Trump Claims Fed is Failing as Global Rates Tumble
Fed is failing says trump as global rates tumble – “Fed is failing says Trump as global rates tumble”
-this bold statement, echoing across the financial landscape, has sparked intense debate and scrutiny. Trump’s pronouncements about the Federal Reserve are not new, but their timing amidst a global economic downturn has raised eyebrows. As interest rates slide downwards in major economies, the world watches to see if this trend signals a shift in global economic fortunes, or if it simply reflects a response to changing economic conditions.
This article delves into the complexities of Trump’s statement, examining the current global interest rate trends, the Fed’s role in influencing these rates, and the potential economic implications. We’ll also explore the impact of these developments on financial markets, shedding light on the potential risks and opportunities presented by this dynamic situation.
Global Interest Rate Trends: Fed Is Failing Says Trump As Global Rates Tumble
Global interest rates have been on a roller coaster ride in recent years, influenced by a complex interplay of factors such as inflation, economic growth, and central bank policies. Understanding these trends is crucial for investors, businesses, and policymakers alike.
Trump’s claims of the Fed failing amidst global rate tumbles seem to be a constant refrain, but a new wrinkle has emerged. The wife of the newly appointed special counsel in the Trump case, donated to the Biden campaign and produced a film featuring Michelle Obama , adding another layer to this already complex political landscape. Whether this connection influences the special counsel’s decisions remains to be seen, but it certainly fuels the ongoing narrative of the Fed’s struggles and Trump’s constant criticism.
Recent Trends in Global Interest Rates
The recent trends in global interest rates vary across different regions, reflecting the unique economic circumstances and policy responses of each country or region. Here is a summary of recent trends in key regions:
| Region | Date | Interest Rate | Key Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
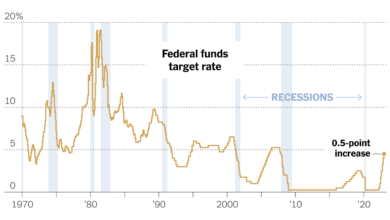
| United States | March 2023 | 4.75%-5.00% (Federal Funds Rate) | Inflation, economic growth, and the Federal Reserve’s efforts to combat inflation. |
| Eurozone | March 2023 | 3.00%-3.25% (Main Refinancing Rate) | Inflation, economic growth, and the European Central Bank’s (ECB) efforts to combat inflation. |
| United Kingdom | March 2023 | 4.00%-4.25% (Bank Rate) | Inflation, economic growth, and the Bank of England’s efforts to combat inflation. |
| Japan | March 2023 | -0.10% (Policy Interest Rate) | Deflationary pressures and the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) efforts to stimulate economic growth. |
| China | March 2023 | 3.65% (Loan Prime Rate) | Economic growth, government policies, and the People’s Bank of China’s (PBOC) efforts to manage inflation and support economic activity. |
Factors Influencing Global Interest Rate Changes
Global interest rates are influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Inflation: When inflation is high, central banks often raise interest rates to cool down the economy and curb price increases. This is because higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, discouraging spending and investment, which can help to slow down economic activity and inflation.
- Economic Growth: When economic growth is strong, central banks may raise interest rates to prevent the economy from overheating. This can help to control inflation and ensure sustainable growth.
- Central Bank Policies: Central banks play a significant role in setting interest rates. Their decisions are based on their assessment of economic conditions and their objectives for inflation and economic growth.
Comparison with Previous Periods
The current interest rate environment is significantly different from the low-interest rate environment that prevailed in the aftermath of the global financial crisis of 2008-2009. Following the crisis, central banks in many developed economies implemented near-zero interest rates and quantitative easing programs to stimulate economic growth and prevent deflation. However, the current inflationary pressures have forced central banks to reverse course and raise interest rates to combat inflation.
Economic Perspectives on Trump’s Claims
The assertion that the Federal Reserve (Fed) is “failing” is a contentious claim often made by former President Donald Trump. This claim has been a subject of debate among economists, with diverse viewpoints on the Fed’s performance and its impact on the economy. Understanding these perspectives is crucial to evaluating the validity of Trump’s claims and the potential economic implications of the Fed’s actions.
Arguments Supporting Trump’s Position
Trump’s primary argument against the Fed’s policies is that they stifle economic growth by keeping interest rates too high. Proponents of this view argue that low interest rates stimulate borrowing and investment, leading to increased economic activity and job creation. They often cite the period of low interest rates during the Trump administration as evidence of the Fed’s ability to promote economic prosperity.
Arguments Opposing Trump’s Position
Opponents of Trump’s position argue that the Fed’s primary responsibility is to maintain price stability and control inflation. They contend that keeping interest rates too low for too long can lead to excessive inflation, which can erode purchasing power and destabilize the economy. Additionally, they argue that the Fed’s actions are based on complex economic data and models, and that political interference in monetary policy can be detrimental.
Economic Implications of the Fed’s Actions
The Fed’s actions can have significant implications for various sectors of the economy. For example, raising interest rates can make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, potentially slowing down investment and economic growth. However, it can also help to curb inflation and stabilize the financial system. Lower interest rates, on the other hand, can stimulate economic activity but may also lead to asset bubbles and financial instability.
“The Fed’s role is to maintain a stable financial system and a healthy economy. This requires a delicate balancing act between controlling inflation and promoting growth. The Fed must consider a wide range of factors, including economic data, market conditions, and global events, when making its decisions.”
Janet Yellen, former Chair of the Federal Reserve
Impact on Financial Markets
Trump’s statement and the subsequent global rate changes have sent shockwaves through financial markets, impacting asset prices, investor sentiment, and trading activity. This section explores the intricate relationship between interest rates and asset prices, analyzing the potential risks and opportunities presented by these developments.
Impact on Stock Markets
The relationship between interest rates and stock prices is generally inverse. When interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, making it more expensive for companies to finance growth and expansion. This can lead to lower corporate earnings, reduced investor confidence, and a decline in stock prices. Conversely, falling interest rates can stimulate economic activity, boost corporate profits, and drive up stock prices.
Trump’s comments, coupled with global rate cuts, initially triggered a surge in stock markets worldwide. Investors saw this as a positive sign for economic growth, particularly in the United States, which is heavily reliant on consumer spending. For instance, the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the S&P 500 Index both experienced significant gains in the immediate aftermath of these announcements.
However, the rally was short-lived as concerns about the global economic outlook and the potential for a trade war dampened investor enthusiasm.
Impact on Bond Markets
Bond prices and interest rates move in opposite directions. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds falls, as investors demand higher yields for new bonds. Conversely, falling interest rates lead to higher bond prices. The global rate cuts have pushed bond yields down, leading to a rally in bond markets. This has been particularly evident in the United States, where the yield on the 10-year Treasury bond has fallen to its lowest level in years.
However, the impact of Trump’s statement on bond markets has been more nuanced. While some investors view his comments as a sign of economic weakness, others see them as a potential catalyst for fiscal stimulus measures, which could boost demand for bonds.
Impact on Other Financial Instruments
The impact of Trump’s statement and global rate changes extends beyond stock and bond markets. Other financial instruments, such as currencies, commodities, and derivatives, have also been affected.For example, the US dollar has weakened against major currencies, such as the euro and the Japanese yen, as investors seek higher returns in other markets. This depreciation has benefited US exporters, making their goods more competitive in global markets.
Commodities, such as oil and gold, have also experienced volatility in response to these developments. Oil prices have fallen on concerns about slowing global economic growth, while gold has risen as a safe-haven asset.
Relationship between Interest Rates and Asset Prices, Fed is failing says trump as global rates tumble
The relationship between interest rates and asset prices can be illustrated using a simple graph:
Interest Rate | Asset Price
–|—|
High | LowLow | High
As interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, making it more expensive for companies to finance growth and expansion. This can lead to lower corporate earnings, reduced investor confidence, and a decline in asset prices. Conversely, falling interest rates can stimulate economic activity, boost corporate profits, and drive up asset prices.
The interplay between Trump’s claims, global interest rate fluctuations, and the Fed’s actions creates a complex economic landscape. While the immediate impact of these developments remains to be fully understood, it is clear that the financial world is on edge. The coming months will likely reveal the true extent of these changes and their long-term implications for the global economy.
Stay tuned for further analysis and insights as this unfolding story continues to unfold.
Trump’s claims of the Fed failing are echoing louder as global interest rates plummet, a trend that’s further amplified by the tech sector’s turmoil. The recent wave of layoffs in the tech industry has left many H-1B visa holders scrambling for new jobs, adding another layer of uncertainty to an already volatile economic landscape. The Fed’s actions, or lack thereof, are at the center of this storm, with many arguing that their policies are exacerbating the current economic woes.
Trump’s claims about the Fed failing might be gaining traction as global rates tumble, but here in Southern California, we’re facing a different kind of economic pressure. Gas prices are soaring again, reaching new highs , and it’s putting a strain on our wallets. With the Fed seemingly struggling to control inflation, it’s hard to see any relief on the horizon.