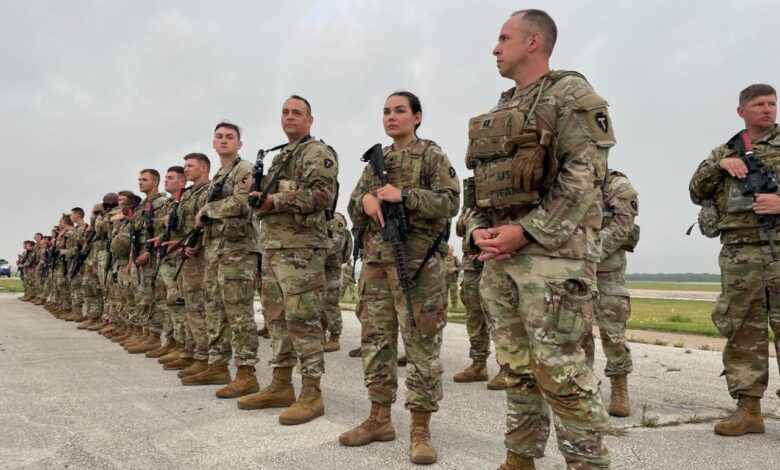
50 Governors Oppose Federal Plan: National Guard Power Grab?
50 governors oppose federal plan to move national guard units power grab – 50 Governors Oppose Federal Plan: National Guard Power Grab? This headline has sparked heated debate across the nation, as states grapple with the potential implications of a federal plan to reshape the National Guard. The proposal, which aims to centralize control over these units, has ignited a fierce battle over states’ rights and federal authority.
At the heart of the controversy lies the fundamental question of who ultimately commands the National Guard: the individual states or the federal government?
This plan, which would shift the National Guard’s command structure, has ignited a firestorm of opposition from governors across the political spectrum. Their concerns are multifaceted, ranging from potential federal overreach to the erosion of state autonomy. This move, they argue, could have far-reaching consequences for the way states respond to natural disasters, maintain domestic security, and even participate in national defense.
The debate raises crucial questions about the balance of power between the federal government and the states, and the potential implications for the very fabric of our nation’s federalism.
The Federal Plan: 50 Governors Oppose Federal Plan To Move National Guard Units Power Grab
The recent proposal by the federal government to shift the command structure of National Guard units has ignited a firestorm of controversy, with 50 governors voicing their opposition. The plan, which aims to centralize control over these units, has been met with fierce resistance, raising concerns about federal overreach and its potential implications for states’ rights and the delicate balance of federalism.
The Federal Plan’s Objectives
The federal plan proposes to transfer the authority to activate and deploy National Guard units from individual state governors to the federal government. This shift would effectively remove the governors’ direct control over these units, placing them under the command of the Department of Defense.
The rationale behind this proposal is to streamline the mobilization process and enhance coordination during national emergencies.
Implications for States’ Rights and Federalism
The potential implications of this plan for states’ rights and federalism are significant. Governors argue that this move represents a dangerous encroachment on their constitutional authority, undermining the principle of federalism that divides power between the federal and state governments.
They emphasize that the National Guard has traditionally served as a critical component of state sovereignty, providing vital support during natural disasters, civil unrest, and other emergencies. Transferring control to the federal government, they argue, would weaken states’ ability to respond effectively to such situations.
Governors’ Concerns About Federal Overreach
The 50 governors who oppose the plan have voiced a range of concerns about federal overreach. They argue that the plan would:
- Undermine State Sovereignty:The governors contend that the plan would erode the traditional role of the National Guard in state affairs, diminishing their ability to protect their citizens and manage their own affairs.
- Create a Centralized Command Structure:The plan, they argue, would establish a centralized command structure that could lead to inefficient decision-making and a lack of responsiveness to local needs.
- Reduce Flexibility and Adaptability:By removing governors’ control, the plan would reduce the flexibility and adaptability of the National Guard in responding to specific local situations.
- Increase the Risk of Political Interference:Governors express concerns that the plan could create opportunities for political interference in the deployment of National Guard units, potentially undermining their neutrality and impartiality.
National Guard
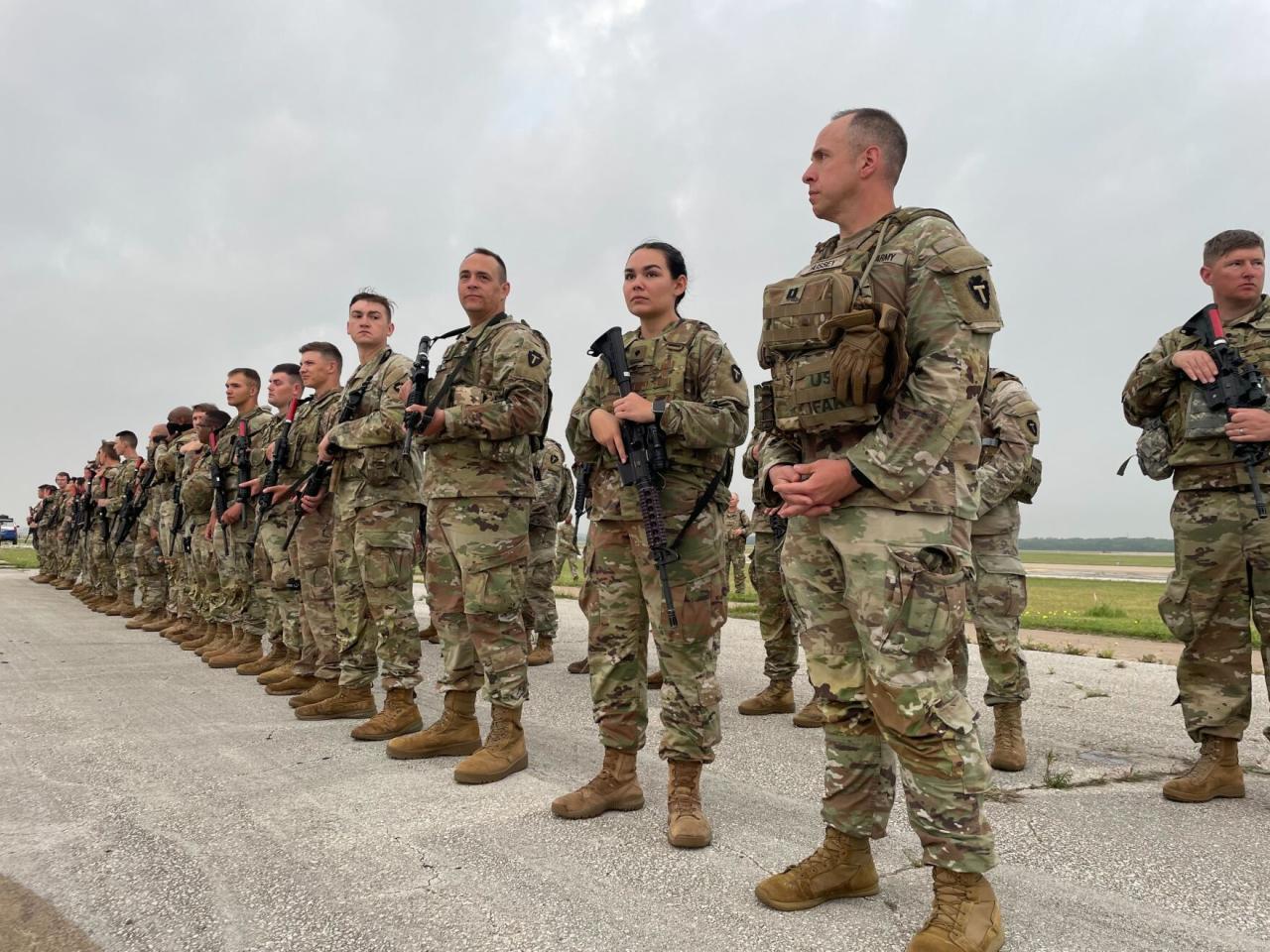

The National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces, consisting of both Army and Air National Guard units. It is a unique force with a dual mission: supporting state and federal authorities in times of need.The National Guard’s history is deeply intertwined with the development of the United States.
Established in 1791, the National Guard was initially organized as a militia force, primarily responsible for maintaining order and security within states. Over time, its role evolved, becoming increasingly integrated with the regular military, especially during times of war or national crisis.
Roles and Responsibilities
The National Guard’s multifaceted nature allows it to play a vital role in various scenarios, from disaster relief to national defense. Its unique position, as both a state and federal asset, makes it a valuable resource for addressing diverse challenges.
It’s fascinating to see how power dynamics play out on both a national and local level. While 50 governors are pushing back against the federal government’s attempt to centralize control of National Guard units, a similar power struggle is unfolding in the car market, where car dealers are raising prices while automakers try to rein them in , leaving consumers caught in the middle.
It’s a reminder that regardless of the scale, power struggles often result in unintended consequences for those at the bottom of the hierarchy.
Disaster Relief
The National Guard plays a crucial role in responding to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods. They provide vital support in search and rescue operations, evacuations, and the distribution of essential supplies.
- During Hurricane Katrina in 2005, the National Guard was deployed to Louisiana and Mississippi, providing critical assistance with rescue, evacuation, and security operations.
- Following the 2010 earthquake in Haiti, National Guard units were dispatched to provide medical aid, logistics support, and engineering expertise.
Domestic Security
The National Guard can be activated by the governor of a state to assist with law enforcement in situations involving civil unrest, riots, or major crime events. However, the use of the National Guard for domestic security purposes is often controversial, raising concerns about the potential for militarization of law enforcement.
- During the 1992 Los Angeles riots, the National Guard was deployed to restore order and protect property.
- In recent years, the National Guard has been increasingly used to support law enforcement during protests, raising concerns about the potential for excessive force and violations of civil liberties.
National Defense
The National Guard also serves as a critical component of the nation’s defense force. In times of war or national emergency, National Guard units can be mobilized to support the regular military in combat operations, providing additional manpower and specialized skills.
- During the Iraq and Afghanistan wars, National Guard units were deployed alongside regular Army and Air Force units, contributing significantly to combat operations.
- The National Guard also plays a crucial role in national defense by providing training and readiness support to the regular military.
State vs. Federal Authority
The debate surrounding the National Guard’s role in national security and state autonomy has been a recurring theme in American history. The issue of federal versus state authority over the National Guard, a force that operates under both jurisdictions, often arises during times of crisis or national emergency.
This dynamic relationship is governed by a complex legal framework that seeks to balance the need for national security with the preservation of state sovereignty.
The news about 50 governors opposing the federal plan to move National Guard units has been a hot topic lately, and it’s got me thinking about how important it is to have a strong, adaptable infrastructure, especially in the face of such changes.
That’s why I’m a big advocate for using React JS for web development – it’s incredibly flexible and allows for building dynamic and responsive user interfaces, which are crucial in today’s ever-changing digital landscape. Check out this article to learn more about why React JS is the way to go.
With its component-based architecture, React JS makes it easier to manage complex projects, and that’s exactly what we need when dealing with issues like the potential power grab over the National Guard.
Historical Instances of Conflict
The history of the National Guard is replete with instances where state and federal authority have clashed. These conflicts often stem from differing interpretations of the legal framework governing the Guard’s deployment and control.
- The Civil War:The Civil War witnessed a stark divide between the Union and Confederate states regarding the National Guard. Southern states, under the leadership of President Jefferson Davis, sought to use their National Guard units to secede from the Union, leading to a direct conflict with federal authority.
The federal government, under President Abraham Lincoln, asserted its right to call upon the National Guard to suppress the rebellion. This conflict ultimately solidified the federal government’s supremacy over the National Guard during times of national emergency.
- The Civil Rights Era:During the Civil Rights Movement, the National Guard was often deployed to quell racial unrest and enforce desegregation orders. In 1957, President Dwight Eisenhower deployed the 101st Airborne Division to Little Rock, Arkansas, to enforce federal court orders that mandated the integration of Central High School.
This deployment sparked controversy, as some argued that the federal government was overstepping its bounds by using the National Guard to enforce civil rights legislation.
- Hurricane Katrina:The response to Hurricane Katrina in 2005 highlighted the complexities of federal-state coordination in disaster relief. The slow and inadequate federal response, coupled with the perceived lack of coordination with state and local authorities, led to widespread criticism of the federal government’s handling of the disaster.
The aftermath of Hurricane Katrina prompted calls for greater federal oversight and control over the National Guard during natural disasters, raising concerns about the potential for federal overreach.
Legal Framework Governing the National Guard
The legal framework governing the National Guard is complex and multifaceted, drawing from both the Constitution and federal legislation. The National Guard is primarily governed by the following:
- The Constitution:The Constitution grants states the power to maintain a militia, which is the basis for the National Guard. The Second Amendment of the Constitution also states that “A well regulated Militia, being necessary to the security of a free State, the right of the people to keep and bear Arms, shall not be infringed.” The National Guard, as a state-based militia, is therefore seen as a key element of the Constitution’s vision for a well-regulated militia.
The fight against federal overreach continues, with 50 governors opposing the plan to move National Guard units. It seems like every day we hear something new that makes us question the direction our country is heading. For example, a GOP congressional candidate recently made headlines for stating that abortion is a human sacrifice to demons.
This type of rhetoric is concerning, and it highlights the importance of standing up for our rights and values. The governors’ opposition to the National Guard plan is a positive step in the right direction, but we need to stay vigilant and continue fighting for our freedoms.
- The Militia Act of 1903:This act formally established the National Guard as a reserve component of the U.S. military. The Militia Act created a dual system of control, with the National Guard serving under both state and federal authority. The act also established the National Guard Bureau, a federal agency responsible for overseeing the National Guard’s training and equipping.
- The National Guard and Reserve Forces Mobilization Act of 1988:This act codified the president’s authority to federalize the National Guard, meaning that the president can take control of National Guard units for federal purposes. The act also Artikeld the process for federalizing the Guard, including the requirement for congressional approval in certain circumstances.
Arguments for and Against Increased Federal Control
The debate over federal versus state authority over the National Guard often centers on two main arguments: national security and state autonomy.
- National Security:Proponents of increased federal control argue that it is necessary to ensure national security, especially during times of crisis or national emergency. They contend that a centralized command structure is essential for effective mobilization and coordination of the National Guard in response to national threats.
They also argue that federal control can help to standardize training and equipment, ensuring that National Guard units are adequately prepared to meet national security challenges.
- State Autonomy:Opponents of increased federal control argue that it undermines state sovereignty and autonomy. They believe that the National Guard should primarily be under the control of state governors, who are more familiar with local conditions and needs. They also argue that federal control could lead to the politicization of the National Guard, as presidents may use it for partisan purposes.
Political Dimensions
The federal plan to shift control of National Guard units from states to the federal government is a highly contentious issue with significant political ramifications. This move has sparked fierce debate, fueled by differing political ideologies and the potential impact on the upcoming elections.
Understanding the political motivations behind this plan and its potential consequences is crucial to navigating this complex issue.
Potential Political Motivations
The federal plan’s origins can be traced to the current political climate, where tensions between the federal government and individual states have escalated. This plan is likely driven by a desire to centralize power and control, potentially giving the federal government greater influence over national security and disaster response.
The potential implications for upcoming elections are significant, as this move could be seen as an attempt to solidify federal control and influence the outcome of future elections.
Consequences for the Relationship Between the Federal Government and States
The plan’s implementation could have profound consequences for the relationship between the federal government and individual states. This shift in authority could be perceived as a power grab by the federal government, potentially leading to increased friction and distrust between the two levels of government.
States, particularly those with differing political ideologies, may view this move as an infringement on their sovereignty and autonomy, further exacerbating existing political divides.
Key Stakeholders Involved
This debate involves various key stakeholders, each with their own vested interests. The two major political parties, Democrats and Republicans, are likely to take opposing stances on this issue, with Democrats potentially supporting the federal plan and Republicans opposing it.
Government agencies, such as the Department of Defense and the Department of Homeland Security, are likely to be involved in implementing the plan, while interest groups representing state governments, military veterans, and national security experts will likely engage in advocacy and lobbying efforts.
Potential Impacts
The proposed federal plan to centralize control of the National Guard carries significant implications for state governments, national security, and individual citizens. This shift in authority could lead to a range of consequences, both intended and unintended.
Impact on State Governments
The federal plan’s impact on state governments is a complex issue with far-reaching implications. Here’s a table summarizing some of the potential consequences:
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced State Autonomy | States may lose control over their National Guard units, impacting their ability to respond effectively to local emergencies and disasters. |
| Increased Federal Oversight | Federal authorities may have greater control over the deployment and use of National Guard units, potentially leading to a decrease in state responsiveness to local needs. |
| Financial Implications | States may face increased costs associated with federal oversight and compliance with federal regulations regarding the National Guard. |
| Political Tensions | The plan could lead to increased tensions between state and federal governments over the control of the National Guard. |
Impact on National Security
The federal plan’s impact on national security is a multifaceted issue with potential benefits and drawbacks. Here are some potential implications:
- Enhanced National Coordination: Centralized control could improve national coordination of National Guard units during national emergencies or large-scale deployments.
- Potential for Reduced Local Responsiveness: The federal government’s focus on national security could lead to a decrease in the responsiveness of National Guard units to local emergencies.
- Potential for Increased Bureaucracy: The centralization of control could lead to increased bureaucracy and potentially slower decision-making processes during emergencies.
Impact on Individual Citizens
The federal plan’s impact on individual citizens is a critical consideration. Here’s a summary of potential consequences:
- Reduced Access to Local Resources: The plan could reduce the availability of National Guard units for local emergencies, potentially impacting citizens’ safety and well-being during disasters.
- Potential for Increased Military Presence: The plan could lead to an increased military presence in communities, potentially raising concerns about privacy and civil liberties.
- Potential for Political Polarization: The plan could exacerbate political divisions and contribute to a sense of distrust between citizens and government institutions.
Timeline of Events
The federal plan’s development has been marked by several key developments and statements from relevant officials. Here’s a timeline outlining these events:
- [Date]: The federal government first announced its proposal to centralize control of the National Guard.
- [Date]: Several governors expressed their opposition to the plan, arguing that it would undermine state autonomy and compromise national security.
- [Date]: The federal government issued a statement reiterating its commitment to the plan, emphasizing the need for national coordination during emergencies.
- [Date]: Congress held hearings on the federal plan, with testimony from state officials, military experts, and civil liberties groups.
- [Date]: The federal government announced its intention to move forward with the plan, despite ongoing opposition from state governments.
- [Date]: Several states filed lawsuits challenging the legality of the federal plan, arguing that it violates the Tenth Amendment to the Constitution.
- [Date]: The federal plan is expected to be implemented, with potential for further legal challenges and political debate.
Potential Solutions, 50 governors oppose federal plan to move national guard units power grab
Resolving the conflict between state and federal authority over the National Guard requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some potential solutions:
- Legal Approaches:
- States could file lawsuits challenging the constitutionality of the federal plan, arguing that it violates the Tenth Amendment’s principle of state sovereignty.
- Congress could pass legislation clarifying the respective roles and responsibilities of the federal government and states regarding the National Guard.
- Political Approaches:
- State and federal officials could engage in dialogue and negotiation to find a compromise that respects the interests of both parties.
- Public awareness campaigns could educate citizens about the implications of the federal plan and encourage them to engage in the political process.
Closing Notes
The debate surrounding the federal plan to shift control of the National Guard is far from over. As states continue to push back against the proposal, the future of this vital institution remains uncertain. The outcome will likely have profound implications for the relationship between the federal government and individual states, and the role of the National Guard in our national security framework.
This is a story that will continue to unfold, with significant implications for the future of American governance.