to Previous Midterm Election Cycles
The current economic climate presents a complex picture, with both positive and negative indicators. While the unemployment rate remains relatively low, inflation has risen to a 40-year high, and concerns about a potential recession persist. This combination of factors makes it difficult to definitively predict the impact of the economy on the upcoming midterm elections.
“The current economic climate is a mixed bag, with both positive and negative indicators.”
Economic Analysis Report
However, historical trends suggest that voters are likely to focus on economic concerns, particularly inflation and the potential for a recession. This suggests that the economy could play a significant role in shaping the outcome of the midterm elections.
Impact on Specific Policy Areas
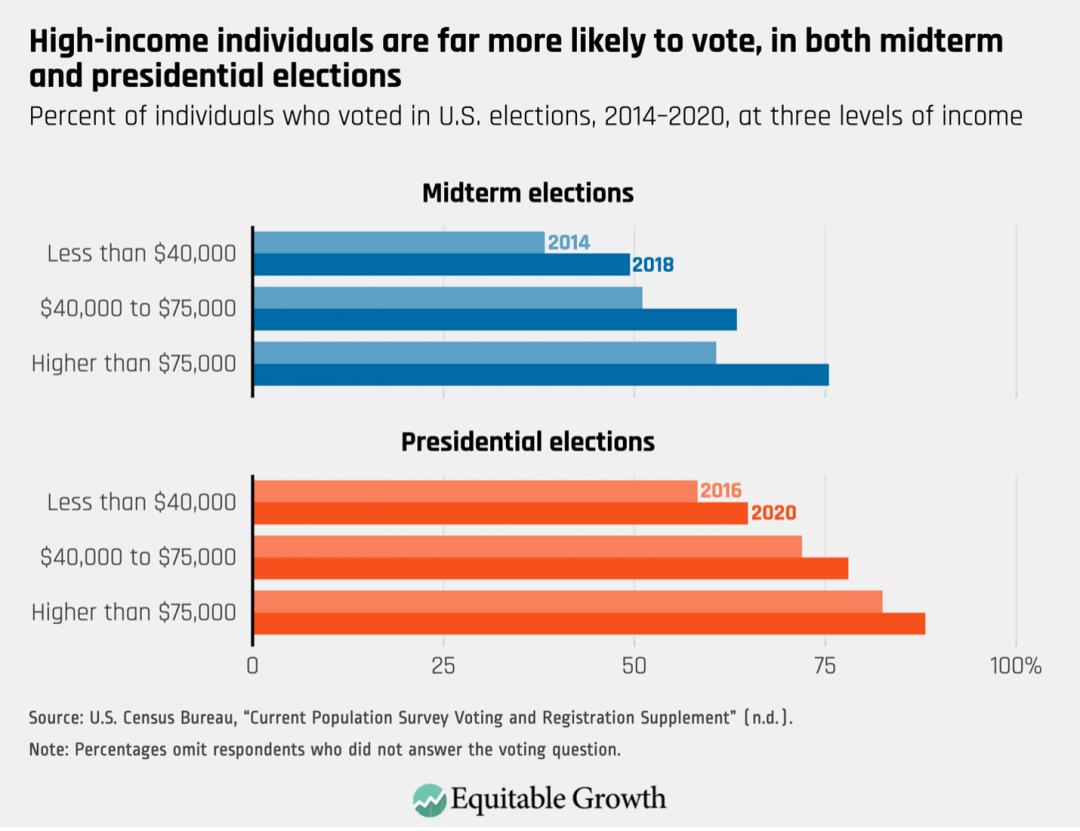
Economic anxieties can significantly influence voters’ preferences for specific policy areas. When voters prioritize economic stability, their choices can have a ripple effect on how government resources are allocated and policies are implemented.
Healthcare
Economic instability can lead to increased healthcare costs and reduced access to care. As unemployment rises, people may lose employer-sponsored health insurance. Additionally, state and local governments may face budget cuts, impacting funding for public health programs. This could lead to:
- Higher healthcare costs: As individuals struggle to afford health insurance premiums and copays, the demand for affordable care could increase, putting pressure on healthcare providers to raise prices.
- Reduced access to care: Fewer people may be able to afford necessary medical treatments, leading to delayed care and potential health complications.
- Cuts to public health programs: State and local governments may face budget cuts, impacting funding for public health programs, such as preventive care, mental health services, and disease control efforts.
Education
Education funding is often one of the first areas to be cut during economic downturns. This can lead to larger class sizes, reduced teacher salaries, and fewer resources for students. The consequences of these cuts can be far-reaching, impacting future generations.
- Reduced funding for schools: State and local governments may be forced to cut education budgets, leading to larger class sizes, fewer teachers, and limited access to resources.
- Lower student achievement: Reduced funding and resources can negatively impact student achievement, leading to lower test scores and graduation rates.
- Increased inequality: Economic downturns can disproportionately affect students from low-income families, exacerbating educational inequalities.
Infrastructure
Investing in infrastructure is crucial for economic growth, but these projects often face budget constraints during economic downturns. This can lead to deferred maintenance, inadequate repairs, and a decline in the overall quality of infrastructure.
- Deferred maintenance: Economic instability can lead to delayed repairs and maintenance of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure, resulting in safety hazards and increased costs in the long run.
- Reduced investment in new projects: Governments may prioritize immediate needs over long-term infrastructure projects, leading to a decline in investment and economic growth.
- Impact on transportation and logistics: Poor infrastructure can negatively impact transportation and logistics, leading to increased costs for businesses and consumers.
As the midterm elections approach, the economy will continue to be a defining issue for voters. The impact of economic concerns on voter turnout and election results is undeniable. The political landscape is being reshaped by the economic climate, and candidates are keenly aware of the need to address voters’ anxieties and concerns. The outcome of the midterm elections will likely be heavily influenced by how effectively candidates address the economic issues that are top of mind for voters.